Method and kit for detecting presence or proportion of donors in acceptor sample
A sample and donor technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitability for regular monitoring, low detection sensitivity, high detection cost, and achieve intuitive quantitative results , The effect of low detection sensitivity and short detection period
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
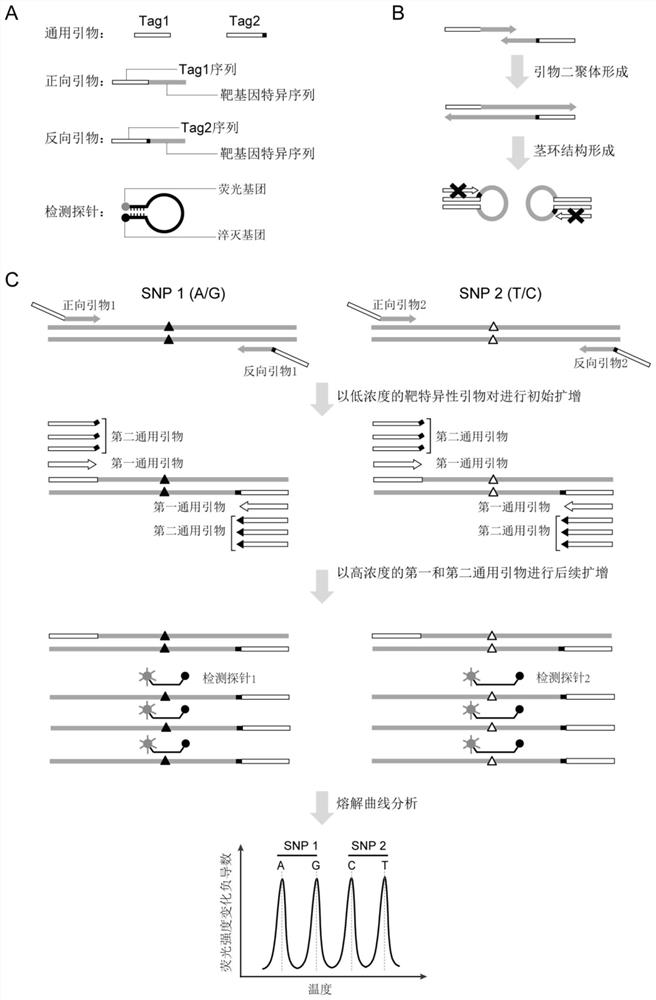
[0419] Embodiment 1. Selection of candidate SNP sites
[0420] The SNP site covered by the present invention is selected from the single nucleotide polymorphism site library (dbSNP) of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), and the SNP site of the present invention preferably meets the following conditions: (1) Fst (population fixation coefficient) between different races 1Mb; (5) In order to avoid linkage between different loci, try to choose to be located on different chromosomes on the site. Carry out the screening of SNP locus according to above-mentioned standard, present embodiment has selected preferred 23 SNP loci, specifically as shown in table 1, SNP locus information and sequence are queried from the dbSNP database of U.S. National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) And download, the allele frequency refers to the Asian population frequency from the Thousand Genomes database, and these sites are evenly distributed on each chromosome of...
Embodiment 2
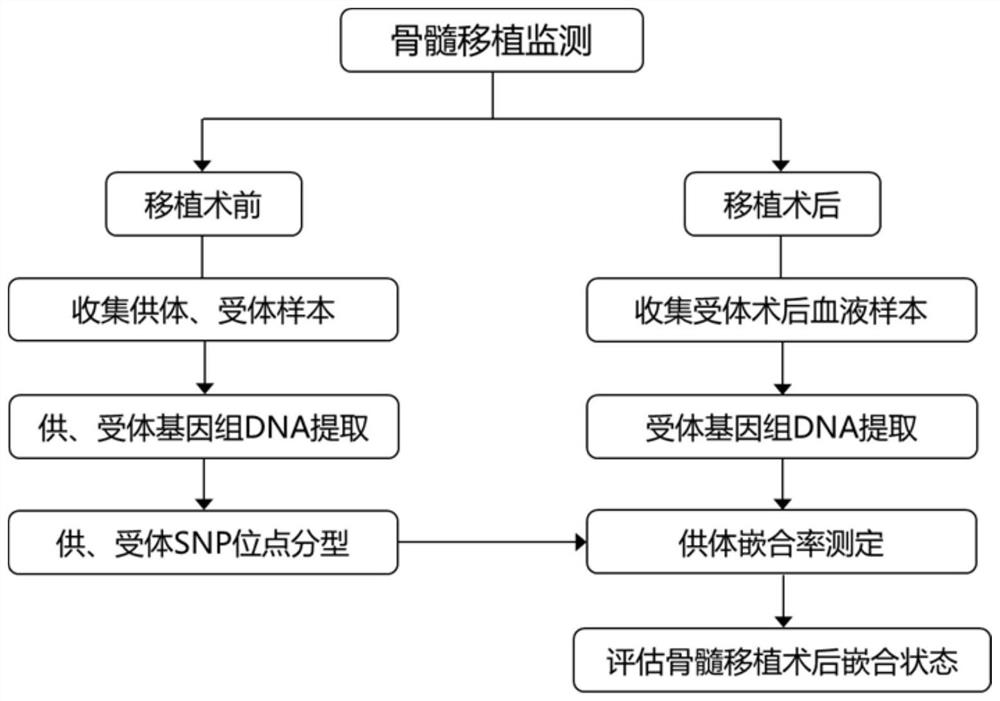
[0424] Example 2. Determination of Chimeric Rate of Bone Marrow Transplant Donors
[0425] The detection process of this example is as follows figure 2 As shown, taking two bone marrow transplant sample groups as an example, the following two parts of samples were collected: 1. Collect and extract the donor samples and recipient samples of bone marrow transplant patients before transplantation for SNP typing, SNP typing principle such as figure 1 shown. 2. Collect peripheral blood at various time points during the recipient monitoring period after transplantation, and extract genomic DNA for quantification of target SNP sites, detection of donor chimerism after bone marrow transplantation, and evaluation of chimerism after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation state.
[0426] The specific operation steps of the above detection process are as follows:
[0427] 1. Collect 2 bone marrow transplantation sample groups (each group includes donor samples before tr...
Embodiment 3
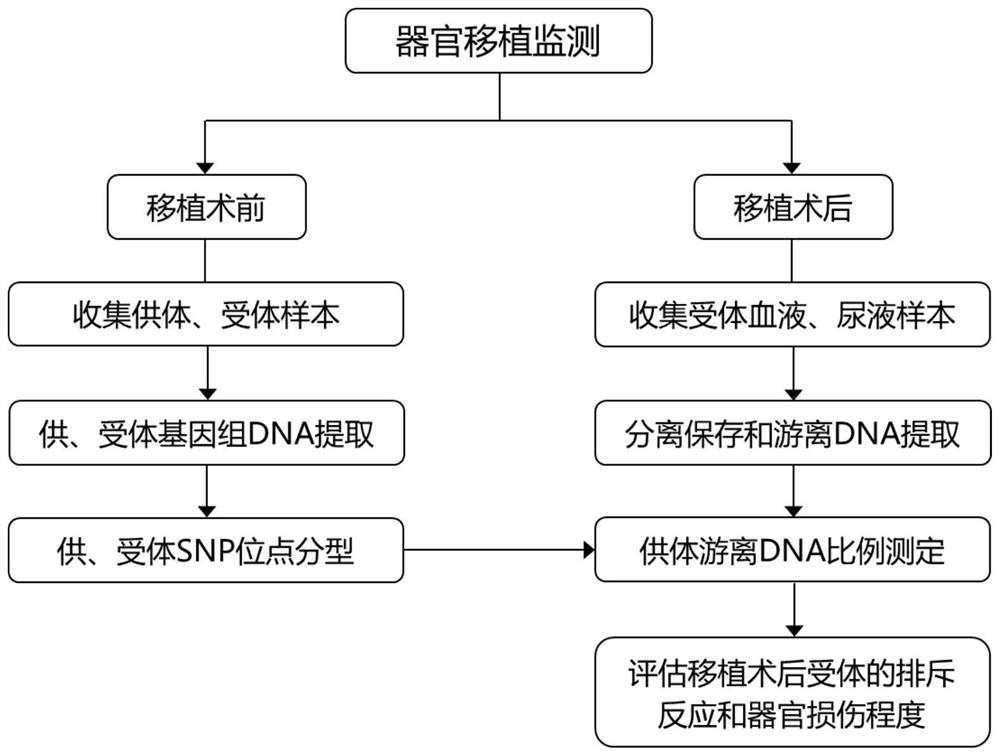
[0459] Example 3. The determination of the donor's free DNA ratio in organ transplantation (with donor information)
[0460] In this example, the determination of the proportion of donor cfDNA in the plasma and urine samples after a kidney transplantation was taken as an example to monitor the organ damage of kidney transplantation case 3, and investigate the feasibility of the method of the present invention for measuring the proportion of dd-cfDNA in organ transplantation and detection performance.
[0461] The detection process of this example case is as follows image 3 As shown, taking a kidney transplant sample group as an example, the following two parts of samples need to be collected: (1) Collect and extract the donor samples and recipient samples of kidney transplant patients before transplantation for SNP typing. Type principle such as figure 1 shown; or collect post-transplant recipient blood cell sediment, saliva, tissues other than transplanted organs, skin, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com