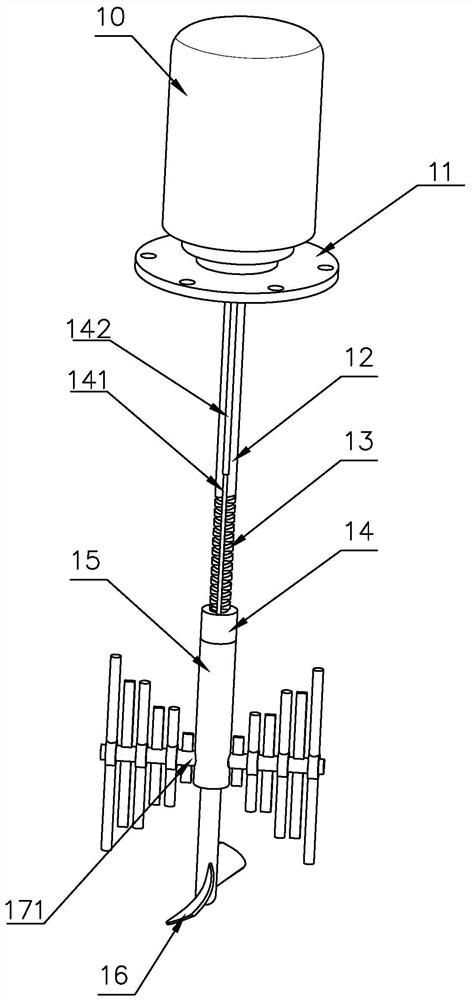
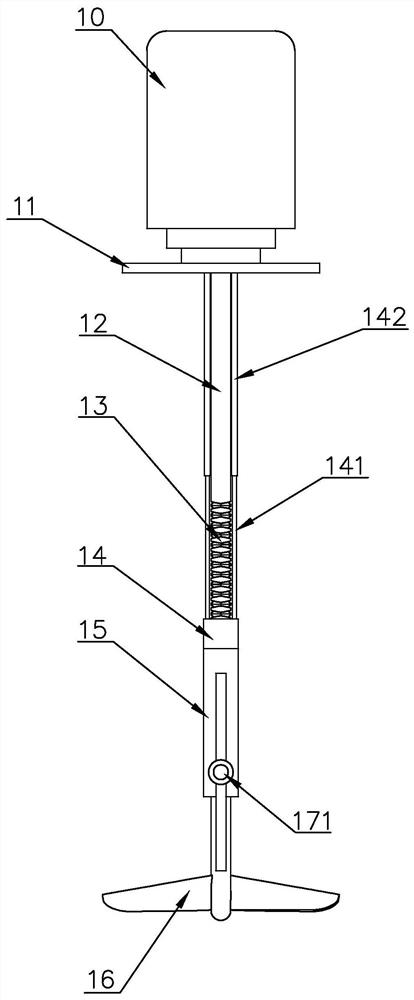
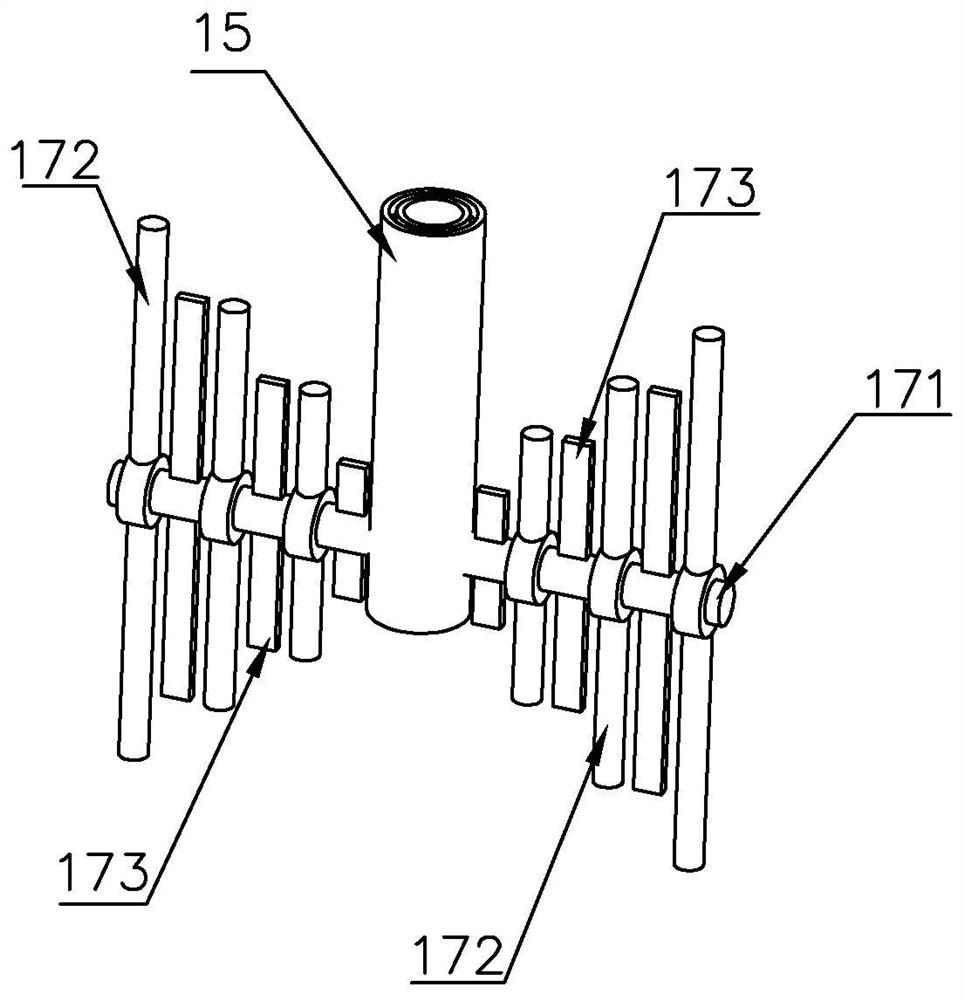
Modified fulvic acid chelated medium trace element sustained release preparation and preparation method thereof
A medium and trace element, slow-release preparation technology, applied in ammonium nitrate fertilizer, nitrate fertilizer, fertilizer mixture, etc., can solve the problems of easy agglomeration or precipitation, inability to mix quickly and evenly, and high local concentration, and achieve chelation. It has obvious effect, promotes the formation of soil aggregate structure, and has quick effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] A modified fulvic acid chelated trace element slow-release preparation is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 10 parts of modified fulvic acid, 6 parts of calcium ammonium nitrate, 2 parts of magnesium nitrate, and 0.2 parts of ferrous sulfate 0.8 part of boric acid, 0.2 part of manganese sulfate, 0.5 part of zinc sulfate, 0.3 part of copper sulfate, 0.01 part of ammonium heptamolybdate, 1 part of slow-release aid, and 79 parts of water.
[0044] The modified fulvic acid is prepared by the following method: disperse 10g of fulvic acid in 100ml deionized water, add 10g NaOH, stir at 100°C for 30min to obtain dispersion A; weigh 8g of sodium sulfite and 3mL Add formaldehyde slowly to the dispersion A under stirring, then react at 80-100°C for 30-60min, filter, collect the clear liquid, dry it, and grind it.
[0045] The slow-release aid is a mixture of polyethylene glycol and carboxymethylcellulose hydrogel; the mass percentage of the cellulose h...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Compared with Example 1, the difference is that a modified fulvic acid chelated trace element slow-release preparation is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 15 parts of modified fulvic acid, 9 parts of calcium ammonium nitrate 4 parts of magnesium nitrate, 0.5 parts of ferrous sulfate, 1 part of boric acid, 0.4 parts of manganese sulfate, 1 part of zinc sulfate, 0.55 parts of copper sulfate, 0.5 parts of ammonium heptamolybdate, 2.5 parts of slow-release additives, 65.55 parts of water .
[0056] The modified fulvic acid is prepared by the following method: disperse 10g of fulvic acid in 50ml of absolute ethanol, add 0.5wt% Tween 80, and stir at a constant temperature of 40°C for 30min to obtain dispersion A; Take 5g of chitosan oligosaccharide and dissolve it in 200m L of distilled water at 50°C under stirring to obtain solution B; slowly add solution B to the dispersion A under stirring within 30 minutes, and then stand at 0-4°C After 20 ho...
Embodiment 3
[0065] Compared with Example 1, the difference is that a modified fulvic acid chelated trace element slow-release preparation is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20 parts of modified fulvic acid, 12 parts of calcium ammonium nitrate 6 parts of magnesium nitrate, 0.8 parts of ferrous sulfate, 1.2 parts of boric acid, 0.6 parts of manganese sulfate, 1.5 parts of zinc sulfate, 0.8 parts of copper sulfate, 0.1 parts of ammonium heptamolybdate, 5 parts of sustained-release aids, 52 parts of water .
[0066] The modified fulvic acid is prepared by the following method: disperse 10g of fulvic acid in 100ml deionized water, add 10g NaOH, stir at 100°C for 30min to obtain dispersion A; weigh 8g of sodium sulfite and 3mL Add formaldehyde slowly to the dispersion A under stirring, then react at 80-100°C for 30-60min, filter, collect the clear liquid and dry it, then grind it;
[0067] The slow-release aid is a mixture of polyethylene glycol and alginic acid ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com