Corynespora cassicola CcTLS1 protein, coding gene and application thereof
A technology of Corynebacterium multimaster and coding gene, which can be used in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problem of less cloning and functional identification of pathogenic related genes, and cannot fully represent the pathogenic mechanism of Corynebacterium multimaster. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
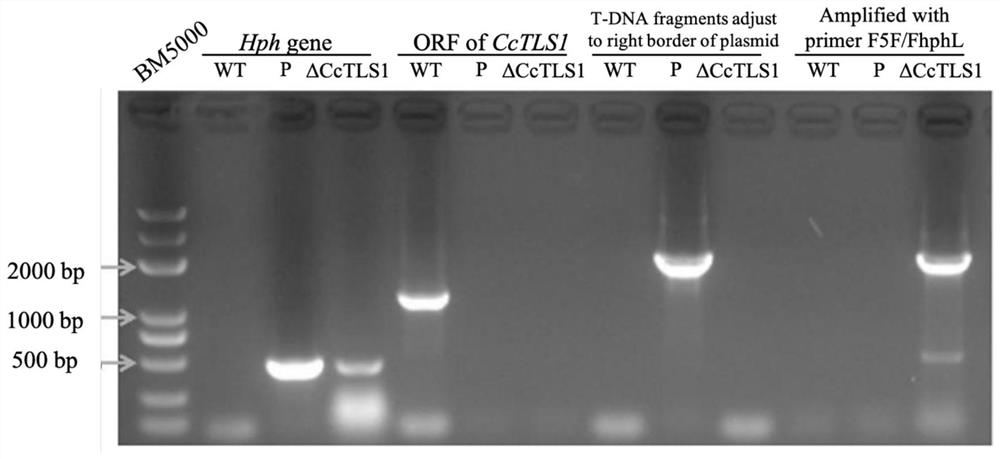
[0079] Example 1 Obtaining of Corynespora polymata CcTLS1 knockout mutant
[0080] 1. Construction of pCAMBIA1300-ΔCcTLS1 knockout vector
[0081] For the amino acid sequence of CcTLS1 in Corynespora polymata, see Sequence 1 in the Sequence Listing, for the CDS sequence encoding CcTLS1 protein, see Sequence 2 in the Sequence Listing, and for the gene sequence of CcTLS1 in Corynespora polymata, see Sequence 4 2049-3270 in the Sequence Listing shown. According to the analysis of the uniprotKB database (https: / / www.uniprot.org / uniprot / ), the CcTLS1 protein does not contain a structural domain. Currently, the specific biological function of the CcTLS1 gene in Corynespora polybasicum is not clear.
[0082] The binary vector pCAMBIA1300 was cut with restriction endonuclease Xho I to remove the hygromycin resistance gene, and self-ligated with T4 ligase, and the resulting plasmid was named pCAMBIA1300-XhoI.
[0083] Using the CTAB method to extract the genomic DNA of Corynespora po...
Embodiment 2
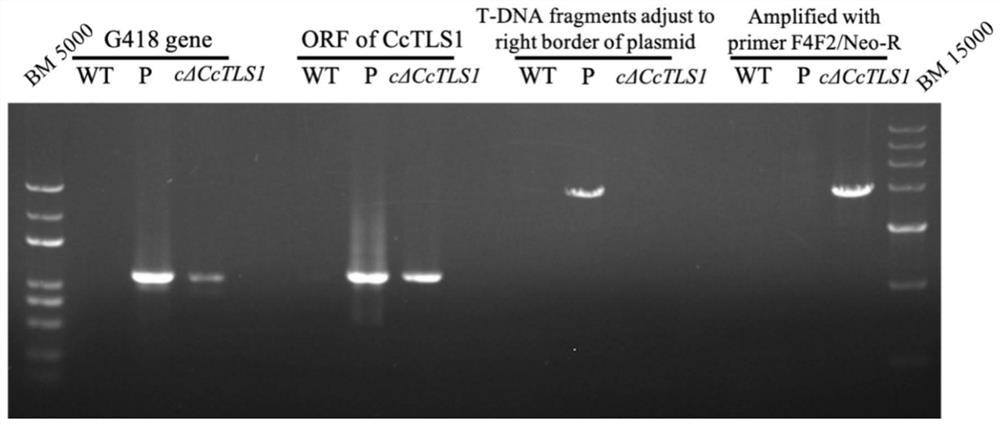
[0120] Example 2, the acquisition of the CcTLS1 anaplerotic mutant of Corynespora polymata
[0121] 1. Construction of pCAMBIA1300-cΔCcTLS1 complementation vector
[0122] Using the CTAB method to extract the genomic DNA of Corynespora polybasicum HG14102524, using the genomic DNA as a template, using MaxDNAPolymerase, with primer pair 4 (primer pair consisting of F4 and R4), PCR amplification was carried out to obtain the CcTLS1 gene and its 5' end 3265kb fragment (containing the 6th-3270th position of sequence 4):
[0123] F4: 5'-CCATGATTAC GAATTC GCTCGGGATTTGGCACACG-3' (the sequence indicated by the underline is the EcoR I enzyme recognition site sequence);
[0124] R4: 5'-CTAGAGGATCCCCGGGTACCTTACAATGGCTGTCGTACTGGG-3' (the sequence indicated by the underline is the Kpn I enzyme recognition site sequence).
[0125] Using the above genomic DNA as a template, using MaxDNAPolymerase, PCR amplification was carried out with primer pair 5 (primer pair consisting of F5 and R...
Embodiment 3
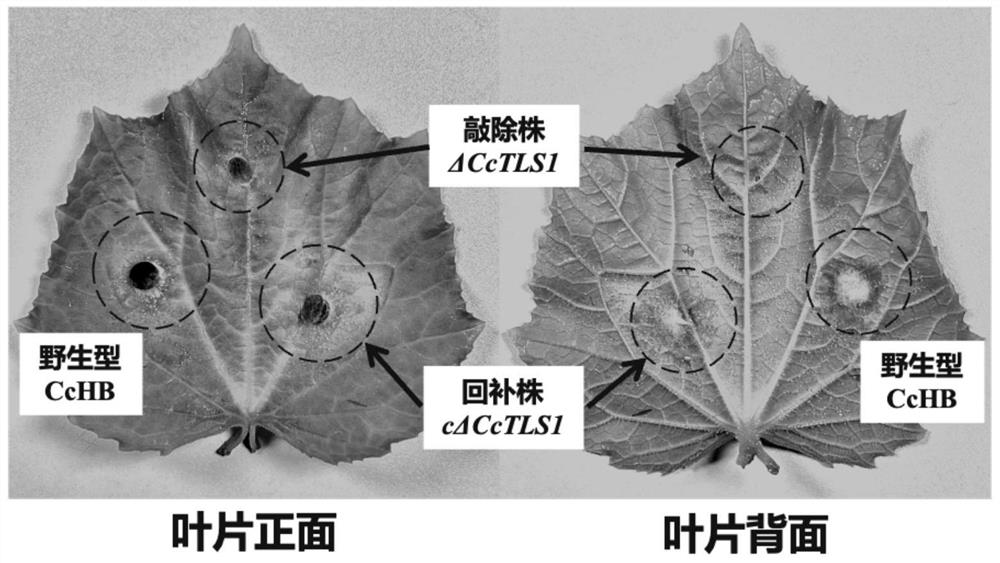
[0159] Pathogenicity detection of embodiment 3 mutants
[0160] The mutants to be tested are the CcTLS1 knockout mutant ΔCcTLS1 constructed in Example 1 (abbreviated as the knockout strain ΔCcTLS1), and the anaplerotic mutant cΔCcTLS1 constructed in Example 2 (abbreviated as the anaplerotic strain cΔCcTLS1), and the control is the wild-type multi-rod Bacillus sp. HG14102524 (abbreviated as wild-type HG14102524).
[0161] The pathogenicity is identified by the isolated patch culture method, and the specific steps are as follows: Prepare a clean moisturizing box and spray an appropriate amount of water to keep it moisturized. Arrange the collected cucumber leaves with their leaf backs facing upwards in a humidifying box (three pieces in a box). Corynespora polybasicum (knockout strain ΔCcTLS1, complementation strain cΔCcTLS1 and wild-type HG14102524) activated on the PDA medium were punched into bacterial cakes at the edge of the colony with a 0.5 cm puncher, and sterilized Th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com