Dairy product that does not contain emulsification salts and process for making same
A technology of emulsifying salt and milking, applied in the field of preparing dairy food, dairy food
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
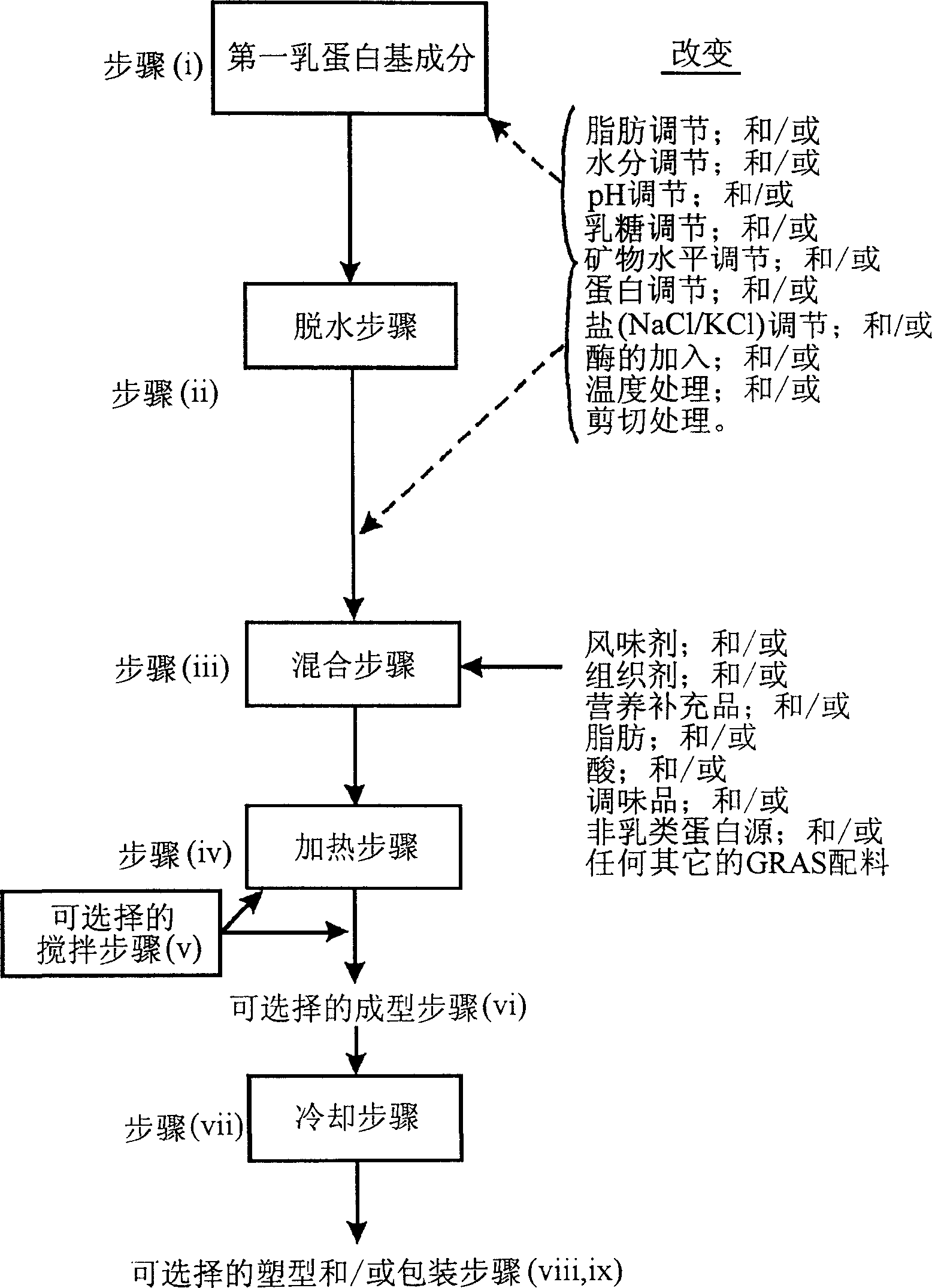
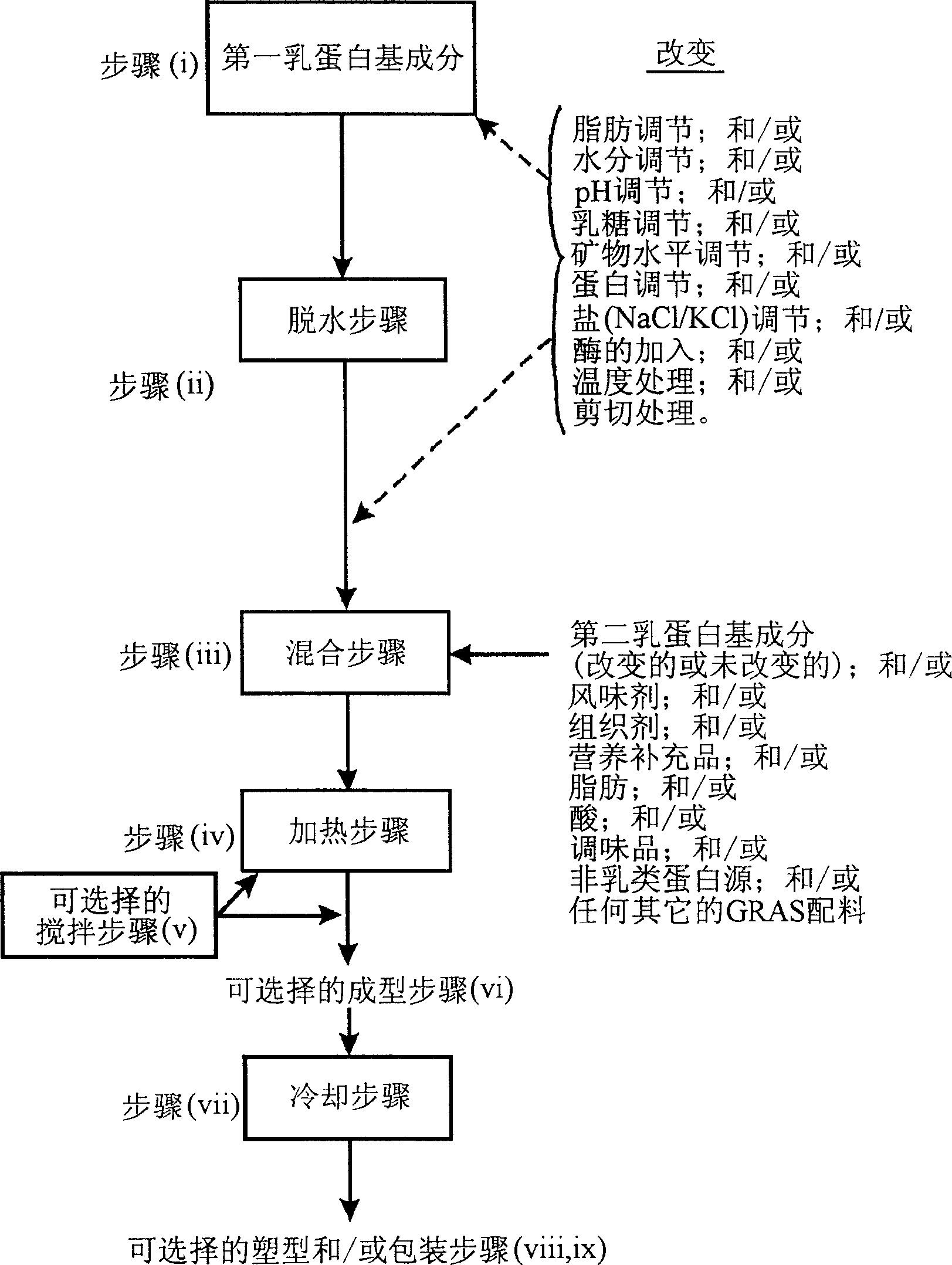
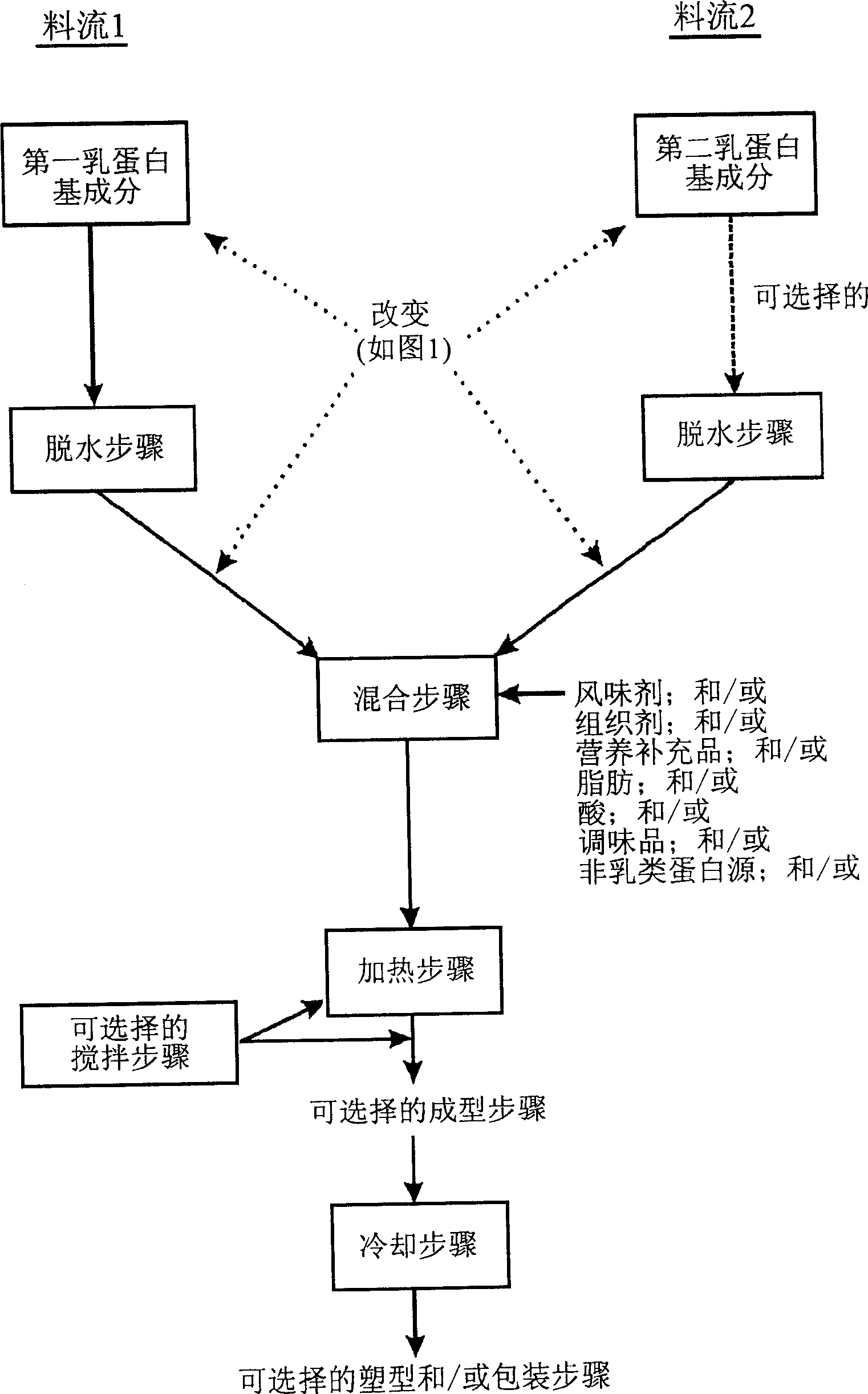
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0124] This example illustrates the preparation of a cheese product with properties similar to Colby cheese.
[0125] 3500 kg of fresh whole milk was standardized to 3.5% fat content and pasteurized (73° C. for 16 seconds). Standardized whole milk was heated to 50°C and then concentrated by continuous ultrafiltration filtration (Koch HFK 131 spiral wound membrane from Koch Membrane Systems, Wilmington, MA, USA) with a concentration factor of approximately 4.2 kg feed / kg of retentate. This resulted in 830 kg of UF retentate formed with a total solids content of 29.2%.
[0126] The retentate was cooled to 4°C and diluted with water at 4°C to obtain a retentate with a refractive index of 12° Brix, the pH was lowered to 5.8 by careful addition of 3% w / w lactic acid and mixing.
[0127] The acidified retentate was then heated to 50°C and subjected to diafiltration. Water was added continuously to maintain the refractive index at 12°Brix, and the pH of the retentate was changed ...
Embodiment 2
[0139] This example illustrates the preparation of a cheese product with properties similar to cheddar cheese.
[0140] The fresh whole milk was separated to obtain 3300 liters of skim milk with a fat content of 0.08%. The skim milk was pasteurized (73.5°C for 16 seconds) and cooled to 4°C. The cream removed from the separation was pasteurized and cooled to 4°C, set aside, and added back to the mix in a later step.
[0141]The pH of the skim milk was lowered to 5.9 by carefully adding 3% w / w lactic acid with mixing and held for 105 minutes. The skim milk was then concentrated by continuous ultrafiltration (Koch HFK 131 membrane) at a temperature of 15° C. with a concentration factor of about 5.2 kg feed / kg retentate. The apparatus was continuously fed with dialysis filtered water at a ratio of approximately 1 part water per 16 parts skim milk. This resulted in 630 liters of UF retentate with a composition of 20% total solids, 15.8% milk protein and approximately 40% of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0152] This example illustrates the preparation of a cheese product with properties similar to Colby cheese.
[0153] The fresh whole milk was separated to obtain 9800 liters of skim milk with a fat content of 0.08%. The skim milk was pasteurized (73.5°C for 16 seconds) and cooled to 6°C. The cream removed from the separation was pasteurized and cooled to 4°C, set aside, and added back to the mix in a later step.
[0154] The pH of the skim milk was lowered to 5.9 by carefully adding 3% w / w lactic acid with mixing and held for 80 minutes. The skim milk was then concentrated by continuous ultrafiltration (Koch HFK 131 membrane) at a temperature of 15° C. with a concentration factor of about 4.5 kg feed / kg retentate. The apparatus was continuously fed with dialysis filtered water at a ratio of approximately 1 part water per 42 parts skim milk. The UF retentate thus obtained was 2170 liters with a composition of 18.7% total solids, 14.5% milk protein, and about 42% of the tota...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com