Preparation method of super-amphiphobic coating with stable sea-island structure
A structurally stable, super-amphiphobic technology, applied in coatings and other directions, can solve the problems of limited improvement in mechanical stability of super-amphiphobic coatings and loss of adhesive bonding performance, and achieve excellent mechanical stability and super-amphiphobicity. performance, improve mechanical stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
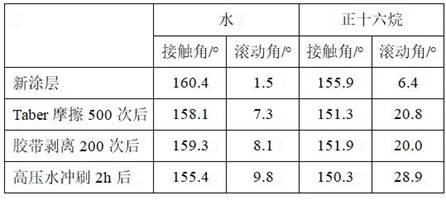
[0025] (1) 12g of hydrophilic silica nanoparticles dispersed into 440mL ethanol, stirred for 10min after ultrasonic dispersion for 5min, followed by 60mL of ammonia stirred for 5min, added 14g of perfluorodecyl trimethoxysilane, reacted at room temperature for 2h, centrifuged, dried, crushed and set aside.
[0026] (2) 2g of ABS polymer binder was dissolved in 8g of butyl acetate, and then 4g of ethanol was added drop by drop under room temperature stirring conditions to make it undergo non-solvent phase separation to form ABS binder microparticle dispersion.
[0027] (3) The 1g silica fluoride nanoparticles were dispersed into the ABS binder microparticle dispersion liquid, stirred for 1h and assisted by ultrasonic dispersion for 10min to obtain the "core-shell" structure of the ABS polymer binder @ silica fluoride particle dispersion.
[0028] (4) The 1g FEVE binder was added to the ABS polymer binder @ silica fluoride microparticle dispersion liquid of the "core-shell" structure ...
Embodiment 2
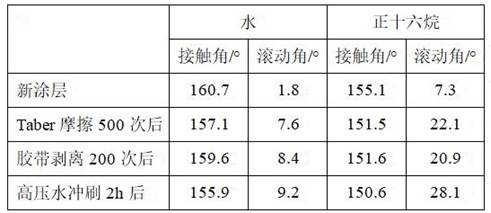
[0032] (1) 9g of hydrophilic silica nanoparticles were dispersed into 470mL ethanol, stirred for 10min and then ultrasonically dispersed for 5min, followed by 30mL of ammonia stirred for 5min and then added 16g of perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane, reacted at room temperature for 4h, the resulting suspension was centrifuged, dried, and crushed for backup.
[0033] (2) 2g of ABS polymer binder was dissolved in 8g of butyl acetate, and then 4g of ethanol was added drop by drop under room temperature stirring conditions to make it undergo non-solvent phase separation to form ABS binder microparticle dispersion.
[0034] (3) The 1g silica nanoparticles prepared are dispersed into the ABS binder microparticle dispersion, stirred for 1h and assisted by ultrasonic dispersion for 10min to obtain the "core - shell" structure of the ABS polymer binder @ silica fluoride microparticle dispersion.
[0035] (4) The 1.5gFEVE binder was added to the ABS polymer binder @ silica fluoride microparticle ...
Embodiment 3
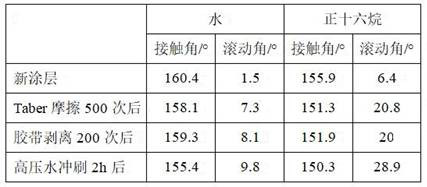
[0039](1) 18g of hydrophilic silica nanoparticles dispersed into 490mL ethanol, stirred for 10min after ultrasonic dispersion for 5min, followed by 10mL of ammonia stirring for 5min, added 30g of perfluorodecyltriethoxysilane, reacted at room temperature for 4h, and then centrifuged, dried, crushed and set aside.
[0040] (2) The 2g ABS polymer binder was dissolved in 8g of ethyl acetate / butyl acetate mixed solvent, and then 6g of methanol was added drop by drop under the condition of room temperature stirring, so that non-solvent phase separation occurred to form abS binder microparticle dispersion.
[0041] (3) The 1.2g silica nanoparticles prepared are dispersed into the ABS binder microparticle dispersion liquid, stirred for 1h and assisted by ultrasonic dispersion for 10min to prepare the "core-shell" structure of THE ABS polymer binder @ silica fluoride microparticle dispersion.
[0042] (4) The 1gFEVE binder was added to the ABS polymer binder @ fluorinated silica micropa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com