Water soluble vinylon and non-woven cloth containing the same vinylon
A polyvinyl alcohol-based, water-soluble technology, applied in the direction of fiber chemical characteristics, dry spinning method, wet spinning method, etc., can solve the problems of reducing stretching temperature or stretching ratio, constraints, and inability to increase fiber crystallinity, etc., to achieve The effect of cheap manufacturing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] (1) PVA having a viscosity average degree of polymerization of 1700 and a degree of saponification of 96.0 mol % was added to DMSO so that the PVA concentration was 23% by mass, and dissolved by heating at 90° C. under a nitrogen atmosphere. The obtained spinning stock solution was passed through a nozzle with a hole diameter of 0.08 mm and a number of holes of 108, and dry-wet spinning was carried out in a solidification bath composed of methanol / DMSO=70 / 30 (mass ratio) at a liquid temperature of 5°C.
[0094] (2) The obtained cured yarn was immersed in a second bath having the same methanol / DMSO composition as the curing bath, and then wet stretched three times in a methanol bath at a liquid temperature of 25°C. Thereafter, it was immersed in a methanol bath (extraction bath) in which 10 g / l of glyoxylic acid manufactured by Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd. was dissolved, and then dried with hot air at 120° C. to obtain a spinning yarn. Next, the obtained spinning ...
Embodiment 2
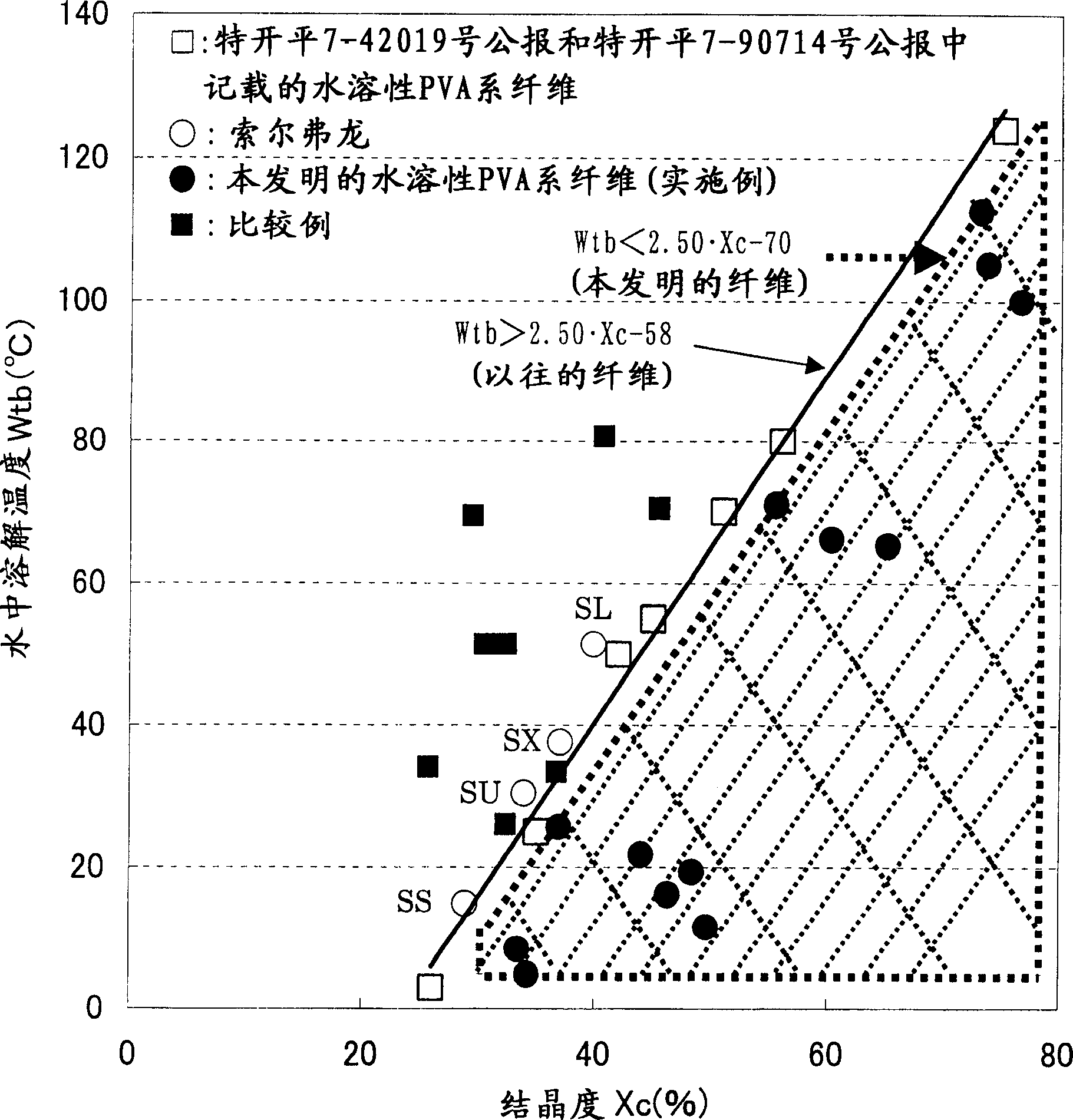
[0101] (1) A fiber was obtained by spinning and drawing under the same conditions as in Example 1, except that 50% of the carboxylic acid portion of glyoxylic acid was neutralized with sodium hydroxide. The performance evaluation results of the obtained fibers are shown in Table 1. In the obtained fiber, the reactivity of glyoxylic acid was 0.8 mol%. In addition, the fiber physical properties of the obtained fiber are: single filament fineness 2.1dtex, fiber crystallinity Xcf=43%, water dissolution temperature Wtb=15°C, fiber strength 7.6cN / dtex, fiber crystallinity Xcf and water dissolution temperature Wtb The relationship between satisfies the condition of formula (I), so the appearance of the fiber is good, without silk spots, etc., which is better than the conventional water-soluble PVA-based fiber.
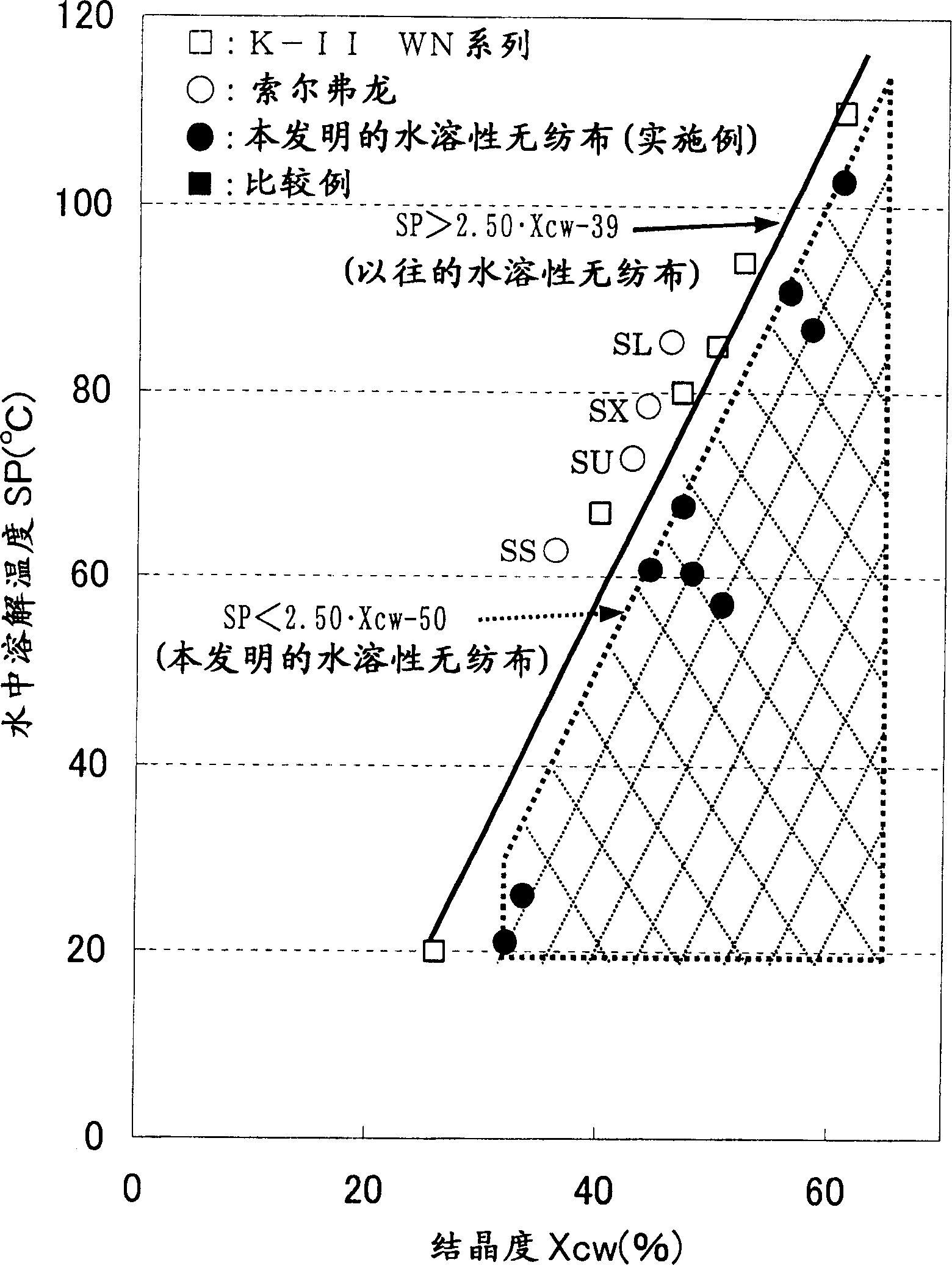
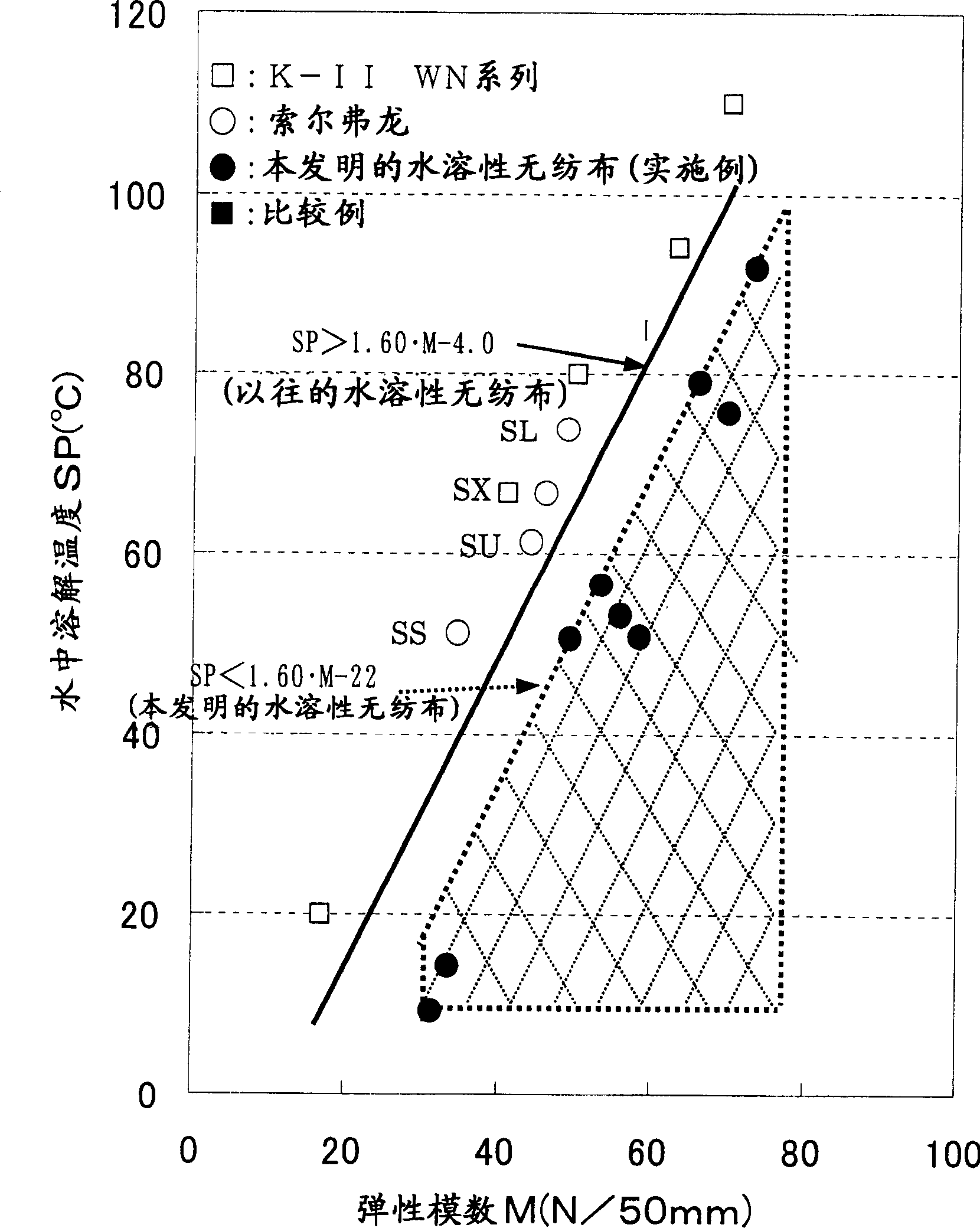
[0102] (2) The fibers obtained in the above (1) were subjected to heat embossing treatment under the same conditions as in Example 1 to obtain a nonwoven fabric. Table 3 sh...
Embodiment 3
[0105] (1) A fiber was obtained by spinning and drawing under the same conditions as in Example 1, except that PVA having a degree of saponification of 88 mol % was used. The performance evaluation results of the obtained fibers are shown in Table 1. The fiber appearance that obtains is good, does not have silk spots etc., and monofilament fineness is 2.1dtex, and fiber strength is 3.6cN / dtex, and the crystallinity Xcf=32% of fiber, dissolves temperature Wtb=5 ℃ in water, and the crystallinity Xcf of fiber and water The relationship of the dissolution temperature Wtb satisfies the condition of formula (I).
[0106] (2) Except having made the embossing temperature 140 degreeC, the fiber obtained by said (1) was heat embossed under the same conditions as Example 1, and the nonwoven fabric was obtained. Table 3 shows the evaluation results of the obtained nonwoven fabric. The weight per unit area of the obtained nonwoven fabric was 41 g / cm 2 , Dissolving temperature in water...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| modulus | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com