Oil-resistant saccharomyces cerevisiae genetically engineered bacterium and construction method thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in the field of oil-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetically engineered bacteria and its construction, can solve the problem that the activity cannot completely break through the limitations of cell lipid synthesis and storage, and achieve improved cell tolerance and intracellular lipid The effect of qualitative component enhancement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Construction of oil-resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains
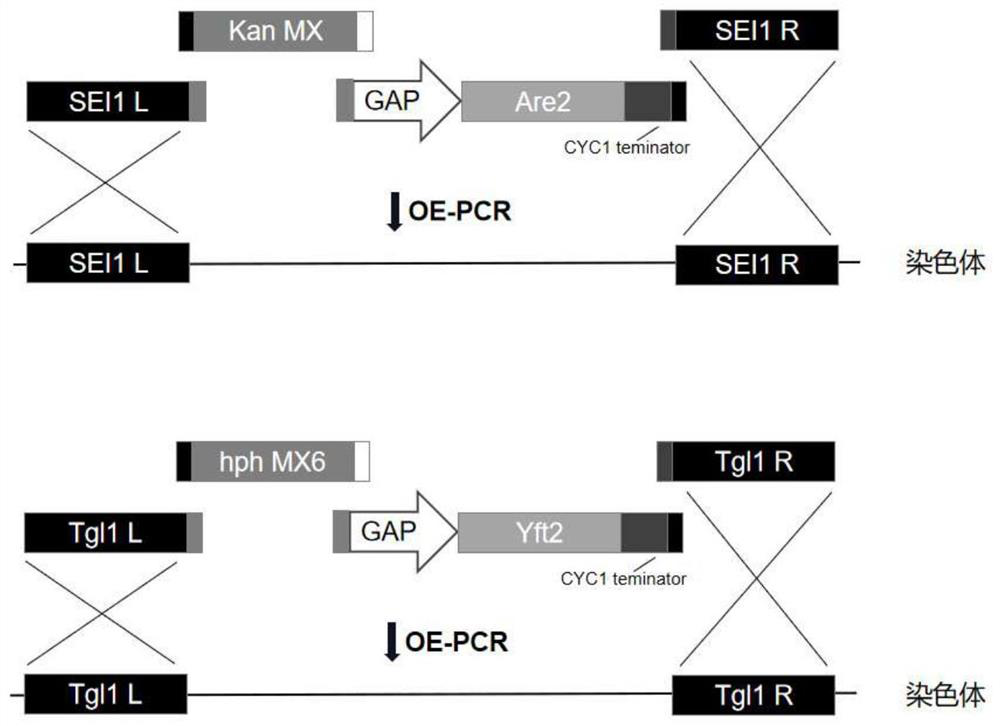
[0032] 1.1 Construction of SEI1::Are2 gene replacement module
[0033] (1) Using the genomic DNA of the original Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 and the pUG6 plasmid as a template, the upstream of the SEI1 gene, the G418 resistance gene, the GAP promoter, the Are2 gene, the CYC1 terminator, and the downstream homology arm of the SEI1 gene were amplified by common PCR amplification. PCR reaction system is shown in Table 1. PCR reaction conditions are as follows: 1) Pre-denaturation at 98°C for 5 minutes; 2) Denaturation at 98°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 58°C for 30 seconds, extension at 72°C for 2 minutes, three steps for 30 cycles, 72°C Extend for another 10 min. Among them, the annealing temperature depends on the Tm value of the primer, and the extension time at 72°C depends on the length of the amplified fragment (1kb·min -1 ). The above gene fragments were obtained by agarose gel elect...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2: Comparison of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell viability under oleic acid-induced stress
[0056] Pick a single colony of wild-type BY4741 and modified bacteria, inoculate it in YPO seed solution and cultivate it for 24 hours, collect the cells, and dilute the fine concentration to OD with YPO medium 600 After = 0.1, the starting bacteria and the modified strains were respectively inoculated in 96-well plates (200 μL / well) and cultured for 72 hours. Three replicate wells were made for each group of experiments, and the cell viability of tetrazolium salt (MTT) was detected every 24 hours during this period.
[0057] The above YPO medium formula is as follows: 0.3% yeast powder, 0.5 peptone, 0.6% glucose, 0.5% KH 2 PO 2 , 0.2% oleic acid, and add 0.2% tween-80 to dissolve the oleic acid.
[0058] Quantitative analysis of MTT cell viability. After culturing at 30°C for 24, 48, and 72 hours, the cell viability of the original strain BY4741 and the modified strain...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3: Nile Red Stained Cell Lipid Droplet Structure and Lipid Content Comparison
[0061] The present invention adopts the Nile red staining method to stain the lipid droplet structure of the cells. Collect BY4741 and BY4741-SEI1::Are2 / Tgl1::Yft2 lipid-tolerant cells cultured in YPD medium at 30°C for 24 hours, and take 1 mL of bacterial liquid for staining experiment. Dissolve Nile Red in DMSO, then add it to the post-incubation solution, keep its final concentration at 2 μg / ml, and incubate at 30°C for 20 min. Pipette 5 μL of the incubated mixed solution and drop it on a glass slide, place it under a fluorescent electron microscope, and use the optical channel and the RFP fluorescent cube channel (Ex=531 / 40; Em=593 / 40) for observation. Oval or spherical Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells with a width of 2.5-5 μm and a length of 4.5-10 μm were observed in the 100× field of view, as well as lipid droplets with a diameter of about 1 μm and yellow fluorescence in the ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com