A method for preparing a sample for transmission electron microscopy
An electron microscope and sample technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, material analysis using radiation, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, etc., can solve problems such as damage, failure to show contrast of protective layer, and damaged structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
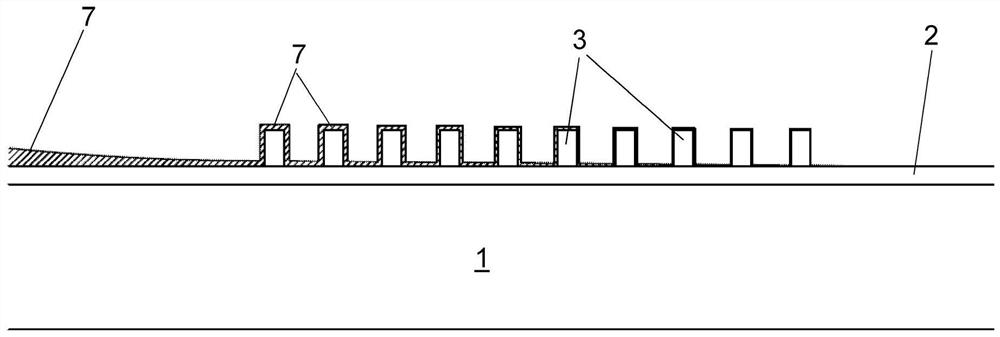
[0022] A preferred embodiment of the invention will be described for the case of a set of parallel polymeric resist lines. Said materials and processes known per se are mentioned by way of example only and are not intended to limit the scope of the invention. figure 1 Shown is a substrate 1 , which may be a glass substrate, which has a silicon layer 2 on its surface. On the Si layer is a patterned area 8 comprising an array of parallel polymer resist lines 3, produced by a lithographic patterning technique per se known in the art . The pitches of the line arrays are of the same order of magnitude. The goal is to obtain TEM samples that allow verification of these dimensions. To do this, a protective spin-on-carbon (SoC) layer is deposited on the resist line 3 and either side of the lamella oriented in a direction perpendicular to the line 3 is milled away in a focused ion beam (FIB) tool. materials to generate substrate TEM samples. The profile of sample 4 is at figure 1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com