Detection method related to human papilloma virus infection immune response and application
A technology of human papillomavirus and immune response, which is applied in the field of biomedicine to achieve the effect of assisting clinical detection and testing, with simple methods and clear results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
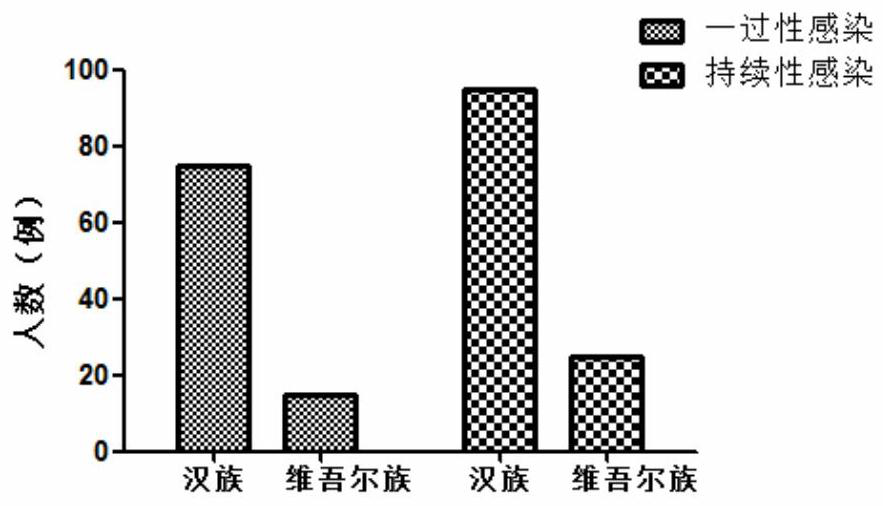
[0033] Example 1 The risk of persistent HPV16 infection is lower in Uighur women than in Han women
[0034] 210 samples were collected, including 90 cases of transient infection and 120 cases of persistent infection. Among the patients with transient infection, there were 75 cases of Han nationality, of which 76% (57 / 75) were infected with HPV16 type; 15 cases of Uyghur nationality, of which 73.3% (11 / 15) were infected with HPV16 type; among the patients with persistent infection, 95 cases were of Han nationality , of which 77.9% (74 / 95) were HPV16 infection; 25 Uighur cases, of which 64% (16 / 25) were HPV16 infection. Persistent HPV16 infection, the proportion of Han women is higher than that of Uyghur women.
[0035] Table 1 Collection of samples meeting the screening criteria in 2017-2018 (example)
[0036]
Embodiment 2
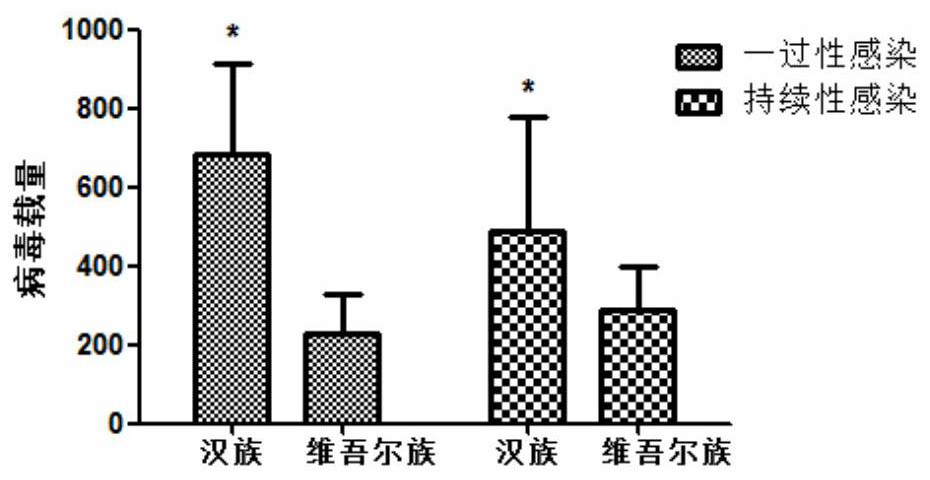
[0037] Example 2 Uyghur women are more likely to cause cervical cancer and the degree is more serious than Han women when the viral load is significantly lower than that of Han women
[0038] In patients with transient and persistent infection, the viral load of HPV positive patients in Han nationality (682.8.3±231.6; 488.4.3±289.6) was significantly higher than that in Uygur nationality (228.3±174.7; 287.2±189.7) (P<0.05) . Combined analysis with my team's research data on cervical cancer of Uyghur women in Xinjiang in the past 10 years, it is found that Uyghur women are more likely to cause cervical cancer and the degree is more serious than Han women when the viral load is significantly lower than that of Han women.
Embodiment 3
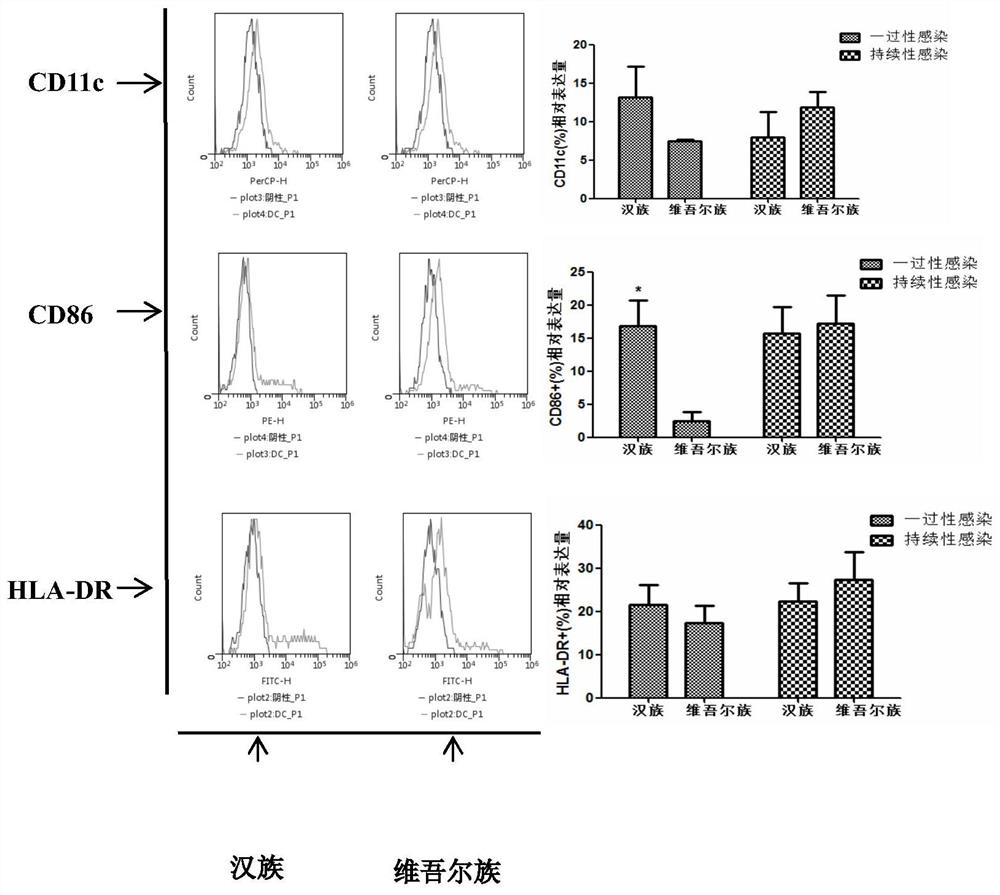
[0039] Example 3 CD86 expression in Uygur women is significantly lower than that in Han women in transient infection
[0040] In peripheral blood DC cell surface markers, there was no significant difference in the expression of CD11c in Han nationality (13.2±3.942; 7.999±3.266)% and Uygur nationality (7.46±0.17; 11.83±2.012)% in transient and persistent infection ( P>0.05); CD86 expression was significantly higher in Han nationality (16.84±3.871)% than in Uygur nationality (2.40±1.380)% in transient infection (P0.05) . There was no significant difference in HLA-DR expression in Han (21.45±4.645; 22.25±4.190)% and Uygur (17.37±3.926; 27.37±6.436)% (P>0.05).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com