Fructosylamine oxidase
A technology based on amine oxidase and fructosyl, which is applied in the fields of enzymes, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0081] Example 1 : Screening and identification of microorganisms producing FAO
[0082] (1) Screening of microorganisms producing FAO
[0083] Glycation of VHL produces fructosyl valine-histidine-leucine (FVHL) identical to the N-terminal sequence of the glycohemoglobin beta chain. Methods for this are known to those skilled in the art.
[0084] FVHL medium
FVHL
Magnesium Sulfate Heptahydrate
vitamin mix *
metal solution **
5g
1g
1g
0.5g
0.1g
0.1% (v / v)
1.0% (v / v)
q.s
total capacity
1000ml
[0085] Thiamine Hydrochloride
1mg
2
thbrthdrexvbdr
Vitamin B 6 HCl
2
2
0.1
1
2
0.1
q.s.
t...
Embodiment 2
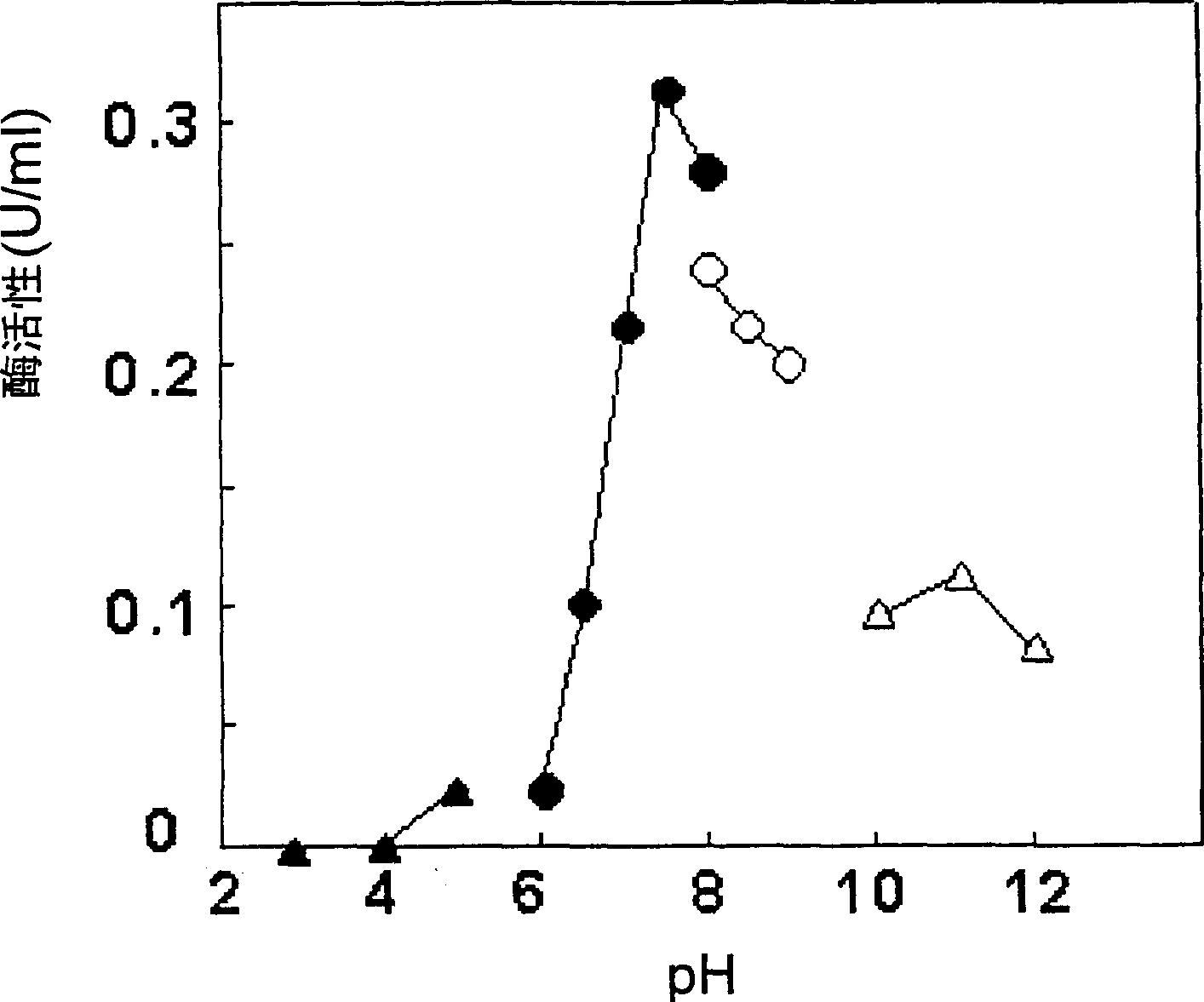
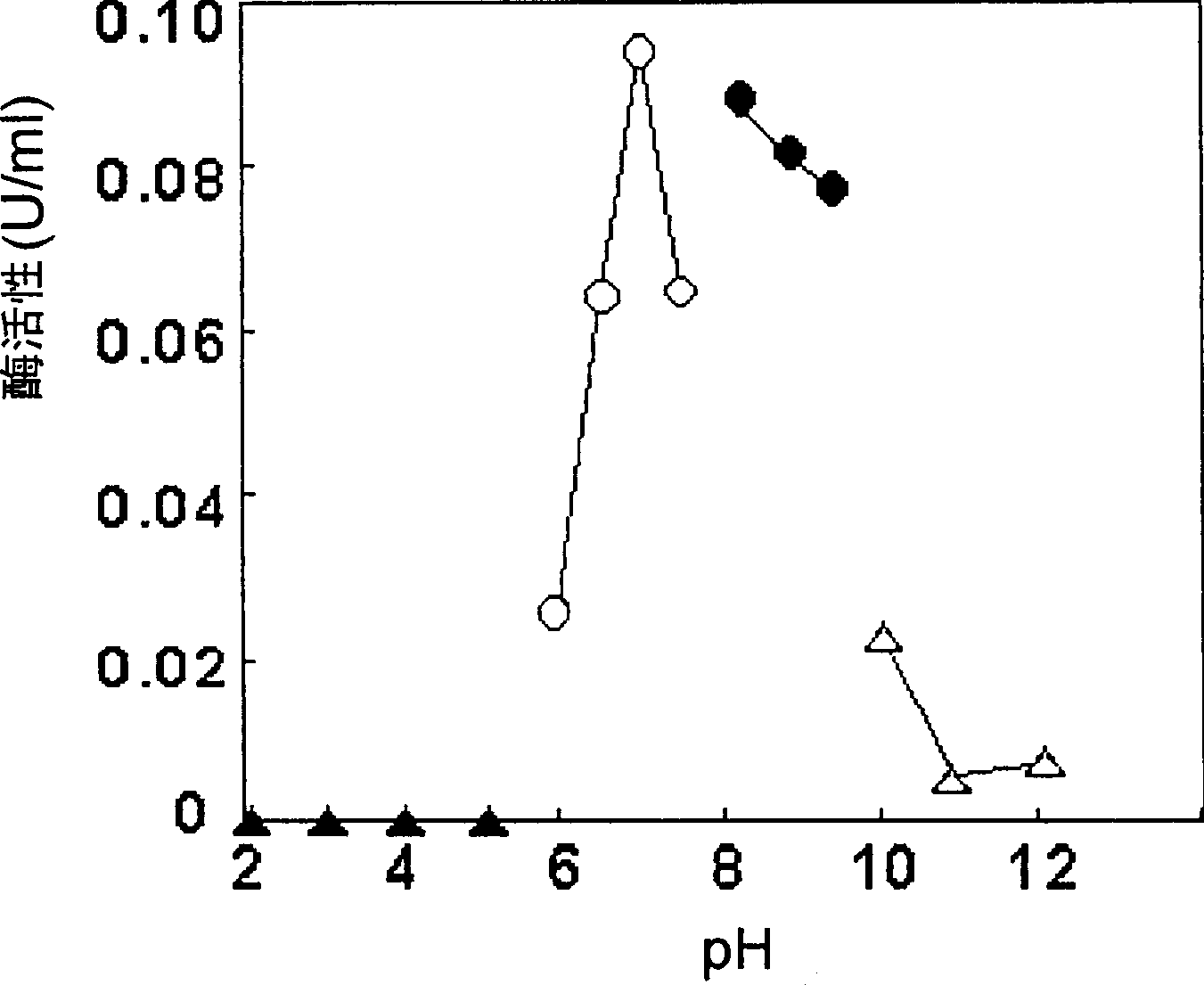
[0110] Example 2 : Preparation and identification of FAO using GL2-1
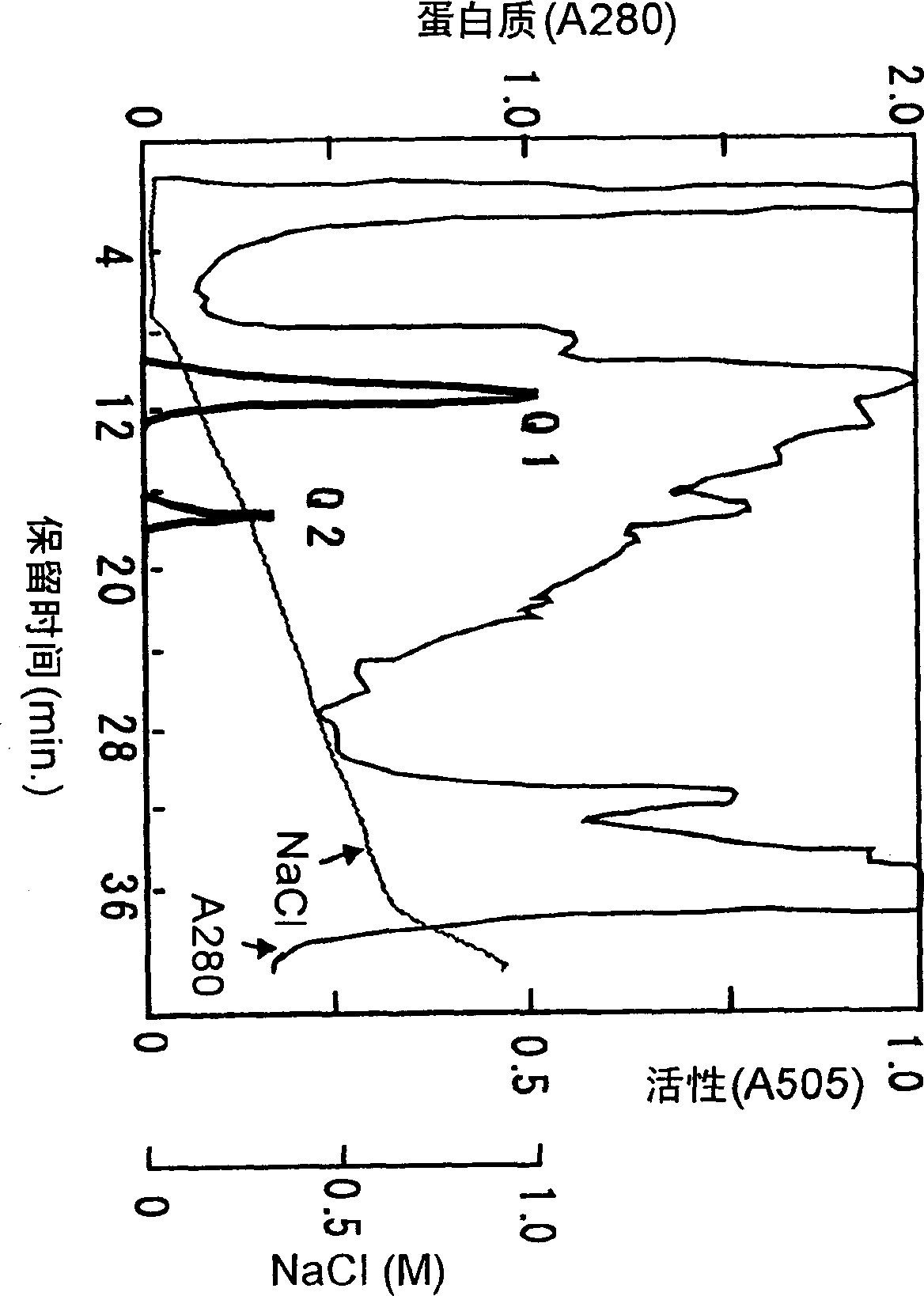
[0111] (1) Partial purification of FAO
[0112] 1) Culture and prepare cell-free extract
[0113] Under the same medium composition and culture conditions, the GL-2 bacterial strain identified in Example 1 was cultured in the 100 ml GV browning medium described in Example 1 (2).
[0114] After culturing, the medium was filtered through a filter to collect mycelia. The obtained mycelium (0.6g) was suspended in 0.1M Tris-HCl buffer solution (pH8.0) containing 1mM DTT, and the Mini-BeadBeater TM (0.5 mm glass beads) and centrifuge (4° C., 10,000×g, 10 minutes) to obtain the supernatant, which is the cell-free extract.
[0115] 2) Ammonium sulfate classification
[0116] The cell-free extract obtained from 1) was dissolved in 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer containing 1 mM DTT and dialyzed against the same buffer for ammonium sulfate (30-80% saturation) fractionation.
[0117] 3) Resource Q column chromatography ...
Embodiment 3
[0146] Example 3 : Cloning of FAO cDNA
[0147] Genomic DNA of GL2-1 was prepared. Using genomic DNA as a template, the cDNA of FAO can be obtained by PCR.
[0148] (1) Genomic DNA preparation of GL2-1 strain
[0149] Genomic DNA was prepared from the GL2-1 strain according to a method comprising the following steps.
[0150] 1. GL2-1 strain was cultured in 15 ml of DP medium (1% Dextone, 1% peptone, 0.5% sodium chloride, pH7.4) at 30°C for 2-3 days.
[0151] 2. Collect fungal cells (wet weight, 0.3 g) by filtering through a glass filter (3GL).
[0152] 3. The resulting fungal cells are homogenized in a mortar containing liquid nitrogen with a pestle, further crushed under the action of a motor or the like, and collected into Corning tubes.
[0153] 4. After adding 2 ml of ice-cold TE buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM EDTA), the mixture was vortexed slightly.
[0154] 5. After adding 2 ml of 50 mM EDTA and 0.5% SDS solution, the mixture was stirred several times by ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com