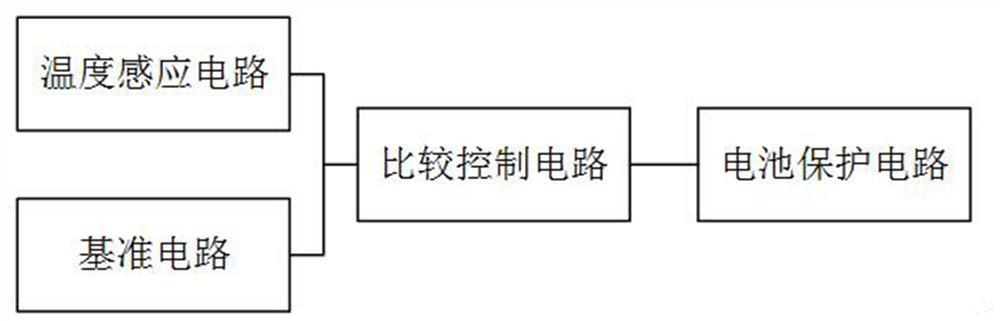
NTC-based battery temperature protection circuit
A technology for protecting the temperature of circuits and batteries, applied in emergency protection circuit devices, emergency protection devices with automatic disconnection, circuit devices, etc., can solve the problems of decreased stability of chemical substances, low detection sensitivity, and increased hidden dangers of batteries, etc., to achieve Effects of improved sensitivity, simple circuit structure design, high flexibility and practicality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
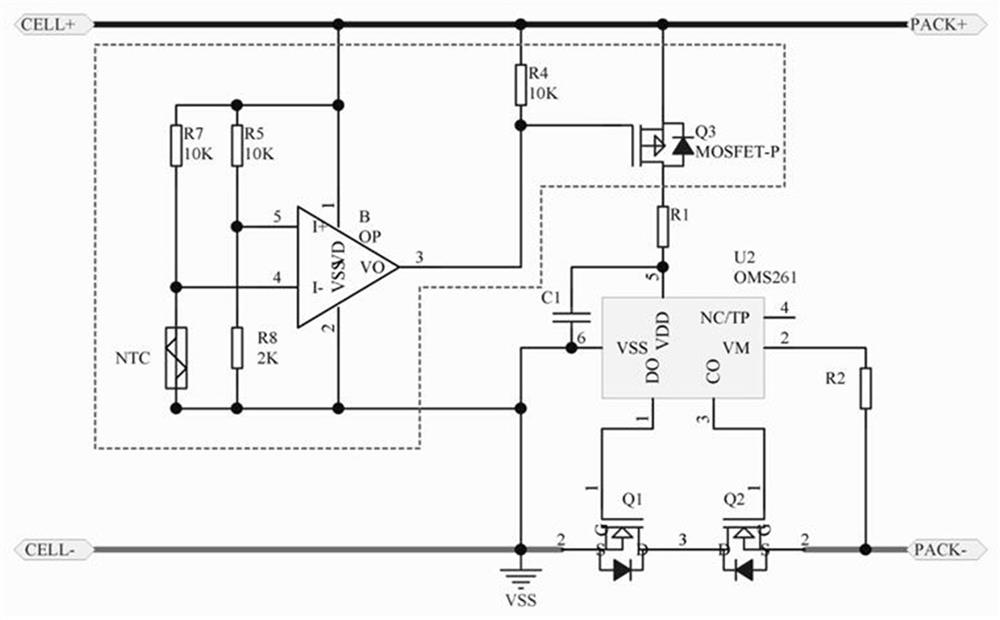
[0043] Embodiment 1: Circuit with charge and discharge high temperature protection
[0044] like figure 2 As shown, in this embodiment, the positive electrode CELL+ of the battery cell is respectively connected to the seventh resistor R7, the fifth resistor R5, the power supply terminal of the operational amplifier OP, the fourth resistor R4, and the source of the control MOS transistor (third MOS transistor Q3) and the positive pole of the battery PACK+, the other end of the seventh resistor R7 is respectively connected to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier OP and the NTC thermistor, and the other end of the fifth resistor R5 is respectively connected to the non-inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier OP and the reference resistor (that is, the first Eight resistors R8), the output terminal of the operational amplifier is respectively connected to the other end of the fourth resistor R4 and the gate of the third MOS transistor Q3, and the...
Embodiment 2
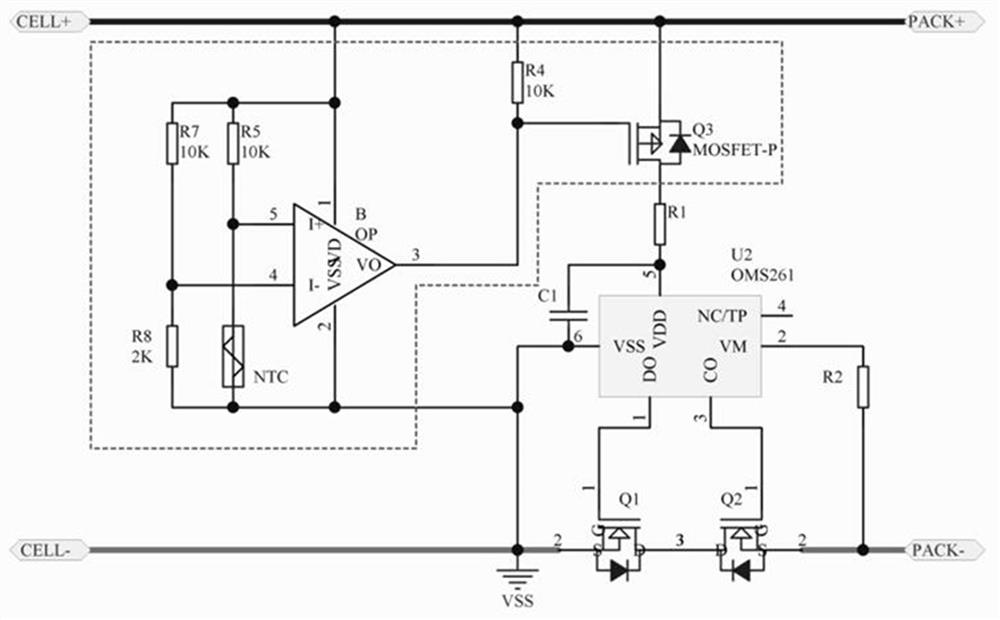
[0050] Embodiment 2: Circuit with charge and discharge low temperature protection
[0051] like image 3 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that this embodiment exchanges the positions of the eighth resistor R8 and the NTC thermistor on the basis of Embodiment 1, that is, the NTC thermistor’s voltage divider is input to the non-inverting input of the operational amplifier OP Terminal, the divided voltage of the eighth resistor R8 is input to the inverting input terminal of the operational amplifier OP.
[0052] At normal temperature, the resistance of the NTC thermistor is higher (lower than the resistance of the eighth resistor R8), and the divided voltage of the branch where it is located is smaller than the divided voltage of the eighth resistor R8 in the branch where it is located, VI+ If it is less than VI-, the operational amplifier OP outputs a low voltage, the third MOS transistor Q3 is turned on, and the battery protection chip U2 works normally. At this t...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3: Circuit with charging high temperature protection
[0057] like Figure 4 As shown, the difference from Embodiment 1 is that in this embodiment, the power supply terminal of the battery protection chip U2 is directly connected to the battery positive electrode PACK+ through the first resistor R1, and the charging output terminal CO of the battery protection chip U2 is connected to the control MOS tube (third The source of the MOS transistor Q3), the gate of the third MOS transistor Q3 is connected to the output terminal of the operational amplifier OP, its drain is connected to the battery negative pole PACK- through the third resistor R3, and the drain of the third MOS transistor Q3 It is also connected to the gate of the charging switch tube (that is, the second MOS transistor Q2).
[0058] Under normal temperature, the resistance value of NTC thermistor is relatively high, and the divided voltage of the NTC thermistor in its branch is greater than the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com