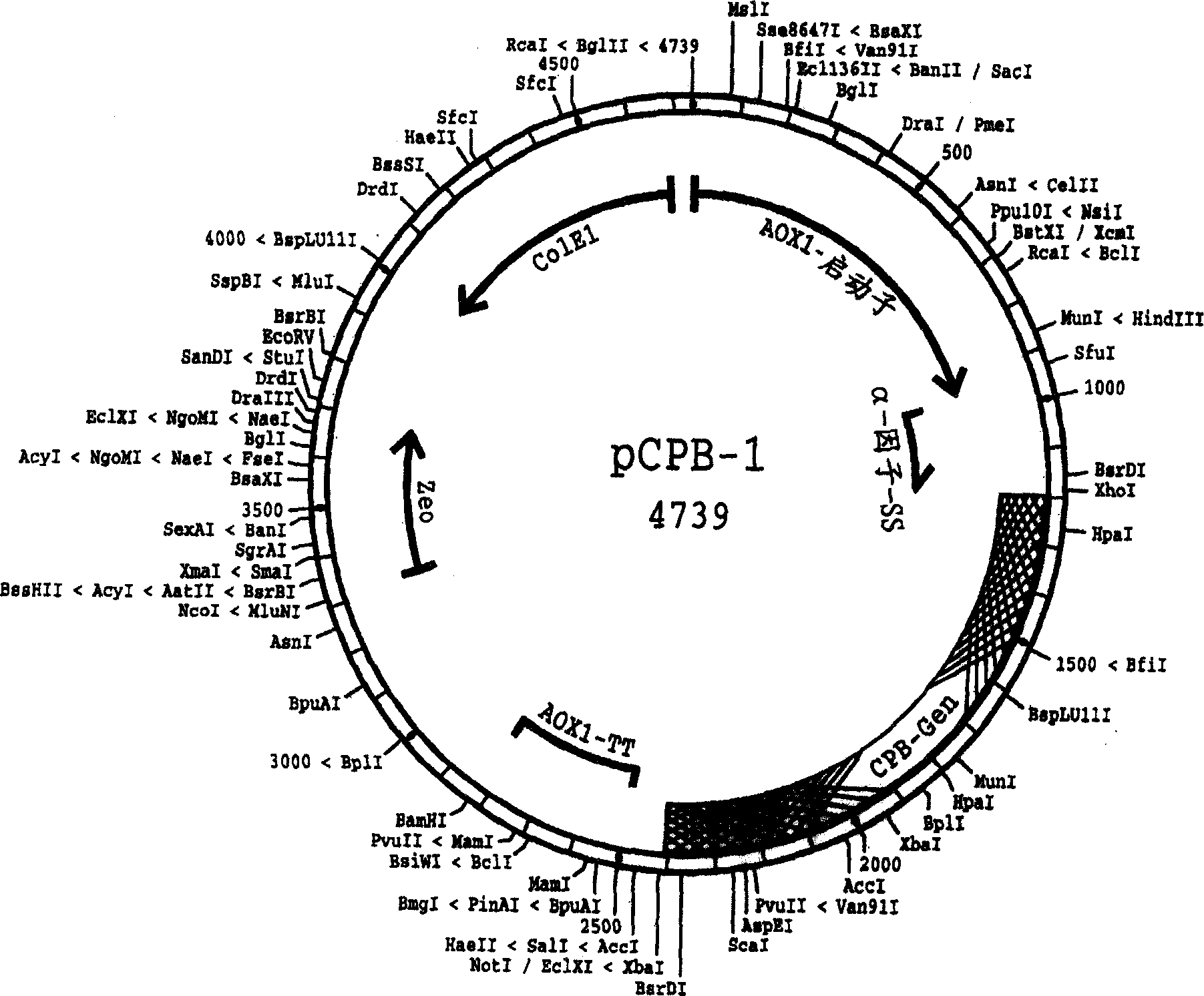
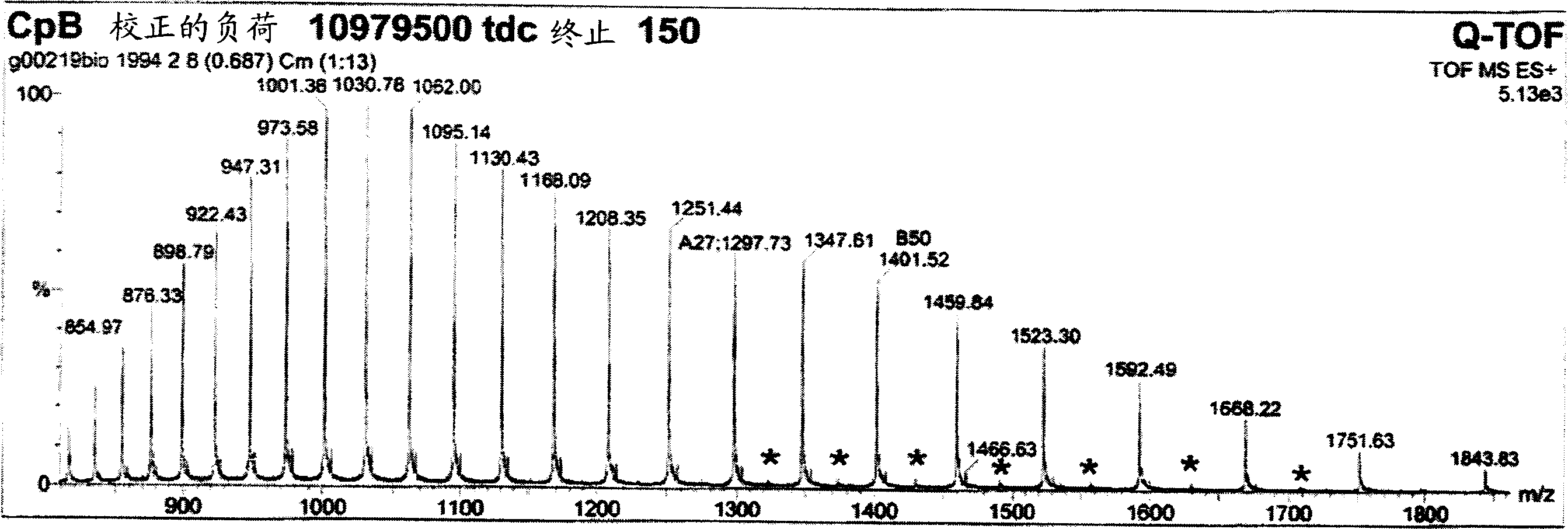
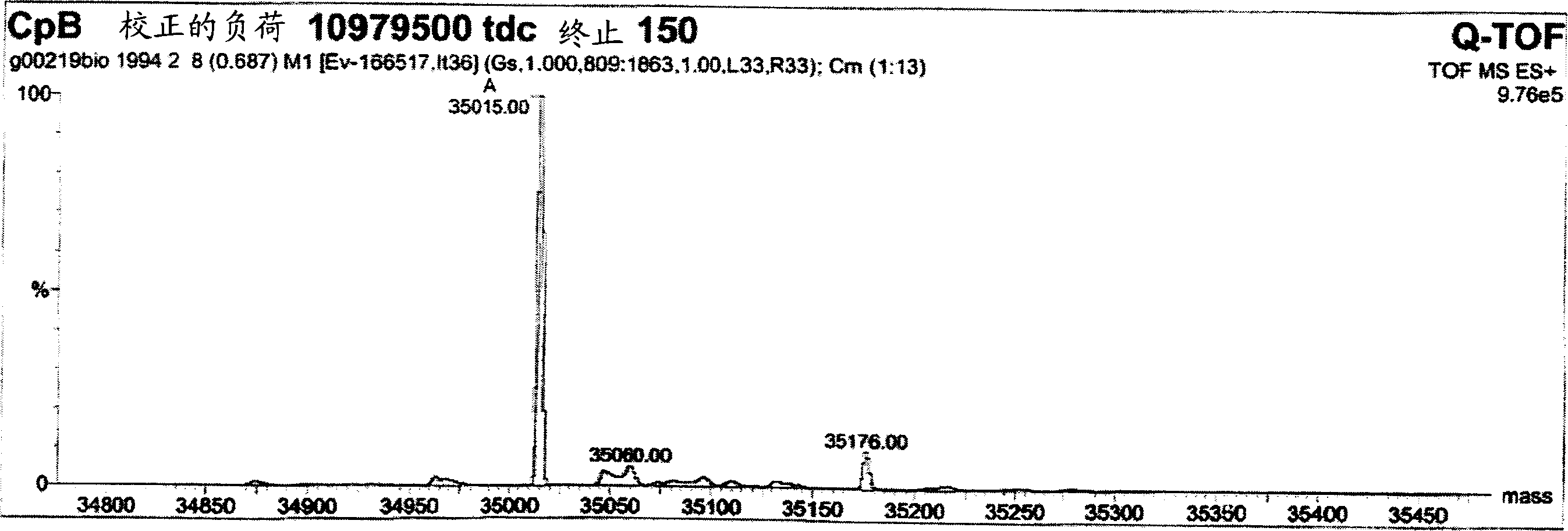
Recombinantly expressed carboxypeptidase b and purification thereof
A carboxypeptidase, precarboxypeptidase technology, used in the production and further processing of inactive precursors, the field of protein activation, and can solve the problem that there is no known specific method to distinguish activated carboxypeptidase B from inactive forms, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 9
[0094] Example 9 shows that after the first purification step as in Example 7, the collected pool contains almost equal amounts of products with and without C-terminal tyrosine product of. Terminal tyrosine residues are gradually removed during processing. After the second chromatographic purification step, the C-terminal tyrosine was almost completely deleted for most proteinaceous materials. A possible but unproven explanation is therefore that the host organism used to express and secrete the product produces the protein with carboxypeptidase Y activity. Carboxypeptidase Y is known from Saccharomyces cerevisiae with the ability to cleave the C-terminal amino acid with broad specificity. Although carboxypeptidase Y is known to be a vacuolar enzyme (Kato, M. et al., Eur. J. Biochem 270 (2003) 4587-4593), lysed yeast cells can significantly increase carboxypeptidase in the fermentation medium. Y activity. However, since removal of the C-terminal tyrosine did not alter the ...
Embodiment 1
[0110] Synthesis of genes encoding precursor proteins
[0111] DNA manipulation techniques were carried out according to standard protocols (Sambrook, Fritsh & Maniatis, Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 3 rd Edition, CSHL Press, 2001). Reagents used in molecular biology experiments were used according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
[0112] A nucleotide sequence encoding artificial preprocarboxypeptidase B gene as shown in SEQ ID NO:3 was re-synthesized. Several parts of the nucleotide sequence were synthesized as 24 single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides ranging in length from 54 to 90 nucleotides. The single-stranded oligonucleotide represents an alternating overlapping portion of the leading and lagging strands of SEQ ID NO:3. Each oligonucleotide was designed such that its 5' and 3' ends overlapped adjacent oligonucleotides. As an exception, oligonucleotides representing the 5' and 3' ends of SEQ ID NO: 3 only overlap the 5' and 3' ends of their adjacent ...
Embodiment 2
[0118] Vector construction, transformation, expression
[0119] For the construction of the expression vector, transformation, expression of the precursor protein and secretion of histidine-tagged procarboxypeptidase B in the growth medium, the "Pichia Yeast Expression Kit" model M 011102 25 described in the Invitrogen brochure was used -0043, "pPICZ A, B, and C" model D 110801 25-0148, "pPECZα A, B, and C" model E 01030225-0150, and "pPIC9K" model E030402 25-0106 to perform experiments. Reference is also made to other vectors, yeast strains and media mentioned herein. At the same time, such as Sambrook, Fritsh&Maniatis, Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual, 3 rd Edition, CSHL Press, 2001 describes the basic molecular biology methods.
[0120] As a result, a number of vectors were obtained, each of which contained an expression cassette capable of expressing the precursor protein shown in SEQ ID NO:4 among the methylotrophic yeast strains. A preferred yeast strain is a P...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com