Method of combined extraction of magnesium and lithium in salt lake bittern
A salt lake brine and combined extraction technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of high free ammonia concentration, low extraction rate, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effect of low free ammonia concentration, good separation effect and good comprehensive benefit.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
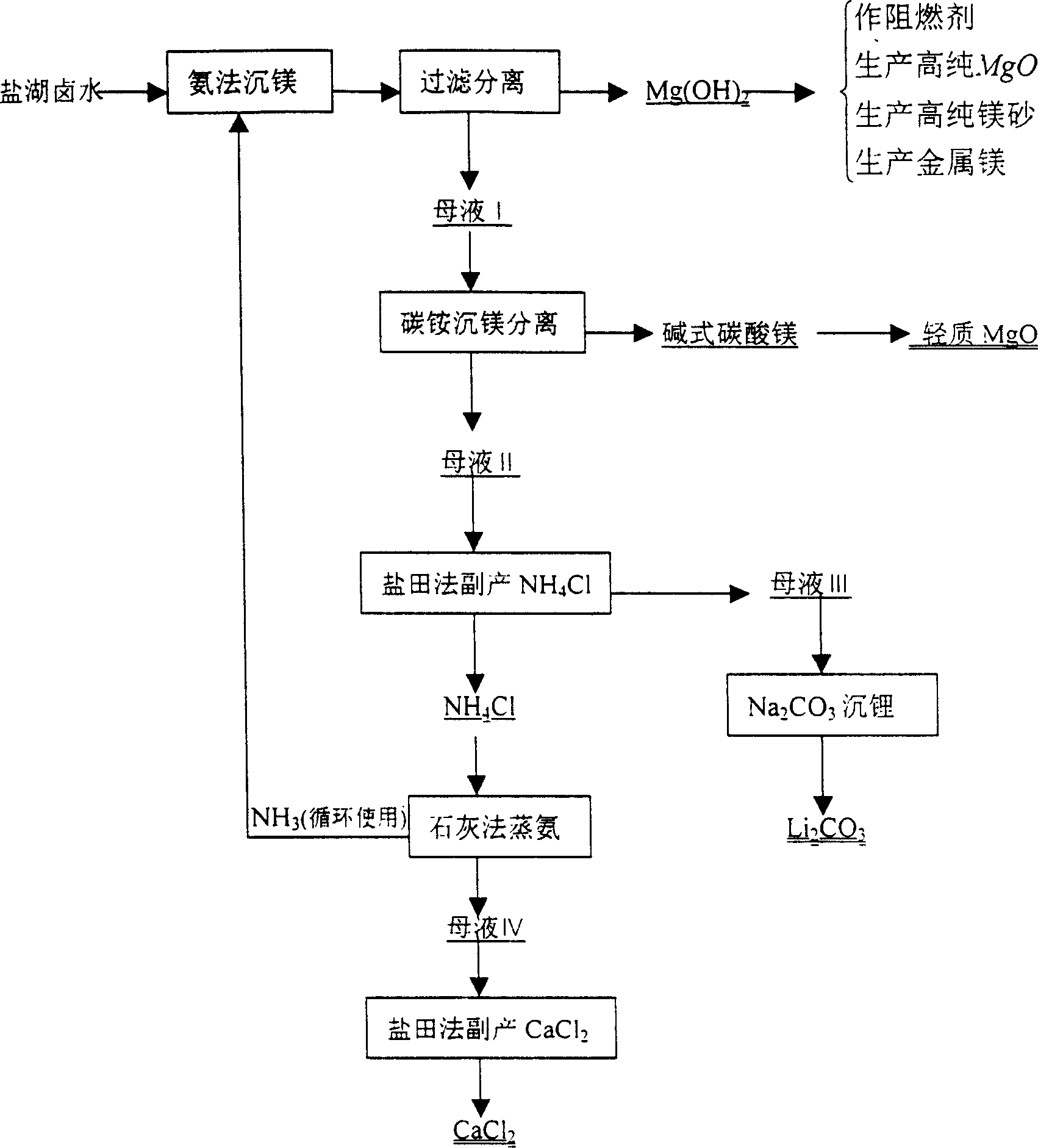
[0045] Combine below figure 1 For further clarification:
[0046] ① Preparation of reaction bottom solution
[0047] Firstly add 500L of deionized water into a 2000L one-stage magnesium sink tank, and then add 30kg of magnesium hydroxide as a seed crystal to form a reaction bottom liquid.
[0048] ②Ammonia steaming with milk of lime
[0049] Add 600kg of water and 385kg of lime into a 2000L ammonia distillation tank and stir it into milk of lime, add 580kg of solid ammonium chloride, heat with steam, and pass the ammonia produced by the reaction into the first-stage magnesium sinking tank. At the same time, under stirring, slowly add 1300kg of brine into a magnesium precipitation tank to carry out the magnesium precipitation reaction, and control the temperature of the magnesium precipitation reaction to be 70°C±80°C.
[0050] ③Sedimentation, filtration and washing of magnesium hydroxide
[0051] After a period of magnesium precipitation reaction, put the reaction material...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com