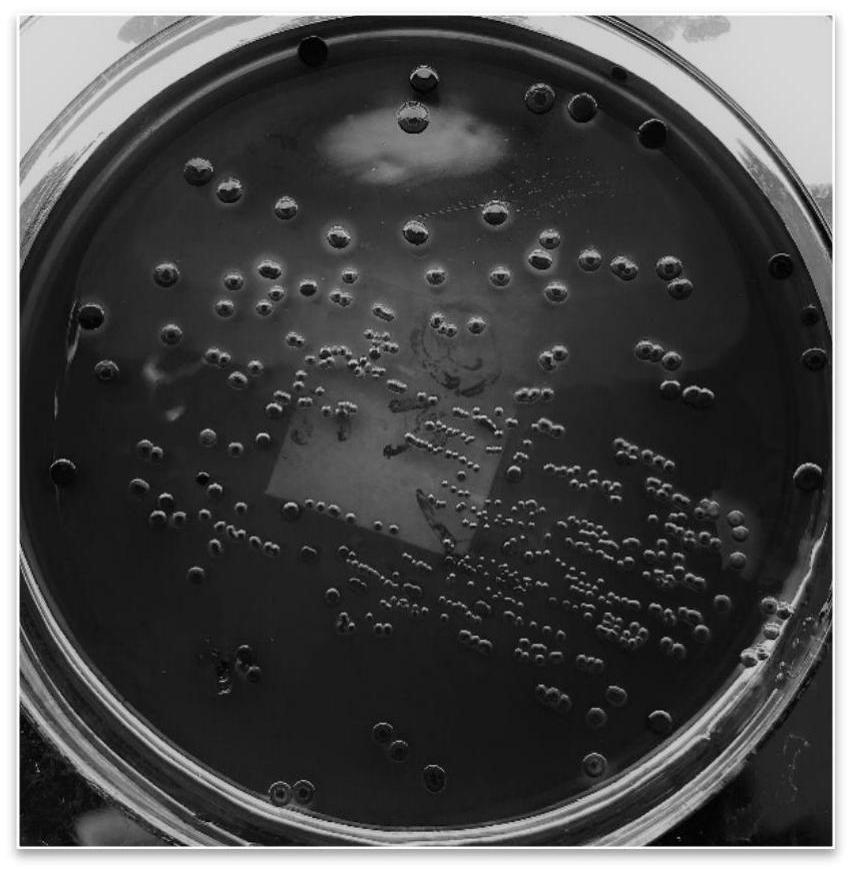
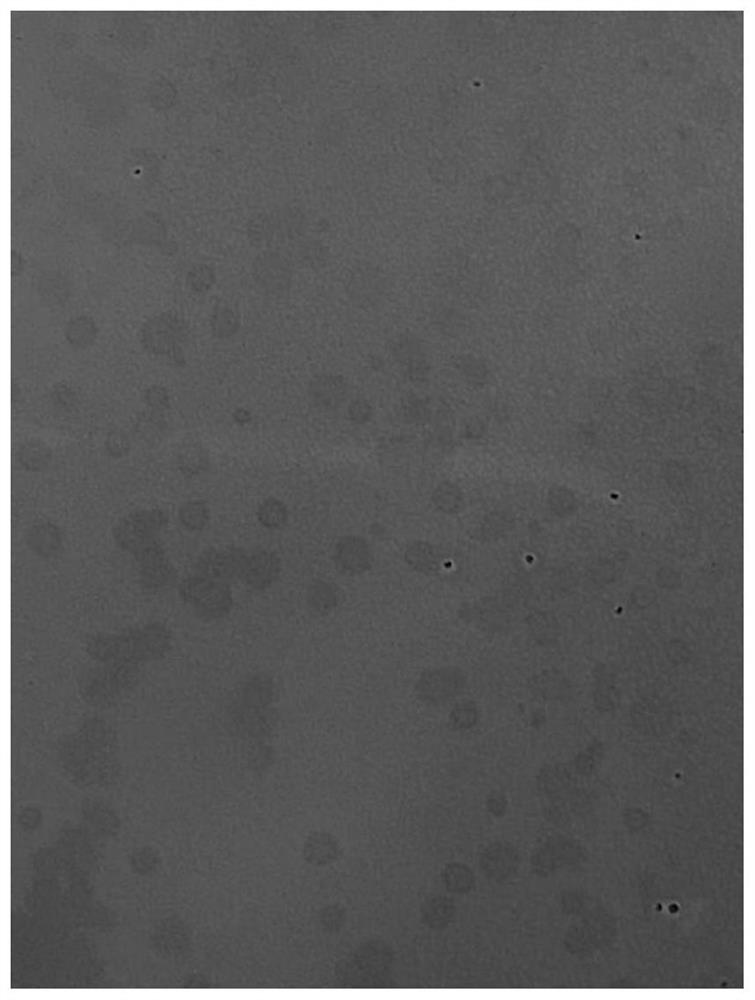
Method for culturing and observing plaque
A plaque and phage technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as pollution, phage inactivation, and interference with experimental results, and achieve the effects of high operating intensity, enhanced selectivity, and avoiding coagulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] 1. Experimental materials
[0031] 1.1 Medium and reagents
[0032] ①Lactose-peptone liquid medium
[0033] 10g of peptone, 3g of beef extract, 5g of lactose, 5g of NaCl, 1.0ml of 16g / L bromocresol purple ethanol solution, 1000ml of distilled water, pH 7.2~7.4, put into test tubes, 5ml in each tube, and put a small inverted tube inside 115 Sterilize at ℃ for 30min.
[0034] ② Eosin-methylene blue medium (EMB) medium
[0035] Peptone 10g, lactose 10g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 2g, agar 18-20g, distilled water 1000ml, pH 7.2-7.4, sterilize at 115°C for 30min, add 20g / L eosin aqueous solution 20ml, 5g / L methylene blue aqueous solution 13ml , mix well, pour into a plate, and store in a refrigerator at 4°C after solidification.
[0036] ③Beef extract peptone liquid medium
[0037] Beef extract 3g, peptone 10g, NaCl 5g, CaCl 2 10mM, 1000ml of water, pH 7.0-7.2, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0038] ④Water agar
[0039] Agar 18-20g, water 1000ml, sterilized at 12...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com