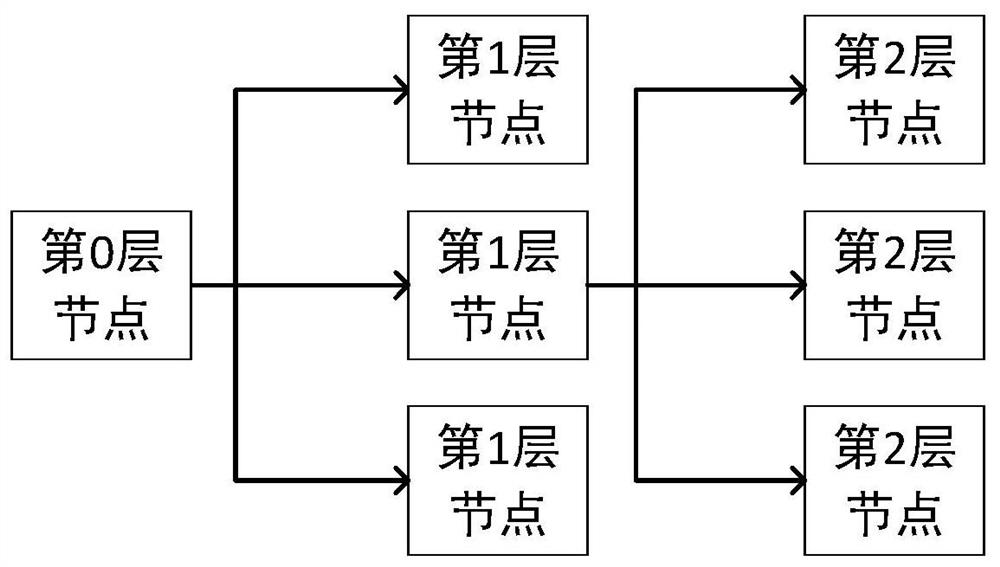
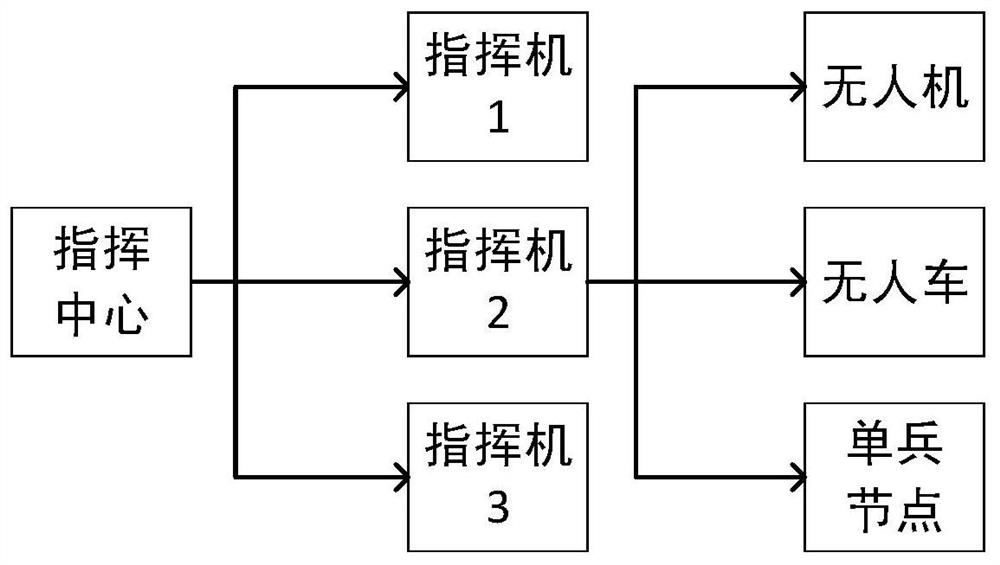
Group communication method and system based on tree structure symmetric key pool
A group communication and symmetric key technology, which is applied in key distribution, can solve problems such as low security, large key quantity, and large capacity, and achieve the effects of enhanced use security, good protection measures, and security assurance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] Example 1: Group communication when members are trusted
[0083] In the case of trusted members, secure communication is performed between any two members A and B in the group. Here we set the replacement key stored by A as KR A , the replacement key stored by B is KR B . Since the relationship between any two nodes in a group may be a parent-child relationship, a brother relationship, or neither a father-son relationship nor a brother relationship, we will discuss these three cases separately below.
[0084] Case 1.1: Communication between two nodes with a parent-child relationship
[0085] 1.1.1: Suppose the parent node is A, the child node is B, the message to be sent by group member A is NTF, and a timestamp TNTF is generated for the message.
[0086] A first needs to calculate the replacement key of B, namely KR B =F KRID (ID B ,KR A ), and then according to KR B Calculate B's key pool.
[0087] A calculates the group key for this group communication:
[...
Embodiment 2
[0098] Example 2: Group communication when a member is untrustworthy
[0099] Let the group administrator be node A, whose ID is ID A , the replacement key is KR A ;
[0100] The untrusted member is X whose ID is ID X , the replacement key is KR X ;
[0101] The trusted superior of X is B whose ID is ID B , the replacement key is KR B ;
[0102] The leaf nodes of X have a total of N X , record any one as C, and its ID is ID C , the replacement key is KR C ;
[0103] Since X can calculate the symmetric key pool of all leaf nodes of X, the group communication security of all leaf nodes of X is affected. Based on this, A will transfer all leaf nodes of X to X's trusted superior B for management. Taking C as an example, after the parent node of C is changed to B, its ID is changed from the original ID C Replace with ID' C , and ID' C is also unique, whose replacement key is determined by the KR C Update to KR' C .
[0104] Taking C as an example, the specific ste...
Embodiment 3
[0138] Embodiment 3: Group communication of newly added trusted members.
[0139] Let the group administrator be A, the newly added trusted member be Y, and the superior node of Y be B. According to Y's layer number and node number, A allocates a corresponding replacement key and a symmetric key pool for Y.
[0140] A generates an NTF to announce that Y is legal, and A sends the NTF to B step by step through the method in case 1.1. After receiving the NTF, B obtains the news that the newly added member Y is legal.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com