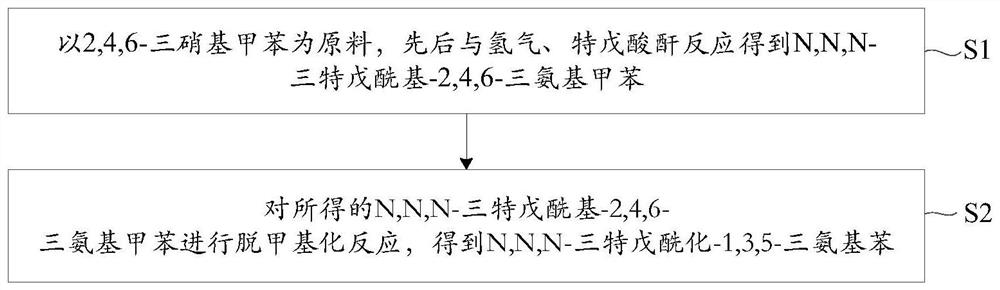
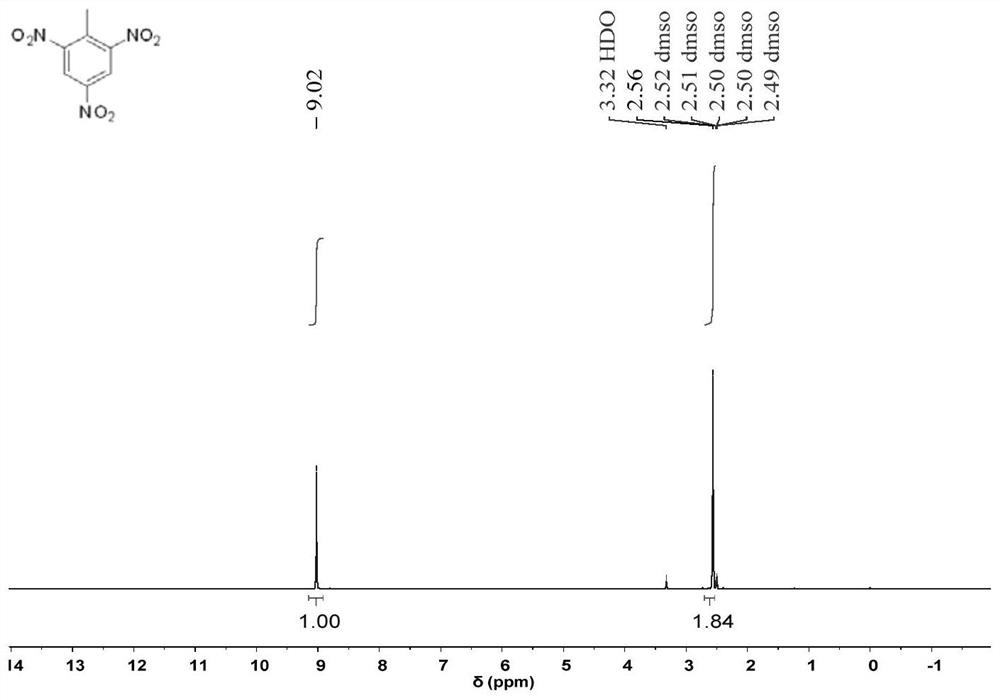
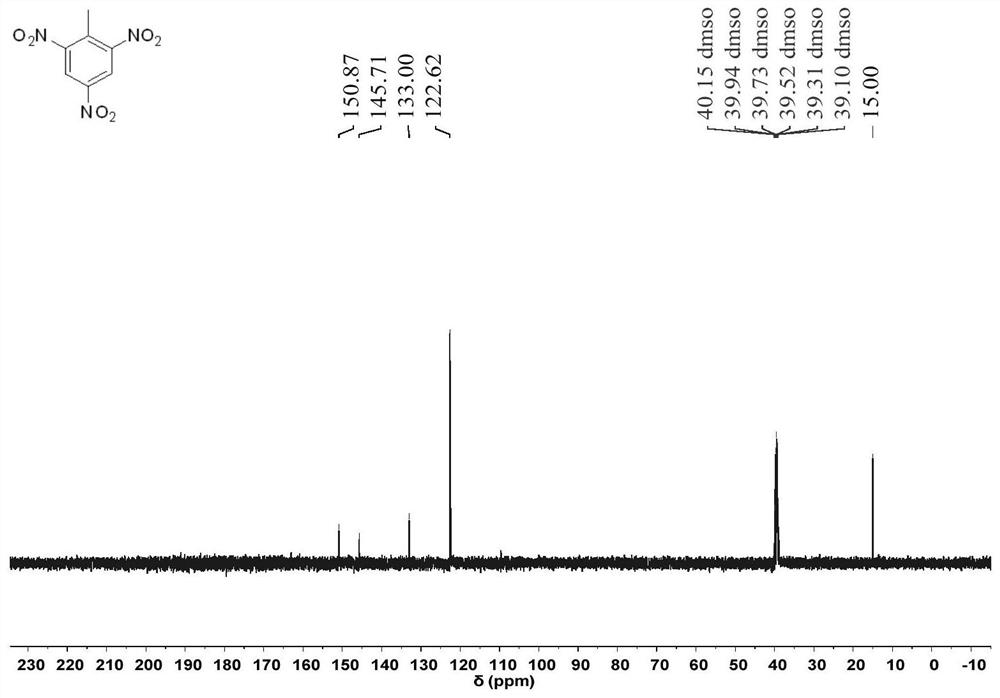
Method for preparing N, N, N-tripivaloyl-1, 3, 5-benzenetriamine
A technology of tripivaloyl and triaminobenzene, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of carboxylic acid amides, preparation of amino compounds, etc., can solve the problems of low N-acylation reaction yield, high synthesis cost and difficult synthesis and other problems, to achieve the effect of compressing costs, improving atomic economic benefits and low prices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076]Step 1: Preparation of N,N,N-tripivaloyl-2,4,6-triaminotoluene represented by structural formula II. In this step, the reduction reaction and the in-situ acylation reaction are combined in the same system. details as follows:
[0077] Dissolve 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT, 3.4g, 0.015mol, 1eq) in a mixture of ethyl acetate (30ml) / pivalic anhydride (87ml, 0.45mol, 10eq) to obtain a TNT solution , put into Pd / C catalyst (0.3g) and triethylamine (64ml, 10eq), transfer to the high-pressure stirred reactor, vacuumize the high-pressure stirred reactor, fill with nitrogen, repeat several times, and finally vacuumize to ensure that there is no air residue , continue to feed hydrogen for high-pressure (0.6MPa) reduction reaction and in-situ N-acylation reaction at room temperature, the reaction lasts for 4 hours, and the reaction temperature is 30 ° C. After the reaction, a dark red solution and Pd / C catalyst are obtained.
[0078] The post-processing step is: after filtering out...
Embodiment 2
[0101] The implementation content of step 1 in this embodiment is similar to the implementation content of step 1 in the above-mentioned embodiment 1, the difference is that the mass ratio of Pd / C catalyst to TNT is 0.05:1, the pressure of hydrogen is 0.8MP, pivalic anhydride and TNT The molar ratio of the base is 5:1, the molar ratio of diisopropylethylamine to TNT is 5:1, the reaction solvent is methanol, the reduction reaction temperature is 15°C, the reduction reaction time is 0.5h, and the acylation reaction temperature is 5°C, the acylation reaction time was 0.5h, and the yield was 88%.
[0102] Step 2: Preparation of 1,3,5-tripivalamidobenzene.
[0103] Dissolve N,N,N-tripivaloyl-2,4,6-triaminotoluene (0.39g, 1.0mmol) and potassium dichromate (0.88g, 3.0mmol) in 5% aqueous dilute sulfuric acid (10ml) and tert-butanol (10ml), and put it on a magnetic stirrer to make it fully dispersed, and keep stirring on a magnetic stirrer at 90°C for 2 hours, until the red color of t...
Embodiment 3
[0107]The implementation content of step 1 in this embodiment is similar to the implementation content of step 1 in the above-mentioned embodiment 1, the difference is: the mass ratio of Pd / C catalyst to TNT is 0.1:1, the pressure of hydrogen is 0.1MP, pivalic anhydride and TNT The molar ratio of the base is 15:1, the base is pyridine and the molar ratio of TNT is 15:1, the reaction solvent is ethanol, the reduction reaction temperature is 30°C, the reduction reaction time is 5h, the acylation reaction temperature is 15°C, the acylation reaction time For 2h, the yield was 83%.
[0108] Step 2: Preparation of 1,3,5-tripivalamidobenzene:
[0109] Dissolve N,N,N-tripivaloyl-2,4,6-triaminotoluene (0.39g, 1.0mmol) and cobalt acetate (0.035g, 0.2mmol) in hexafluoroisopropanol (5ml), Add N-hydroxyphthalimide (1.4g) to the reaction solution, and charge 0.1MPa of O after getting rid of excess air. 2 . Raise the temperature to 60°C, react for 6 hours, discharge excess oxygen, re-rais...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Crystallization temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Crystallization temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com