Method for forming bumps, semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same, substrate processing apparatus, and semiconductor manufacturing apparatus
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, which can be used in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electric solid-state devices, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulty in bonding bumps and large surface roughness of bumps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0058] Here, a silicon semiconductor substrate is exemplified as a substrate, and a method of forming bumps provided for electrical connection with the outside on the semiconductor substrate, a semiconductor device using this method, and a manufacturing method thereof.
[0059] (Bump forming method)
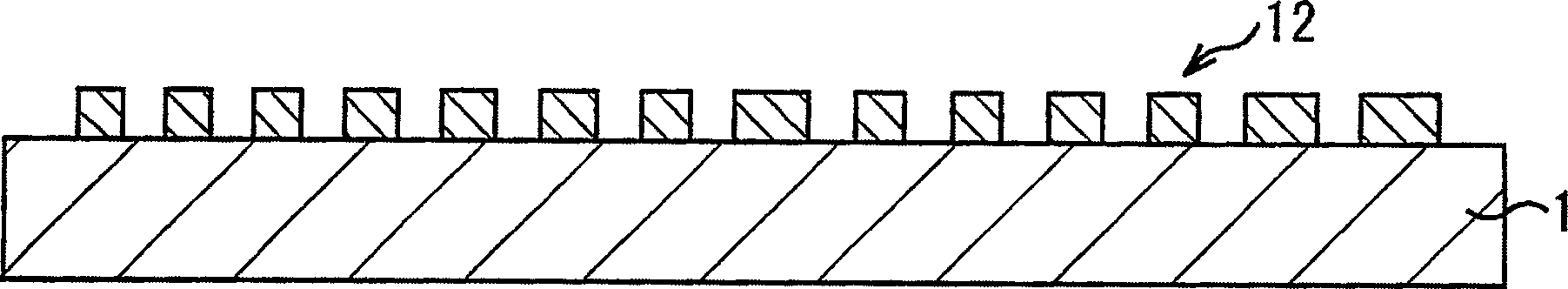
[0060] Figure 1A ~ Figure 1D , Figure 2A , Figure 2B It is a schematic cross-sectional view showing the bump forming method according to this embodiment in order of steps.
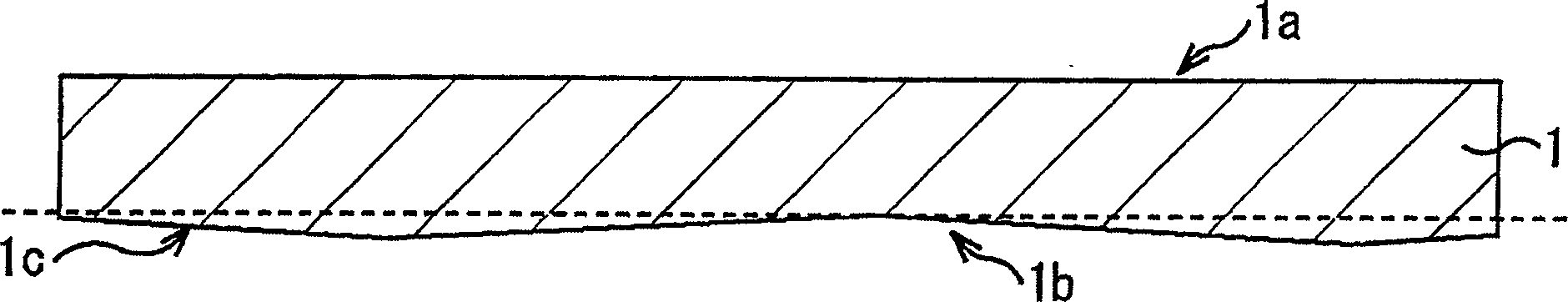
[0061] First, a silicon semiconductor substrate 1 is prepared, and a desired LSI semiconductor element (not shown) is formed on an element formation site on the substrate surface 1a. Hereinafter, each step will be described with respect to the semiconductor substrate 1 in which LSI semiconductor elements and the like are formed on the element formation site in this way.
[0062] Such as Figure 1A As shown in the figure, the silicon semiconductor substrate is generally in a state of varying thickness w...
no. 2 approach
[0093] Next, a second embodiment will be described. In the first embodiment, Au was exemplified as the bump material, but the case of using nickel (Ni) is exemplified in this embodiment.
[0094] Figure 10A ~ Figure 10F It is a schematic cross-sectional view showing the bump forming method according to this embodiment in order of steps.
[0095] First, after the comparison with the first embodiment Figure 1A In the same process as B and B, the back surface of the semiconductor substrate 1 is ground, and the TTL is controlled to a predetermined value or less, specifically 1 μm or less.
[0096] Using this semiconductor substrate 1, as Figure 10A As shown, after the electrode 31 made of aluminum-based metal is patterned on the surface of the semiconductor substrate 1, a nickel-phosphorus plating film 32 with a film thickness of about 5 μm to 10 μm is formed on the electrode 31 by electroless plating.
[0097] The nickel-phosphorus plating film 32 is formed using nickel-ph...
no. 3 approach
[0110] Next, a third embodiment will be described. In the first embodiment, the case where a plurality of semiconductor chips are bonded to the semiconductor substrate was exemplified, but this embodiment discloses a case where the above-mentioned planarization process is performed in the state of the semiconductor chips, and the semiconductor chips are bonded together. .
[0111] Figure 11A , Figure 11B It is a schematic sectional view showing the manufacturing method of the semiconductor device according to this embodiment in order of steps.
[0112] First, if Figure 11A As shown, the backside grinding of the first embodiment is unnecessary, and the individual semiconductor chips 41 are cut out from the semiconductor substrate on which LSI elements and the like are mounted, and a plurality of bumps having different heights (there are still deviations in height) are formed, These are Au bumps 42 here.
[0113] Next, the surface layer of the semiconductor chip 41 is ma...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Film thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com