GH10 family high-temperature-resistant xylanase mutants and application thereof
A technology of xylanase mutation and high temperature resistance, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of inability to express xylanase in large quantities, cannot take into account thermal stability and catalytic activity, and achieve excellent thermal stability and improved thermal stability , the effect of high enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Cloning of embodiment 1 thermostable xylanase mutant coding gene
[0032] Using the high-temperature-resistant xylanase gene HwXyl10A from the GH10 family as the parent, design mutant primers at the loop region of xylanase, and use over-lap PCR to amplify the gene encoding a mutant xylanase with high catalytic efficiency SEQ ID NO.1 (HwXyl10a-G363R), SEQ ID NO.2 (HwXyl10a-T324V), SEQ ID NO.3 (HwXyl10a-N318W), SEQ ID NO.4 (HwXyl10a-N318W / G363R / T324V), mutation method and Cloning method reference (You, et al., 2016).
[0033] The primer sequences used are shown in Table 1:
[0034] Table 1 Primer Synthesis List
[0035]
Embodiment 2
[0036] The preparation of embodiment 2 thermostable xylanase mutants
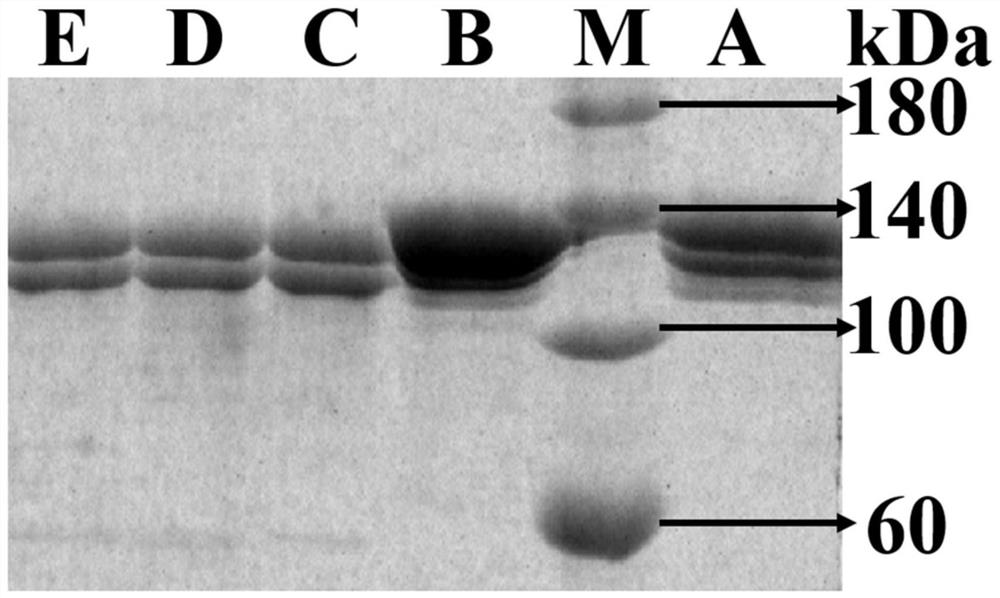
[0037] The expression vector pPIC9r was subjected to double enzyme digestion (EcoR I+Not I), and at the same time, the gene encoding the high-temperature-resistant xylanase mutant was double-enzyme-digested (EcoR I+Not I), and then the enzyme-digested gene encoding the mature high-temperature-resistant xylanase The gene fragment of the mutant glycanase is connected with the expression vector pPIC9r to obtain a recombinant plasmid containing the gene of the mutant xylanase resistant to high temperature and transform it into Pichia pastoris GS115 to obtain a recombinant yeast strain.
[0038]Take the GS115 strain containing the recombinant plasmid, inoculate it in a 1L Erlenmeyer flask with 300mL of BMGY medium, place it at 30°C, and culture it on a shaker at 220rpm for 48h; then centrifuge the culture solution at 3000g for 5min, discard the supernatant, and use 100mL of 0.5% methanol for precipitation. The B...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3 Activity Analysis of Thermostable Xylanase Mutant and Wild Type
[0040] 1. DNS method: the specific method is as follows: under the given pH and temperature conditions, 1mL reaction system includes 100μL enzyme solution, 900μL substrate, react for 10min, add 1.5mL DNS to terminate the reaction, and boil for 5min. After cooling, the OD value was measured at 540 nm. One enzyme activity unit (U) is defined as the amount of enzyme required to decompose xylan to generate 1 μmol reducing sugar per minute under given conditions.
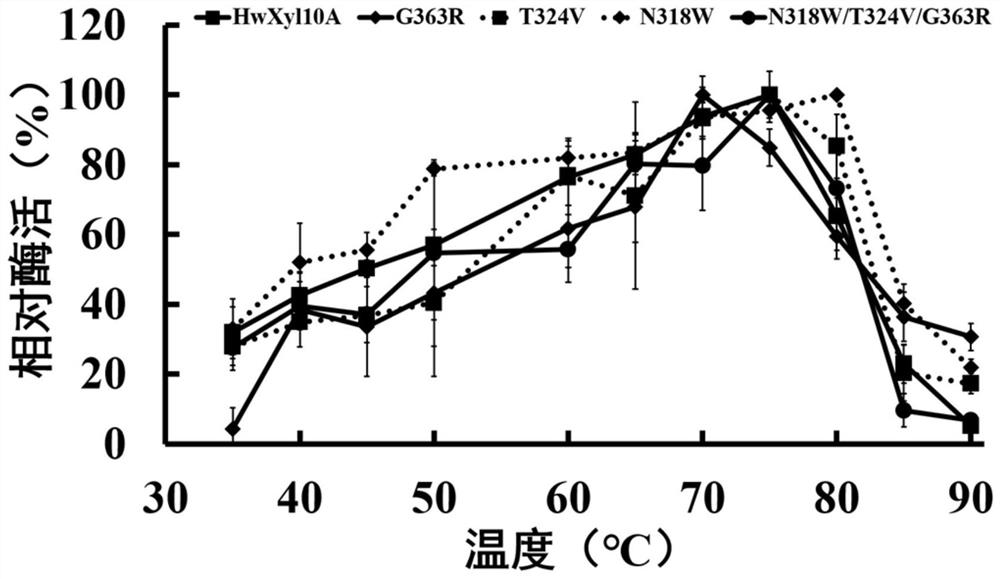
[0041] 2. Determination of the properties of recombinant thermostable xylanase mutants and wild type
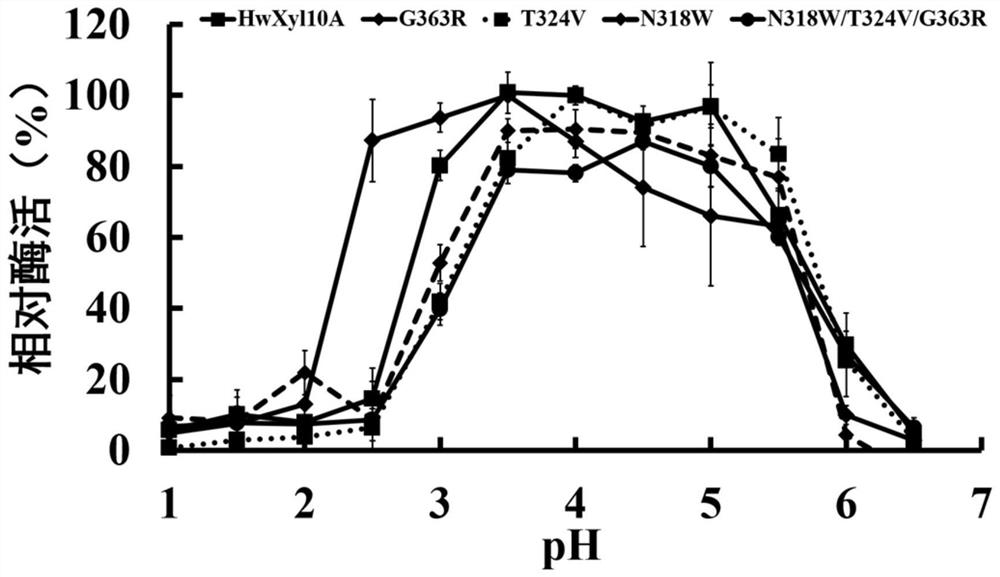
[0042] 1. The optimal pH of recombinant thermostable xylanase mutant and wild type is determined as follows:
[0043] The recombinant thermostable xylanase mutant purified in Example 2 and the wild type were subjected to enzymatic reactions at different pHs to determine their optimum pH. The substrate (beech wood xylan) was diluted wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com