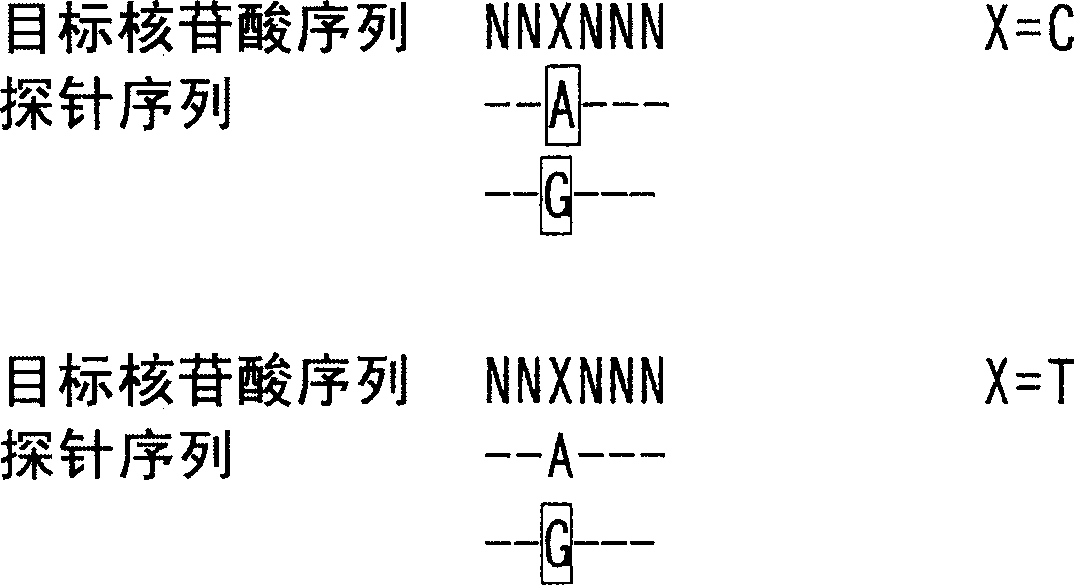
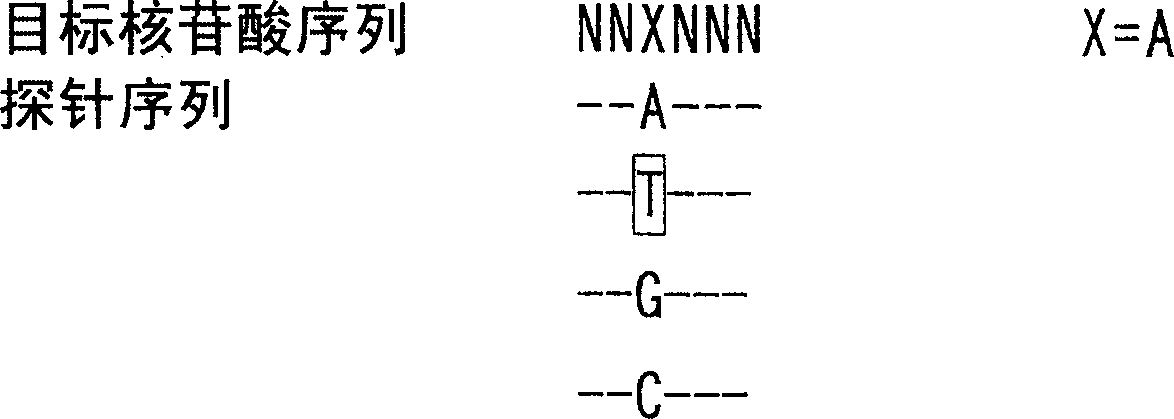Nucleotide derivatives and DNA microarray
A technology of derivatives and nucleotides, applied in the field of nucleotide derivatives and DNA microarrays, can solve the problems of excessive labor, time and cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0114] Synthesis of Nucleotide Derivatives (PyU(5), PyC(5), PyA(7))
[0115] according to Figure 6 and 7 , the nucleotide derivatives (PyU(5), PyC(5), PyA(7)) were synthesized as follows. Among them, the serial number of the compound corresponds to Figure 6 and 7 serial number.
[0116] Scheme i (synthesis of compound 2)
[0117] Propargylamine (1, Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd.) and 1-pyrenylcarboxylic acid (2, Aldrich (Aldrich)) (1:1), in the presence of condensing agent PyBOP (1 equivalent, NOVA Biochem), in N, N - in dimethylformamide, stirred at room temperature for 2.5 hours, extracted, and purified by column chromatography to obtain the product 2 (91%).
[0118] Scheme ii (compound 4: synthesis of nucleoside derivatives of PyU(5))
[0119] 3 (obtained by stirring 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine (Sigma) in 4,4'-dimethoxytrityl chloride (Tokyo Chemical) and pyridine) and 2 (1:1 ) in the presence of (tetraphenylphosphine) palladium (0.15 equivalents, Wako Pure Chemic...
Embodiment 2
[0141] Synthesis of Nucleotide Derivatives (PyG(8))
[0142] according to Figure 8 , the nucleotide derivative (PyG(8)) was synthesized as follows. Among them, the serial number of the compound corresponds to Figure 8 serial number.
[0143] Scheme 1 (synthesis of compound 2)
[0144] Using 1-bromopyrene as a starting material, compound 1 was obtained by Sonogashira coupling reaction with trimethylsilyl acetate glyceride. Next, the protective trimethylsilyl group was removed from sodium methoxide in methanol to obtain compound 2 (pyrene unit) (yield 70%).
[0145] Scheme 2 (compound 6: synthesis of nucleoside derivatives of PyG(8))
[0146] Compound 3 was obtained by adding N-bromosuccinimide to 2'-deoxyguanosine and reacting in water (yield 60%). Next, use tert-butyldimethylsilyl chloride and imidazole to protect the 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of the sugar of compound 3 by tert-butyldimethylsilyl, and then carry out Sonogashira coupling reaction with compound 2 to obta...
Embodiment 3
[0150] Synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides
[0151] Using the nucleotide derivatives (PyU(5), PyC(5), PyA(7)) made in Example 1 and the nucleotide derivatives (PyG(8)) made in Example 2, Synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides containing nucleotide derivatives. Oligodeoxyribonucleotides were synthesized by a 392 DNA / RNA synthesizer from Applied Biosystems in accordance with the usual phosphoramidite method. Extraction from the solid phase carrier and deprotection are carried out by incubating in 25% ammonia water for a certain temperature and for a certain time, and then refining by high performance liquid chromatography.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com