Method for accurately controlling nitrogen content in high-nitrogen stainless steel
A technology for high-nitrogen stainless steel and nitrogen content, which is applied in the field of precise control of nitrogen content in high-nitrogen stainless steel, and can solve problems such as excessive nitrogen content, shortened equipment life, and low nitrogen solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] The target steel grade of this embodiment is 18Cr18Mn2Mo0.9N, and its composition control range and smelting control target are shown in Table 1.
[0076] Table 1 18Cr18Mn2Mo0.9N composition control range and control target (wt%)
[0077] Element C Si mn N Cr Mo P S Fe Control range ≤0.1 ≤0.80 17.5~20.0 0.75~1.0 17.5~20.0 1.5~2.5 ≤0.03 ≤0.015 margin Control objectives 0.10 0.50 18.00 0.90 18.30 2.00 ≤0.03 ≤0.015 margin
[0078] Specific steps are as follows:
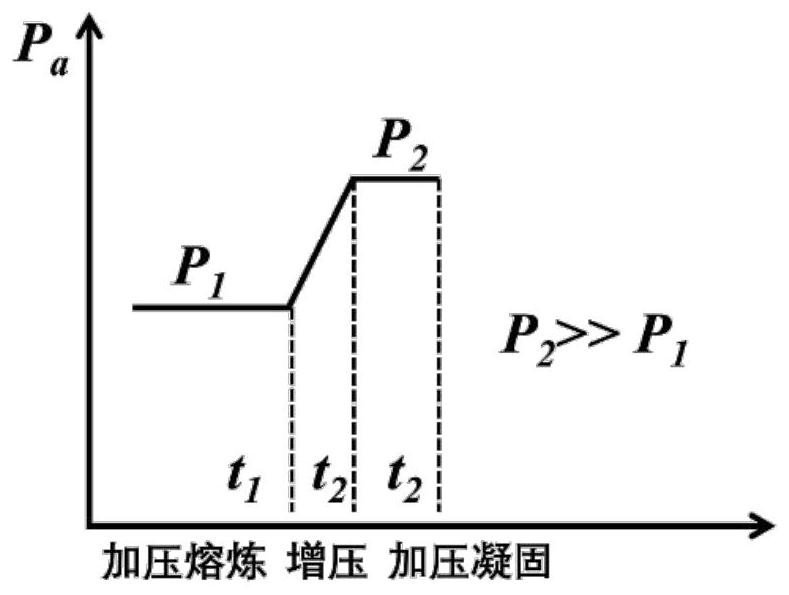
[0079] (I) Put industrial pure iron, metal chromium, metal molybdenum and metal nickel into the induction furnace, put metal manganese, industrial silicon, chromium nitride, graphite and electrolytic aluminum in the feeding bin; vacuum the furnace to 5Pa , and energized to raise the temperature until the smelting raw materials in the pressurized induction furnace are fully melted to melt, and then the furnace is filled with high-purity nitrogen with a purit...
Embodiment 2
[0091] The target steel grade of this embodiment is 19Cr18Mn2Mo0.9N, and its composition control range and smelting control target are shown in Table 3.
[0092] Table 3 19Cr18Mn2Mo0.9N composition control range and control target (wt%)
[0093]
[0094]
[0095] Specific steps are as follows:
[0096] (I) Put industrial pure iron, metallic chromium or ferrochromium, metallic molybdenum or ferromolybdenum, and metallic nickel into the induction furnace, and place metallic manganese, industrial silicon, chromium nitride, graphite, and electrolytic aluminum in the feeding bin; Vacuum the furnace to 5Pa, and turn on the power to raise the temperature until the smelting raw materials in the pressurized induction furnace are fully melted to melt; then fill the furnace with high-purity nitrogen with a purity ≥ 99.999% to P 冶炼 , and then add industrial silicon, manganese metal, chromium nitride, and graphite into the furnace through the feeding bin for alloying, and then add e...
Embodiment 3
[0109] The target steel grade of this embodiment is 19Cr18Mn2Mo0.9N, and its composition control range and smelting control target are shown in Table 5.
[0110] Table 5 19Cr18Mn2Mo0.9N composition control range and control target (wt%)
[0111] Element C Si mn N Cr Mo P S Fe Control range ≤0.1 ≤0.80 17.5~20.0 0.75~1.0 17.5~20.0 1.5~2.5 ≤0.03 ≤0.015 margin Control objectives 0.10 0.50 18.00 0.90 19.00 1.80 ≤0.03 ≤0.015 margin
[0112] Specific steps are as follows:
[0113] Ⅰ. Put industrial pure iron, metallic chromium or ferrochromium, metallic molybdenum or ferromolybdenum, and metallic nickel into the induction furnace, and place easily oxidized or volatile metallic manganese, industrial silicon, chromium nitride, graphite, and electrolytic aluminum into the feeding furnace. In the warehouse; the furnace is vacuumed to 5Pa, and the temperature is raised until the smelting raw materials in the pressurized induction f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com