Porous composite photoelectric energy storage material for photoinduced continuous cathodic protection as well as preparation and application of porous composite photoelectric energy storage material
A technology of energy storage material and cathodic protection, applied in metal material coating process, liquid chemical plating, coating and other directions, can solve the problem of reducing photocathode protection performance, photoelectrochemical response cathodic protection performance can not be sustained, low efficiency, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of enhancing photoelectric conversion and photocathode protection performance, strong photoelectric continuous cathodic protection performance, high storage and slow release performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
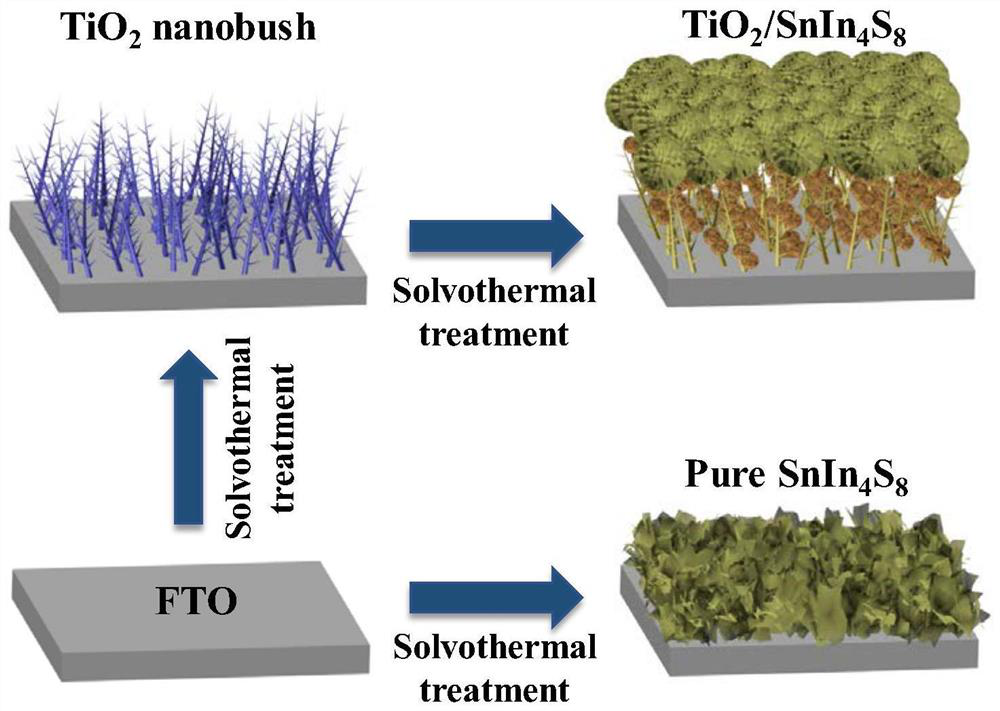
[0045] TiO for sustained photoelectrochemical cathodic protection 2 / SnIn 4 S 8 Preparation of composite photoelectric energy storage photoanode (for the preparation process, see figure 1 ):
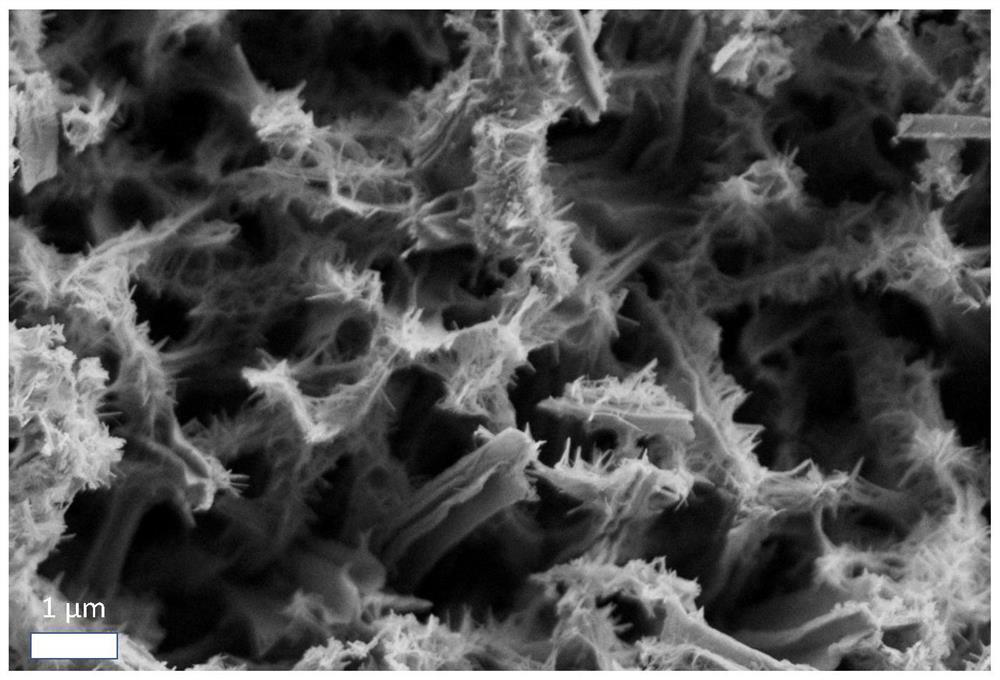
[0046] 1) TiO 2 Preparation of the porous substrate: place the pretreated substrate in the liner of the autoclave, with the conductive side facing down and place it at an angle of 45° to the wall of the autoclave, add solution a into the above autoclave to immerse the substrate, and then place it at 180°C Heated for 9 h to directly grow TiO with porous nanobush structure on the substrate 2 materials; then, after the reactor was cooled, the FTO conductive glass was taken out, washed with deionized water, and dried in an oven at 60°C. Finally, the prepared TiO 2 The nanomaterials were calcined in a tube furnace at 450°C for 1h, and the heating rate was 10°C / min, to obtain TiO 2 Porous substrates (see figure 2 ).
[0047] Described solution a is: take by weighing 0.002mol K 2 Ti...
Embodiment 2
[0055] 1) TiO 2 Preparation of the porous substrate: place the pretreated substrate in the liner of the autoclave, with the conductive side facing down and place it at an angle of 45° to the wall of the autoclave, add solution a into the above autoclave to immerse the substrate, and then place it at 180°C Direct growth of TiO with porous nanobush structure on the substrate by heating for 9 h 2 material (see figure 2 ); Then, after the reactor was cooled, the FTO conductive glass was taken out, washed with deionized water, and dried in an oven at 60°C. Finally, the prepared TiO 2 The nanomaterials were calcined in a tube furnace at 450°C for 1h, and the heating rate was 10°C / min, to obtain TiO 2 Nanoporous substrate (see figure 2 ).
[0056] Described solution a is: take by weighing 0.002mol K 2 TiO(C 2 o 4 ) 2 (Potassium titanium oxalate, PTO) was added with 10 mL of water, and then 20 mL of diethylene glycol DEG was added and the stirring continued for 20 minutes. ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com