Spot diffraction interferometer for measuring surface shape
A technology of point diffraction interferometer and surface shape, which is applied in the fields of interference spectroscopy, phase influence characteristic measurement, spectrum investigation, etc. It can solve the problems of affecting the accuracy of measurement results, increasing the difficulty of instrument assembly, and low light transmittance of small holes. , to achieve good focusing effect, easy assembly and adjustment, and large numerical aperture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
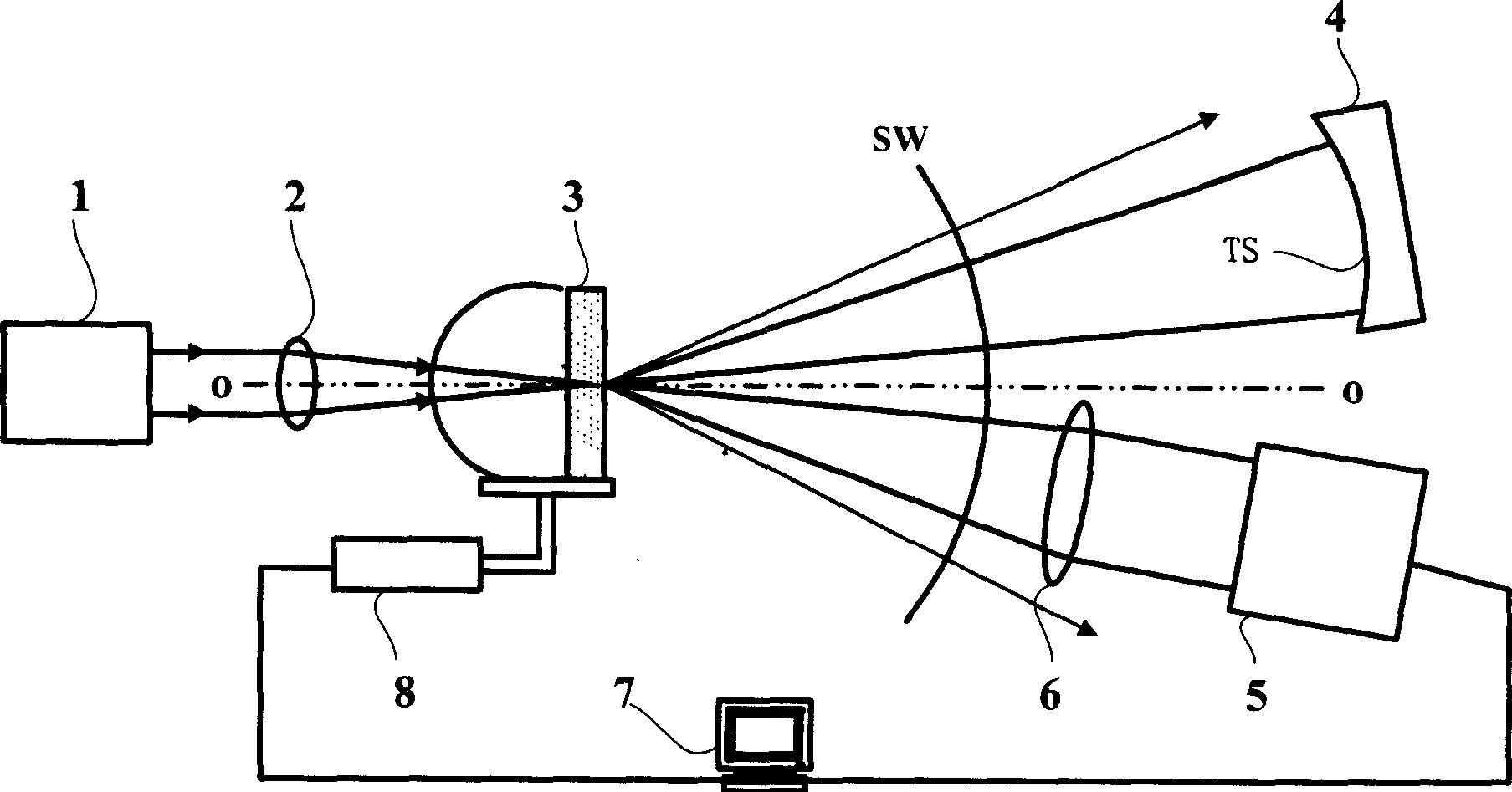
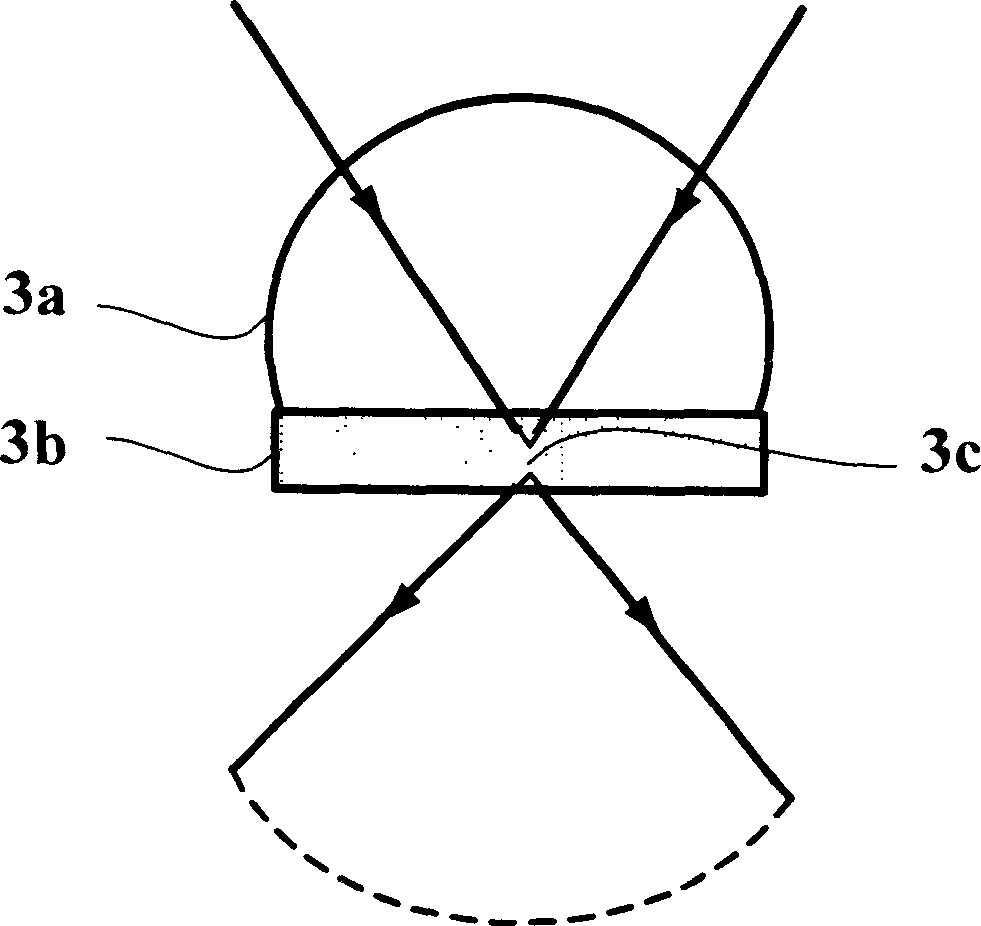
[0035] The schematic diagram of its device structure is shown in figure 1As shown, the light source 1 is a semiconductor laser with a wavelength λ=650nm. The converging lens 2 has a numerical aperture of 0.9 and a working distance of 3 mm. The solid immersion lens 3 a has a radius of 0.764 mm, is made of glass with a refractive index of 1.8198 at 514.5 nm, and has a numerical aperture of 1.5. By adjusting the displacement control device 8, the focus spot falls on the super-resolution mask 3b. The device under test is placed on the piezoelectric ceramic base, and the distance between the device under test 4 and the solid wetting lens 3 is adjusted until clear stripes are obtained on the CCD camera 5 . Collect the data to the computer 7 to complete a measurement.
Embodiment 2
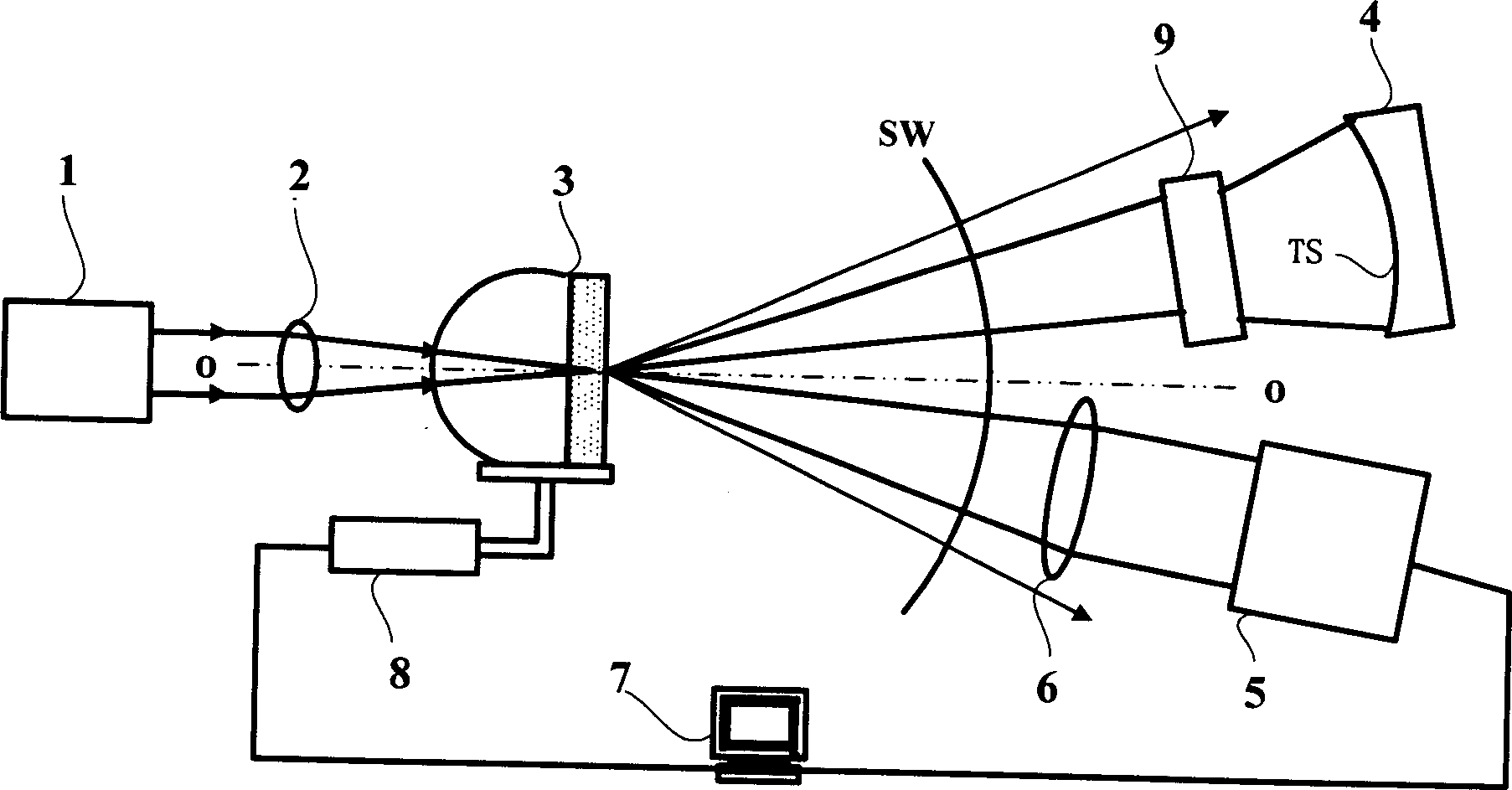
[0037] The schematic diagram of its device structure is shown in image 3 As shown, the devices with the same numbers as those in Embodiment 1 will not be described in detail here. The compensator (NULL element) 9 is placed between the small hole 3c and the device under test 4 to generate a wavefront close to the TS on the entire surface TS of the device under test 4, to solve the problem that the surface TS of the device under test 4 is very different from the ideal spherical surface When the case is large, that is, the case of an aspheric surface, the entire measurement can be completed once. Its accuracy depends on the quality of the compensator 9 .
[0038] The compensator 9 may be a spherical transmissive optical device, a spherical reflective optical device, an aspheric transmissive optical device or an aspheric reflective optical device.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Its device structure is as Figure 4 As shown, the devices with the same numbers as those in Embodiment 1 will not be described in detail here. Light emitted from the light source 1 is split by a beam splitter 12 into a measurement beam and a reference beam. The reference beam passes through a beam splitter 12 to a movable mirror 10 . The optical path difference between the reference beam and the measurement beam can be adjusted by moving the mirror 10 . The reference beam passes through the beam splitter 12 again, is reflected by the mirror 13 to the converging lens 2 , and then is focused to the solid immersion lens 3 by the converging lens 2 . At the same time, the measuring beam is reflected by the beam splitter 12 and encounters the fixed mirror 11 . The measuring beam is reflected back to the beam splitter 12 . Then reflected to the mirror 13, the mirror 13 reflects the measuring beam to the converging lens 2, and is focused by the converging lens 2 to the sol...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| radius | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com