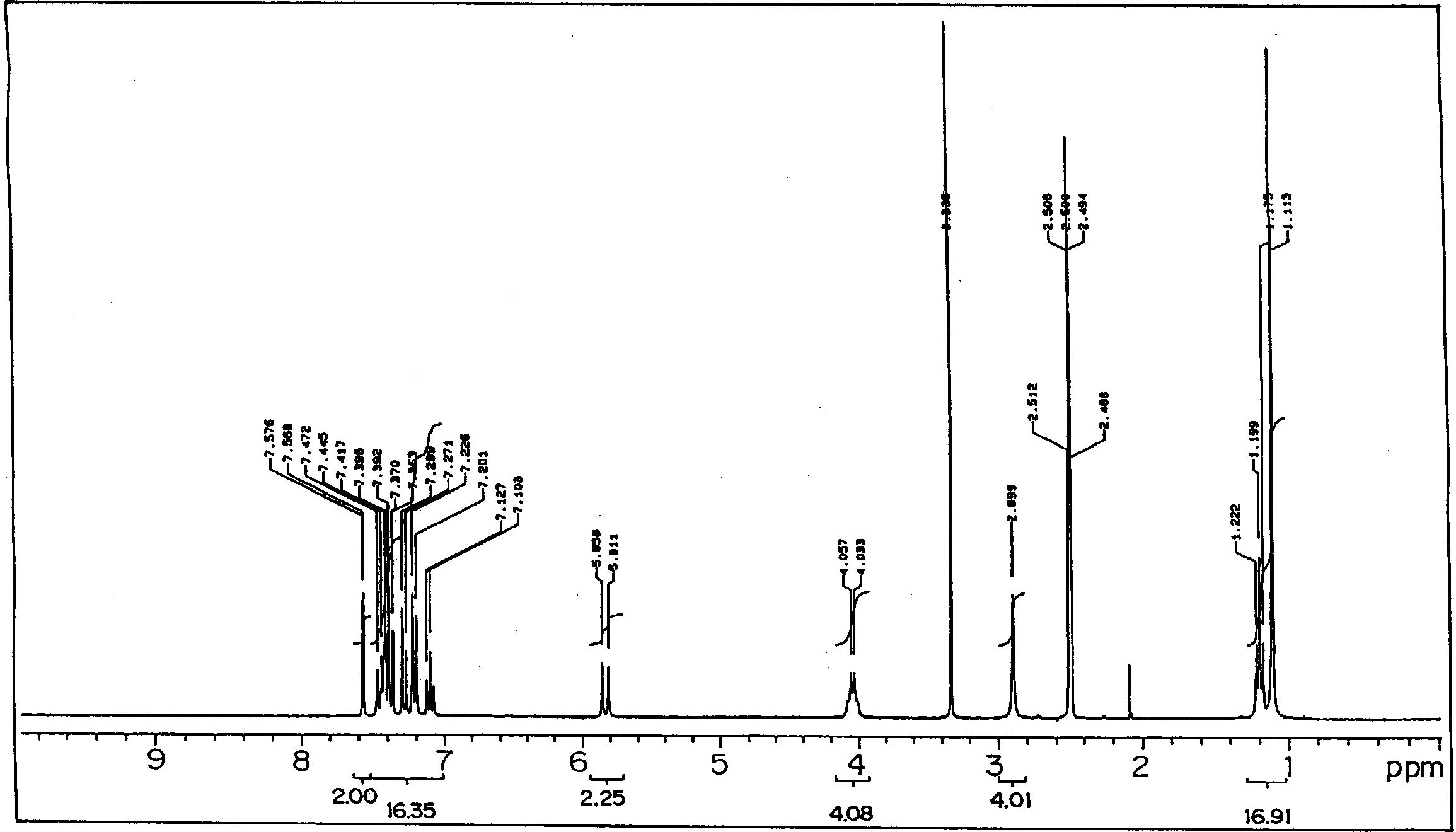
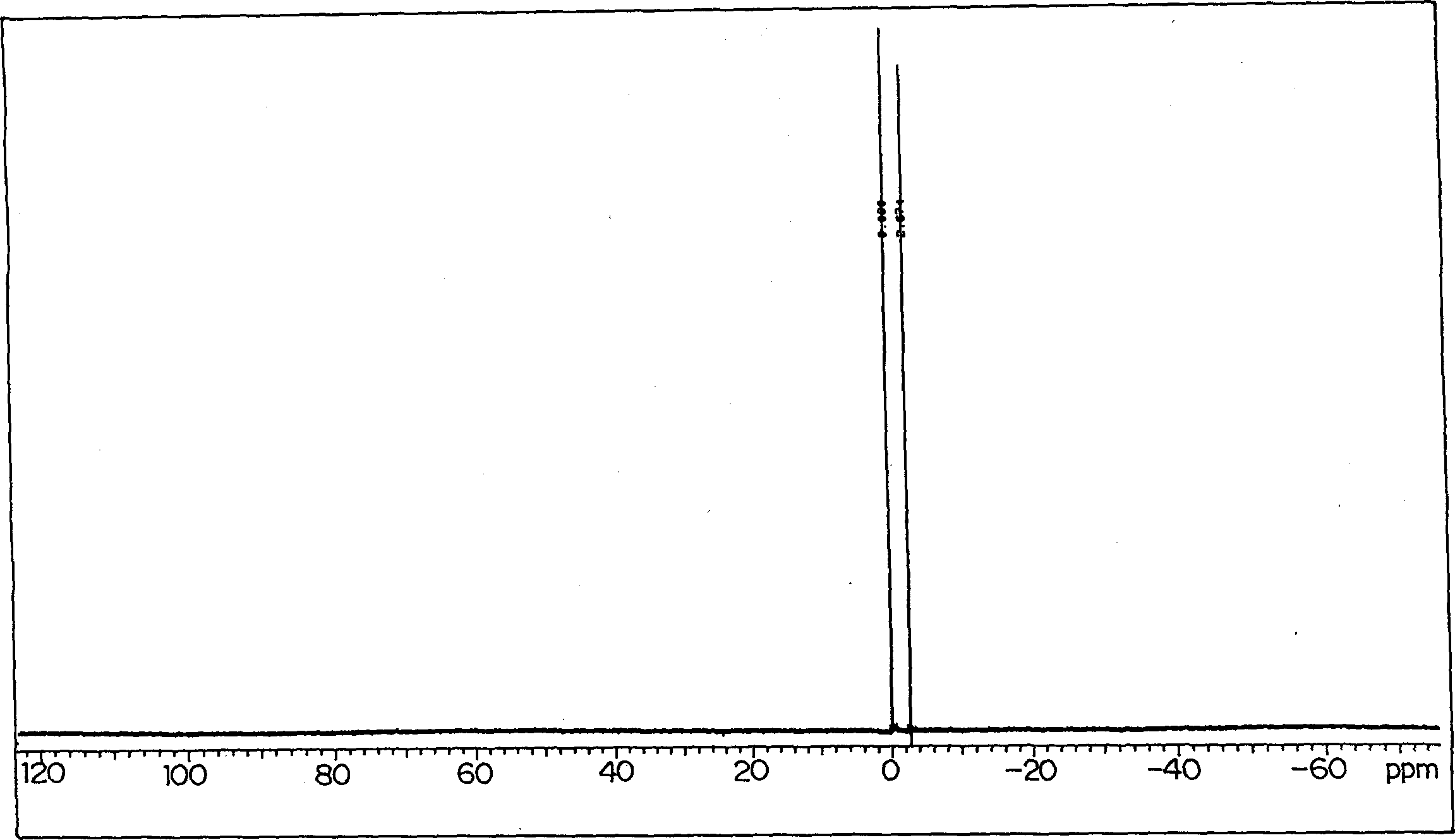
Negative picture recording material and cyanine dye
A technology for recording materials and cyanine dyes, applied in the field of new cyanine dyes and negative image recording materials, which can solve the problems of low image area intensity and unfavorable lithographic printing plates.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1 to 8
[0182] Embodiment 1 to 8: the preparation of carrier:
[0183] Pure and cast molten JIS Al050 alloys containing at least 99.5% Al, 0.30% Fe, 0.10% Si, 0.02% Ti and 0.013% Cu. To purify it, the alloy melt is degassed, from which unnecessary gases such as hydrogen are removed, and filtered through a ceramic tube filter. The alloy melt is cast by direct current casting. The solidified blank with a thickness of 500mm was cut 10mm deep from the surface, and then homogenized at 550°C for 10 hours while preventing the intermetallic compounds therein from forming rough grains. Then it is hot rolled at 400°C, and then annealed in a continuous annealing furnace at 500°C for 60 seconds (this is the annealing treatment), and then cold rolled into an aluminum sheet with a thickness of 0.30mm. In this way, the surface roughness rolled out by rolling can be controlled at the average height of the center line, Ra, and the average height of the center line of the cold-rolled aluminum sheet i...
Embodiment 9 and 10
[0204] A coating liquid [R] for the photosensitive layer was prepared (its composition is shown below). Immediately after preparation, the aluminum sheet was coated with the coating liquid [R] with a wire rod (the preparation method was the same as that in Examples 1-8), and then dried in hot air at 115° C. for 45 seconds. Thus, lithographic printing plate precursors [R-1] and [R-2] were prepared. After drying, the amount of photosensitive layer formed on each precursor was 1.3 g / m 2 . The infrared absorbers and radical generators used in the coating liquid [R] are given in Table 11. Coating liquid [R] for photosensitive layer: Infrared absorber (given in Table 11) 0.10 g free radical generator (given in Table 11) 0.30 g polyfunctional monomer (whose structure is given below ) 1.00 g additional 4,4'-diphenylmethane diisocyanate, ethylene diisocyanate, tetraethylene glycol and 2,2-bis(hydroxymethyl)propionic acid copolymer in a molar ratio of 30 / 20 / 30 / 20 , (weight average m...
Embodiment 11 to 14, comparative example 5 and 6
[0213] However, the printing plate [S-1] of Comparative Example, which printed a large number of good prints, is different from the printing plate of Example 9 of the present invention only in that the photosensitive layer of the former contains an infrared absorber outside the scope of the present invention. The number of good prints printed is less than that printed by the printing plate of the present invention. Examples 11 to 14, Comparative Examples 5 and 6: Preparation of the carrier:
[0214] Aluminum supports were prepared in the same manner as in Examples 1-8, except that the silicate was used for hydrophilization treatment. Inner coating:
[0215] The coating liquid (whose composition is given below) was then applied to the aluminum support with a wire rod and dried in hot air at 90°C for 30 seconds. After drying, the thickness of the inner coating formed is 10mg / m 2 . Inner coating liquid: β-alanine 0.1g propyl phosphoric acid 0.1g methanol 40g pure water 60g Ph...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com