Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 genetically engineered bacterium as well as preparation method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and Escherichia coli, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as limiting physiological performance, and achieve the effects of increasing anti-inflammatory factors, reducing brain inflammation, and reducing inflammatory factors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1: engineering bacteria E. coli Nissle 1917 acquisition and identification
[0020] 1, Nissle 1917 acquisition and identification of
[0021] Healthy human stool using 50% Glycerol, in sterile phosphate buffered saline (PBS) to make dilutions, 3-5 to select the appropriate gradients draw performed 0.1mL streaked on LB medium, each dilution gradient do two repetitions. After the petri dish was placed 37 ℃ incubator for 48 hours aerobically selection smooth, convex, regular edge, white colonies semipermeable microscopy. Suspected colonies were isolated and purified in LB medium again the above steps, until the colonies were completely purified. Purified colonies were serially passaged 3 times and then with 50% glycerol and bacterial suspension 1: 1 mixture stored at -80 ℃.
[0022] 2, building engineering bacteria E. coli Nissle 1917
[0023] Synthesis of GLP-1 target gene, the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 by chemical synthesis, which is then integrated...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Experiment acid bacterium Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 Engineering
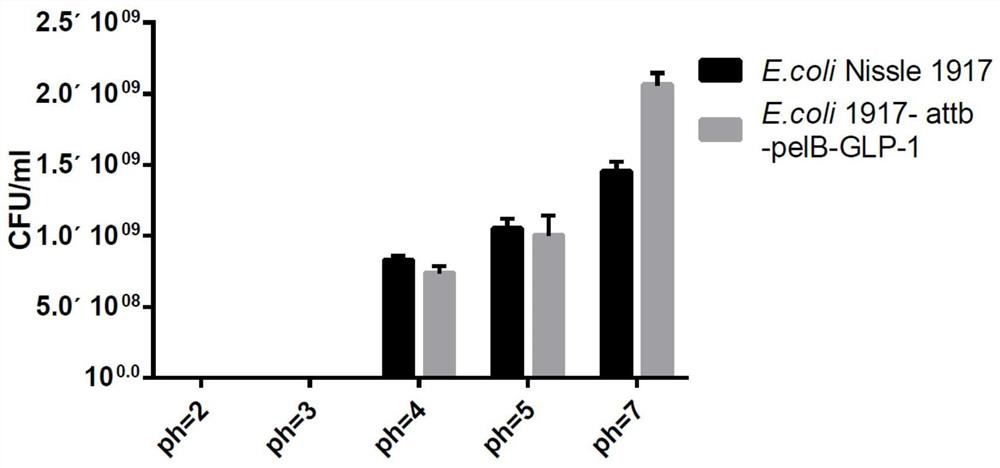
[0050] Inoculated with 1 / 100 volume of E. coli Nissle 1917 and engineering bacteria, 18h subcultured in LB liquid medium. 8000rpm centrifuge 5min, discarded the supernatant retained precipitate was washed with sterile PBS buffer twice, respectively, each of which was dispensed into five 1.5mL centrifuge tube, centrifuged at 8000rpm 5min, wild type E. coli to give Niss le 1917 and Engineering 5 parts of each of the bacterial cell. Were then added to the pre-configured PBS buffer pH 7.0 and 2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0, stationary culture incubator at 37 ℃ 2h, 2h and cultured bacterial suspension taken 0h times over (after 10 fold) dilution, viable cell count was determined by plate count method, and calculates a wild type E. coli strain Nissle1917 survival and engineering.
[0051] Such as figure 2 As shown, in the acid-resistant experiment, in the PBS environment of pH = 4, the number of wild-type E. coli...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Asphalt Stri Salt Experiment of Erobacter Nissle 1917
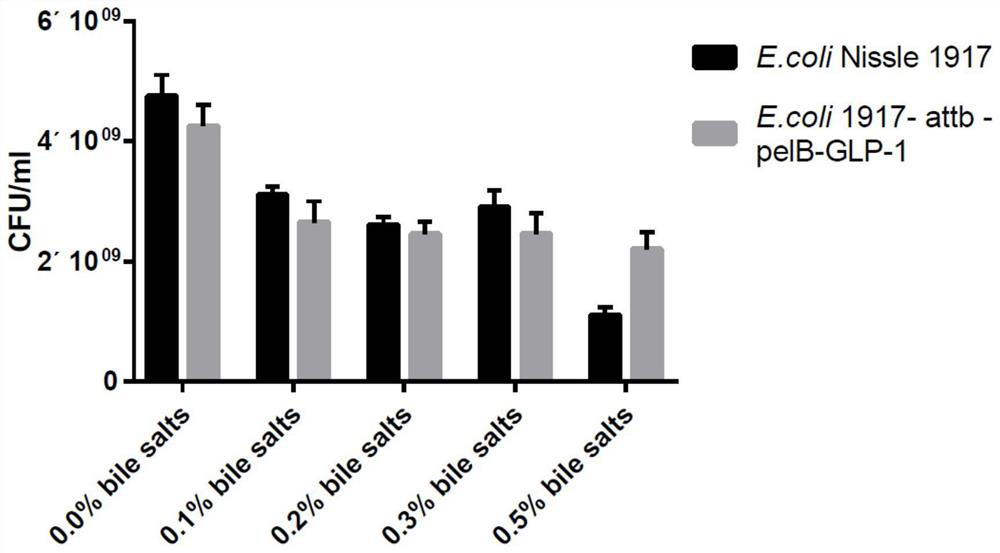
[0053] E. coli Nissle 1917 and the engineering bacteria were seeded at 1 / 100, and the biopsy was incubated in LB liquid medium for 18 h. 8000 rpm was centrifuged for 5 minutes, retaining the deposit, and then washed twice with a sterile PBS buffer, and each of them were dispensed into 5 1.5 ml of centrifuge tube, 8000 rpm centrifuge 5 min, obtained from wild-type E. coli Nissle 1917 and Engineering Five parts of the bacteria. Then, a pre-configured preferred pBS buffer is added to the PBS buffer of 0%, 0.1%, 0.2%, 0.3%, 0.4% and 0.5%, and placed in a 37 ° C incubator to stand for 2 h, and take 0 h after culture. 2H bacteria suspension ratio (10 times) dilution, the number of live bacteria was determined by a flat plate count, and the ventronium Nissle 1917 and the survival rate of Engineering bacterium strains were calculated.
[0054] Such as image 3 As shown, in the aspiral salt experiment, the engineering ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com