Variable admittance assisted large component assembly method and system based on operating intention recognition
An assembly method and technology of variable admittance, applied in general control systems, control/adjustment systems, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as hidden safety hazards, slow changes in the motion state of robots, and unconsidered effects, and achieve high safety and improved operation. Comfort and responsiveness, good handling flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0093] In the following description, numerous specific details are given in order to provide a more thorough understanding of the present invention. It will be apparent, however, to one skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without one or more of these details. In other examples, some technical features known in the art are not described in order to avoid confusion with the present invention.
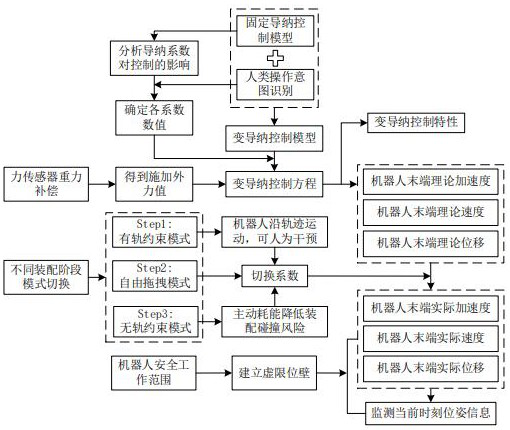
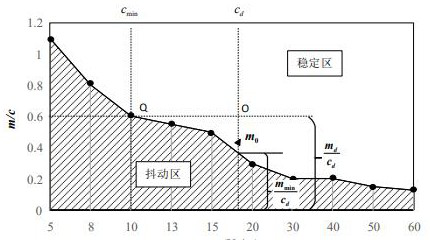
[0094] The applicant's research found that in the existing control scheme, the inertia suppression of the heavy-duty robot is not obvious, and the setting of the admittance coefficient is difficult to accurately track the change of the operation intention under the condition of heavy load, and the comfort and safety of the system operation are low.
[0095] Therefore, in the compliance-assisted assembly of heavy-duty industrial robots, how to select reasonable robot admittance control coefficients and related system parameters to cooperate with human operation i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com