FPGA-based multi-master-to-multi-slave access arbitration method and system and storage medium
An arbitration method and a technology for accessing objects, applied in systems and storage media, in the field of FPGA-based multi-master-to-multi-slave access arbitration methods, can solve problems such as limitations on the application of other hardware on the chip, and achieve data conflicts, stability issues, and transmission The effect of stability and effectiveness improvement and arbitration logic optimization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
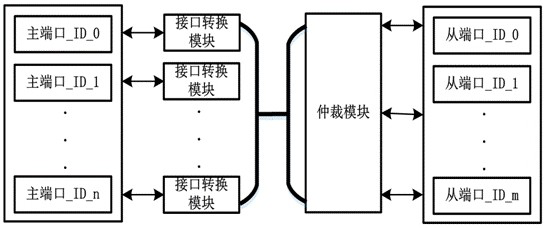
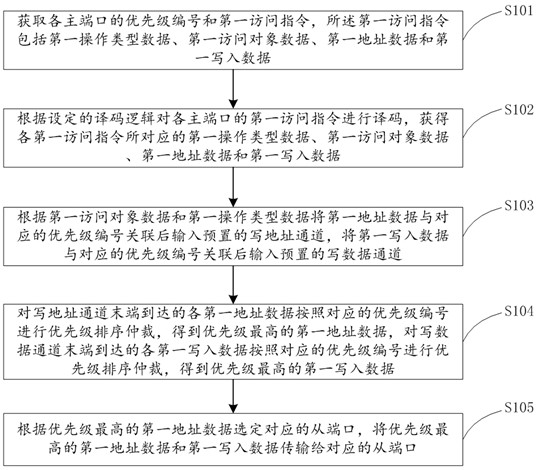
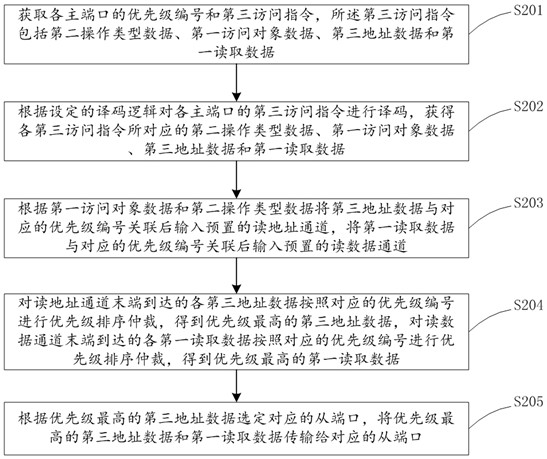
[0062] This embodiment provides an FPGA-based multi-master-to-multi-slave access arbitration method, which can be applied to such as figure 1 The shown FPGA-based multi-master-to-multi-slave access arbitration system, the system includes an arbitration module and several interface conversion modules, the input ends of each interface conversion module are used to connect to the main port, and the interface conversion module can The protocol is flexibly configured as an adapter interface, and a total of six sets of interfaces, including independent write address channel, write data channel, write response channel, read address channel, read data channel and read response channel, are connected to the arbitration module, and the output of the arbitration module The terminal is used to connect with the slave port, and the interface conversion module includes a first status register, a second status register and a first data register. The number of multi-master and multi-slave visi...
Embodiment 2
[0098] The main port of this embodiment takes the SPI interface as an example. The SPI interface transmits 32 bits of data each time, wherein the upper 16 bits are control information and address information, and the lower 16 bits are data information. The allocation of the upper 16 bits of interface data is as follows:
[0099] Bit 15 of the byte: the master port determines the value of this bit according to the current operation, 0 is a write operation, and 1 is a read operation.
[0100] Bit 14 of the byte: the master port determines the current access object to determine the value of this bit, 0 means access to the interface conversion module, 1 means access to the slave port.
[0101] When the access object is the interface conversion module: byte 13-12: a total of 2-bit address encodes the interface conversion module into 4 access intervals, the base address of each access interval is 0x0000, 0x1000, 0x2000, 0x3000, and the function definition of each interval Plan accor...
Embodiment 3
[0106] This embodiment provides a storage medium, on which a first execution instruction is stored. When the first execution instruction runs on the interface conversion module, the interface conversion module executes the interface conversion module in Embodiment 1. functional steps.
[0107] This embodiment provides another storage medium, on which a second execution instruction is stored, and when the second execution instruction runs on the arbitration module, the arbitration module executes the functional steps of the arbitration module in Embodiment 1 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com