Method for reducing low-molecular-weight carboxyl-terminated fluorine-containing polymer by hydroboron/diisobutylaluminium hydride reduction system
A technology of diisobutylaluminum hydride and borohydride, which is applied in the field of reduction of low-molecular-weight carboxyl-terminated fluoropolymers, can solve the problems of poor selectivity of reduction reaction, high content of metal ions, and difficulty in post-treatment separation, and achieve selectivity High, high reduction rate, excellent chemical stability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] In a three-necked flask, 5 g of low molecular weight carboxyl-terminated fluoropolymer (vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene copolymer, carboxyl mass percentage content 2.5%, number average molecular weight 3600, carboxyl content is 2.8mmoL) was dissolved in 40mL tetrahydrofuran and Add 5.6mmoL sodium borohydride to 10mL diglyme mixed solution at 0°C under inert gas protection, stir for 1 hour, add 5.6mmoL diisobutylaluminum hydride reducing agent, heat up to 60°C, Stirring was continued for 9h. After the reaction is finished, quench the reaction with hydrochloric acid solution, wash with ethanol, and then wash with deionized water for 3 to 4 times, collect the product and dry it in vacuum at 60°C to constant weight, and determine the low molecular weight carboxyl-terminated fluorine-containing polymer by chemical titration. The material reduction rate is 91%.
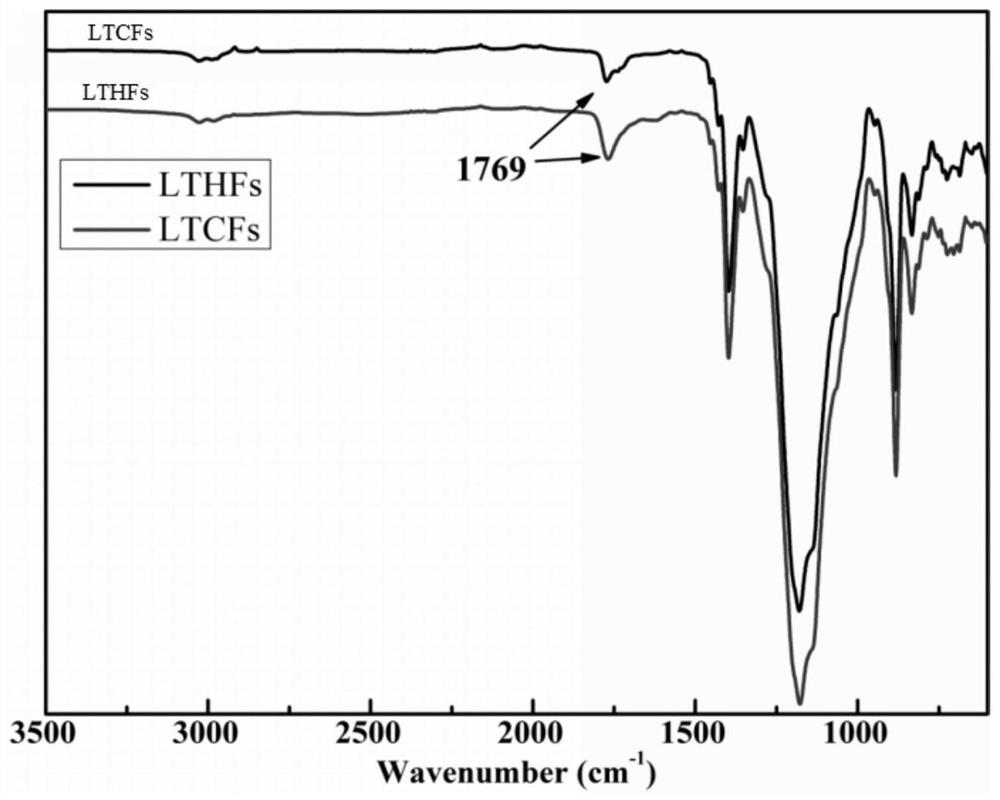
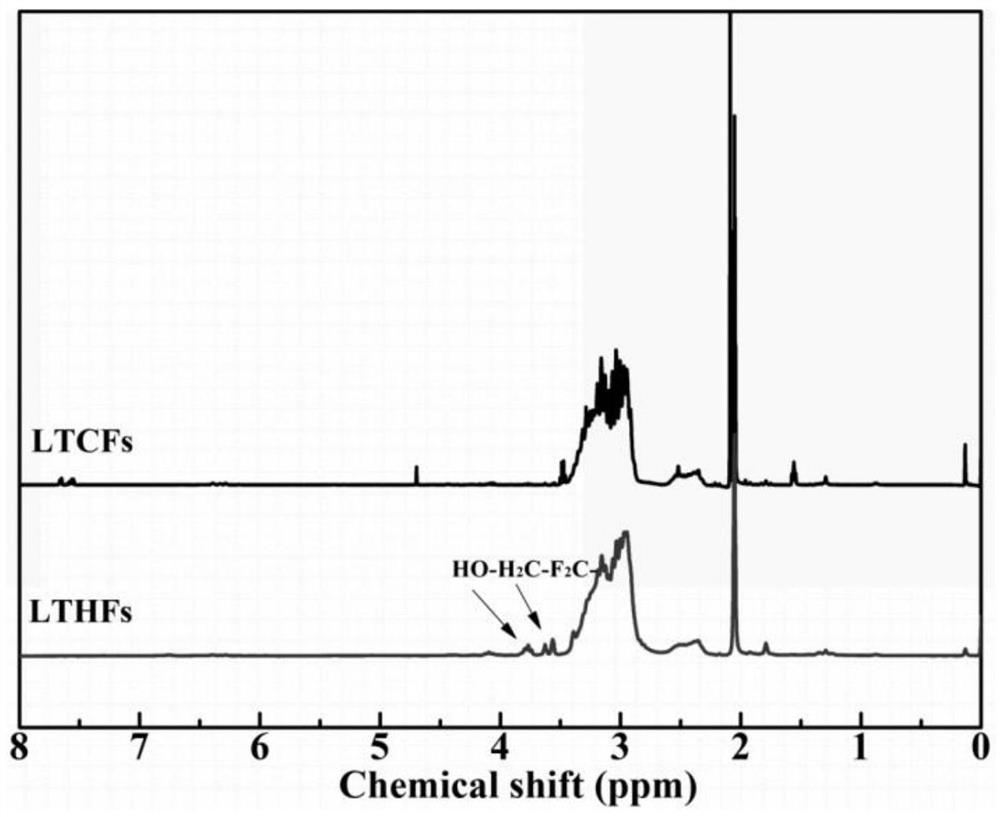
[0026] figure 1 It is the infrared spectrogram of the low molecular weight carboxyl-terminated fluorine-...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Prepare and test according to Example 1. The difference is that the amount of reducing agent is different, and the molar ratio of carboxyl group / sodium borohydride / isobutyl aluminum hydride is 1 / 1 / 1. The reaction condition is 60°C for 9 hours, and the reduction rate up to 75%.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Prepare and test according to Example 1. The difference is that the amount of reducing agent is different, and the molar ratio of carboxyl / sodium borohydride / isobutylaluminum hydride is 1 / 4 / 4. The reaction condition is 60°C for 9 hours, and the reduction rate Reached 91%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com