Method for preparing medium-sized spinous process neurons from non-neuronal cell transformation and application
A neuron cell and neuron technology, applied in the field of cell transformation, can solve the problems of low cell survival rate, difficulty in industrialized preparation, market demand, and difficult realization of cryopreservation recovery utilization, etc., to achieve high cell viability and cryopreservation Recovery utilization, high-purity effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0058] Based on the above preparation method, the specific preparation method of the present invention may include the following steps:
[0059] Step S01, determining the cell transdifferentiation gene combination, wherein the cell transdifferentiation gene combination comprises a combination of the following genes: (1) at least one gene selected from NGN2 and ASCL1; (2) selected from DLX1, DLX2, LHX6, CTIP2 and (3) at least one gene selected from SOX4 and SOX11;
[0060] Step S02, constructing the genes in the above-mentioned cell transdifferentiation gene combination as a single, two, or three (connecting two different genes with 2A sequence or IRES sequence) into a commercially available or self-owned retroviral vector, Lentiviral vectors or AAV viral vectors, the promoters that regulate expression levels in each vector can be any one, two or more combinations of CMV, CAG, EF1α, PGK, TRE Tight, and TRE3G. No restrictions. At the same time, green or red fluorescent reporte...
Embodiment 1
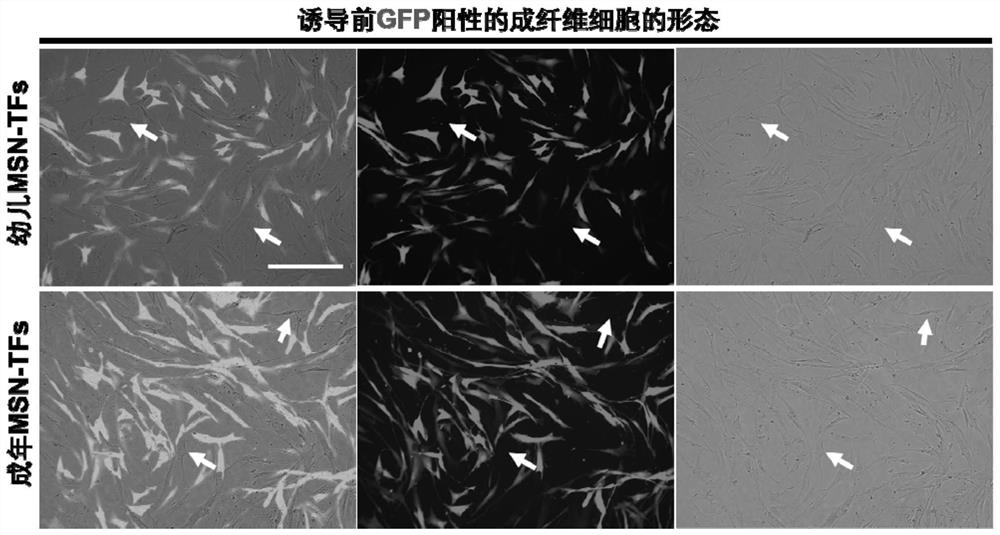
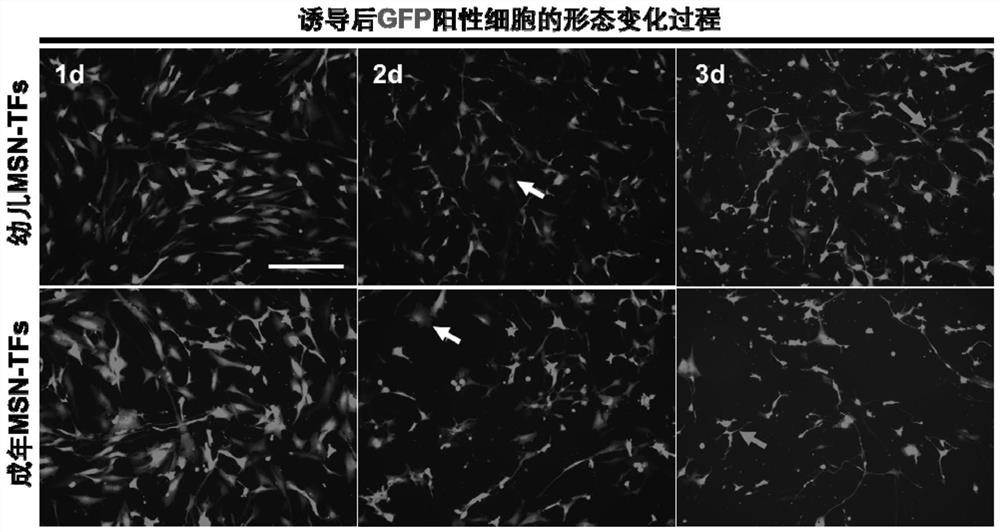
[0087] A method for preparing medium-sized spinous neurons from non-neuronal cells. The materials, equipment and reagents used in the process of preparing medium-sized spinous neurons in this embodiment are as follows:
[0088] 1. Materials
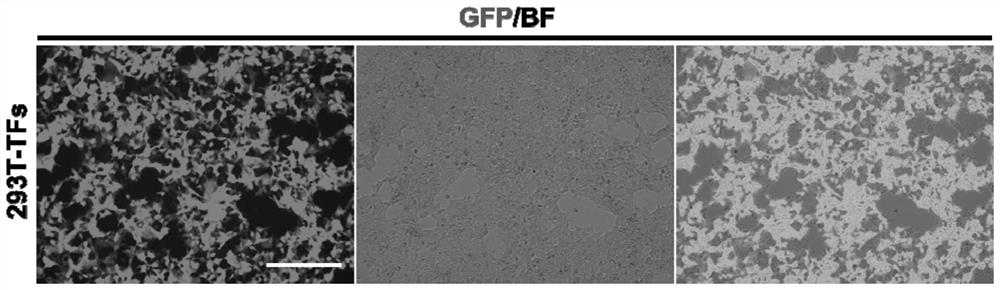
[0089] Cells: 293T cells were purchased from American ATCC (CRL-3216); human skin fibroblasts were purchased from American Sciencell (product number #2310, #2320). The cells were cultured with high-glucose DMEM medium containing 10-20% FBS and 1×P / S double antibody.
[0090] 2. Instruments and reagents:
[0091] (1) CO2 cell incubator (ESCO CLM-170B-8-CN); ultra-clean bench (ESCO AC2-5S1); fluorescence microscope (Thermo EVOS M5000); ultra-low temperature refrigerator (Haier DW-86L388J); liquid nitrogen tank ( Haier YDS-175-216-F); high-speed refrigerated centrifuge (Baiyang BY-R20); room temperature high-speed centrifuge (Xiangyi H1650-W);
[0092] (2) Intelligent high-pressure steam sterilizer (Shanghai Shenan LDZM-80KCS); American S...
Embodiment 2
[0119] 1. Materials, equipment and reagents
[0120] Human lung fibroblast MRC-5 (CCL-171) was purchased from ATCC Corporation of the United States. Other materials, equipment and reagents used in the preparation of medium-sized spiny neurons in this example are the same as those in Example 1.
[0121] 2. Preparation method
[0122] A method for preparing medium-sized spinous neurons from non-neuronal cells, the non-neuronal cells are human lung fibroblasts, so embodiment 2 provides a method for preparing medium-sized spinous neurons from lung fibroblasts, the The method includes the following steps:
[0123] Step S21, construction of plasmids: Ascl1, Dlx1, Dlx2, LHX6, CTIP2, and Sox4 genes were respectively constructed into retroviral vectors, the promoters regulating gene expression levels in the vectors were CAG and CMV, and a green fluorescent reporter was introduced through the IRES sequence at the same time Gene, in order to determine the quality and titer of virus pac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com