Method for reducing metal dendrites in manganese electrodeposition
A metal dendrite and manganese electrodeposition technology, which is applied in the direction of electrolytic components, electrolytic process, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of insignificant inhibition of cathode dendrite growth and dissolution of metal manganese on the surface of the plate, so as to improve the deposition morphology, Effect of reducing metal dendrite formation and homogenizing current density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
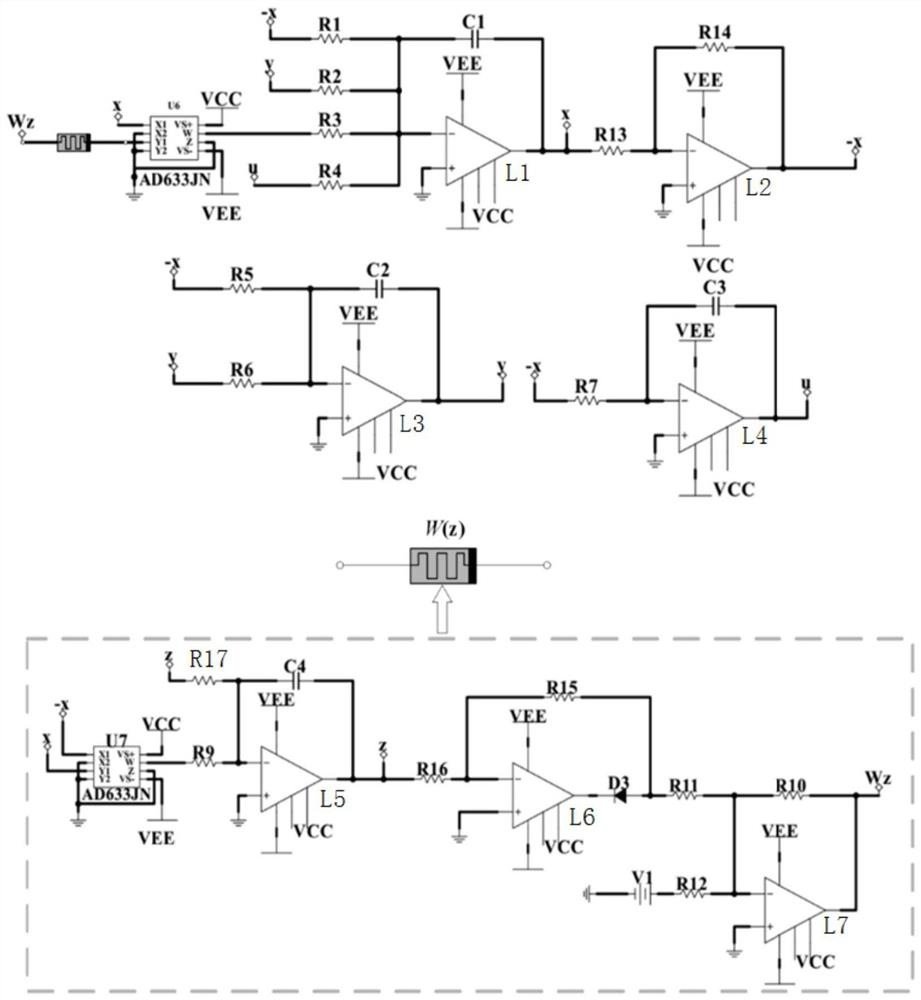
[0031] See Figure 1 to 9 , A method of reducing metal dendrites in manganese electrodeposition, the electrolysis device employed mainly includes a DC power source, a circuit system, an electrode, and an electrolytic cell;
[0032] The circuit system is a chaotic circuit, wherein the chaotic circuit module mainly includes a linear capacitor, a linear resistance, an operational amplifier, a diode;
[0033] The op amp and capacitance of chaotic circuits constitute a reverse integral circuit.
[0034] The chaotic circuit can output a stable hyperlotic signal, by adjusting the resistance of the resistor, the chaotic circuit can cause a periodic state, a quasi-cycle state, a chaotic state, or a super chaotic state.
[0035] The circuit structure of the circuit system is as follows:
[0036] The VS + terminal of the analog multiplier U6 is connected to one end of the DC power supply positive, and the VS-terminal is connected to the DC power supply negative electrode;
[0037] The z termi...
Embodiment 2
[0086] A device for reducing metal dendrites in manganese electrodeposition, including DC power, circuitry, electrode, and electrolytic cells;
[0087] The DC power supply is a circuit system power supply;
[0088] The circuit system transmits an excitation signal to the electrode;
[0089] The circuit structure of the circuit system is as follows:
[0090] The VS + terminal of the analog multiplier U6 is connected to one end of the DC power supply positive, and the VS-terminal is connected to the DC power supply negative electrode;
[0091] The z terminal, X2 terminal, Y1 terminal, and Y2 terminals of the multiplier U6;
[0092] The X1 terminal of the simulated multiplier U6 receives the signal of the operational amplifier L1;
[0093] The Y1 terminal of the simulation of the multiplier U6 receives the signal of the operational amplifier L7 feedback;
[0094] The simulated multiplier U6 is multiplied by the signal received, resulting in multiplied signals;
[0095] The W terminal...
Embodiment 3
[0139] Reduce the use of metal dendrite devices in manganese electrodeposition is as follows:
[0140] Building an electrolysis device, including DC power, circuitry, electrode, and electrolytic cells;
[0141] Preparation of manganese salt solution: acid leaching treatment to manganese ore, to obtain a leaching liquid; add MNO in the leaching liquid 2 , Ammonia water, SDD (dimethyl dithiocarbamate), remove impurities in the leaching liquid; the pH value of the ammonia is in the range of [6, 7]; add activated carbon to the leaching liquid after impurities, stand T time To obtain a manganese salt solution.
[0142] Pour the prepared manganese salt solution in the electrolytic cell;
[0143] The electrode is partially or all in the formation of manganese salt;
[0144] Turn on the DC power supply to power the DC system;
[0145] After the circuit system is powered, an excitation signal is transmitted to the electrode;
[0146] After the electrode receives the excitation signal trans...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com