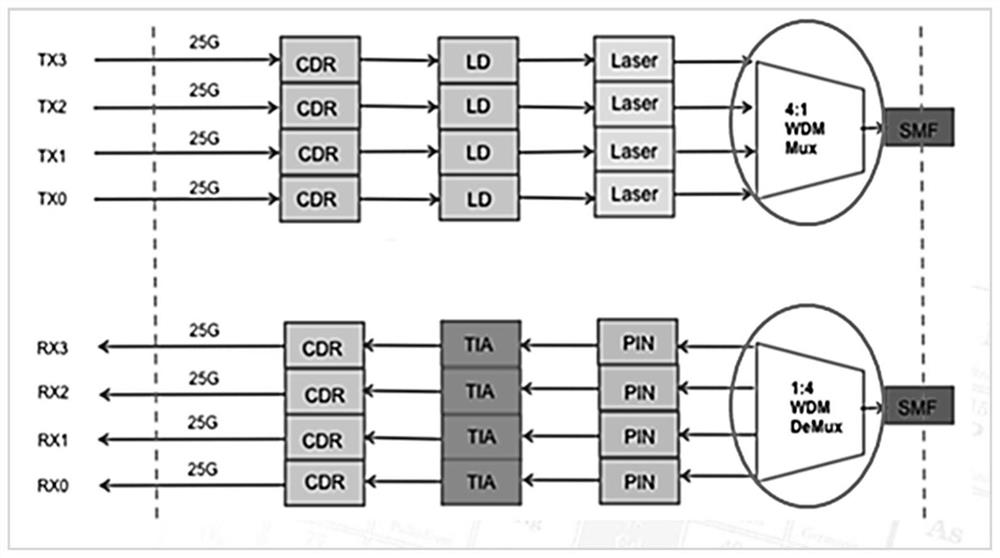
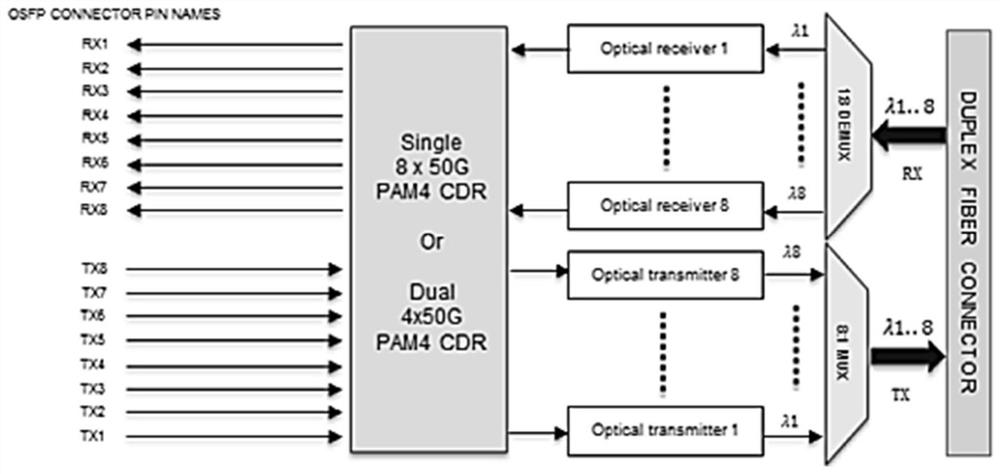
Miniaturized multichannel wavelength division demultiplexing optical receiving assembly
A technology of wave division multiplexing and multiplexing of light, which is applied in the field of optical communication devices, can solve the problems of large wavelength drift with temperature, high insertion loss, narrow bandwidth, etc., achieve small wavelength variation coefficient with temperature, reduce assembly difficulty and cost low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
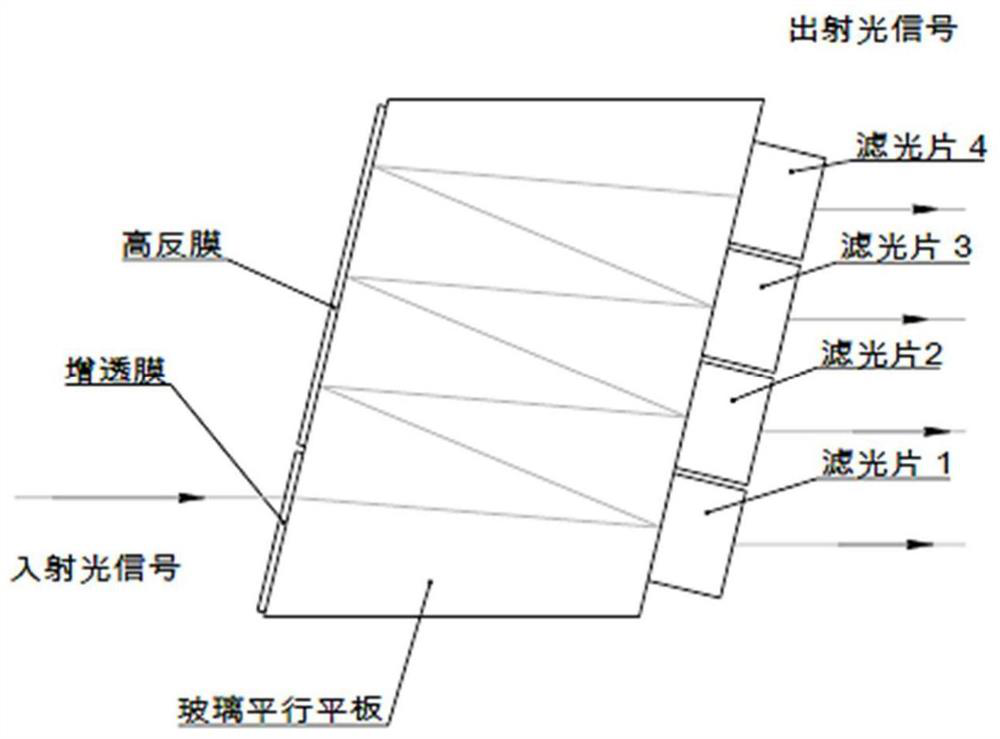
[0089] The 3D schematic diagram of Embodiment 1 of the present invention is as follows Figure 4 As shown, the two-dimensional structure schematic diagram is shown in Figure 5 or Figure 6 shown.
[0090] Miniaturized multi-channel wave division multiplexing optical receiving components, including:
[0091] Fiber collimator 1, for inputting collimated signal light;
[0092] The first wave division multiplexing subassembly 2 is used to decomplex the signal light input by the fiber collimator into several beams of signal light;
[0093] Right-angle prism 3, its rectangular surface is opposite to the output end of the wave division multiplexing subassembly and is used to receive some beams of collimated light decomplexed by the first wave division multiplexing subassembly 2, and then after being reflected by its slope, several A beam of collimated light is output from another rectangular surface of the rectangular prism 3;
[0094] The lens array 4 is arranged on the right-...
Embodiment 2
[0112] The structural representation of embodiment 2 of the present invention is as Figure 9 or Figure 10 shown. In this embodiment, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that the second wave division multiplexing subassembly 6 (1x2 beam splitter structure) of Embodiment 1 is replaced with a 1x2 Z-BLOCK structure; compared with the beam splitter structure, The Z-BLOCK structure greatly reduces the difficulty of WDM coating, which helps to improve yield and reduce cost.
[0113] Other details of this embodiment are implemented in the same manner as in Embodiment 1 (that is, components corresponding to the numbers are the same as those in Embodiment 1), and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0115] The structural representation of Embodiment 3 of the present invention is as follows Figure 11 or Figure 12 Shown; In this embodiment, the only difference from Embodiment 1 is that the lens array is attached to the exit surface of the rectangular prism 3, and at this time, a lens array with a shorter focal length can be selected to obtain a smaller focal length on the focal plane. The size of the light spot, this structure can meet the application occasions where the PD receiving area is small. At this time, it can be ensured that the position of the focal plane of the focused spot coincides with the position of the PD receiving surface by strictly controlling the thickness of the optical substrate 5 .
[0116] In order to achieve a smaller phase difference, when selecting the lens array, you can use such as Figure 13 , Figure 14 Convex sinking lens array (Recession Lens Array) shown. At this time, the steps of the convex surface can be attached to the exit surf...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com