Monolithic integrated edge emitting laser and preparation method thereof
An edge-emitting laser and monolithic integration technology, which is applied to lasers, laser components, semiconductor lasers, etc., can solve the problems of low system stability and bulky laser radar system
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] In this embodiment, the monolithic integrated edge-emitting laser operates at a wavelength of 940 nm and is based on gallium arsenide (GaAs) material.
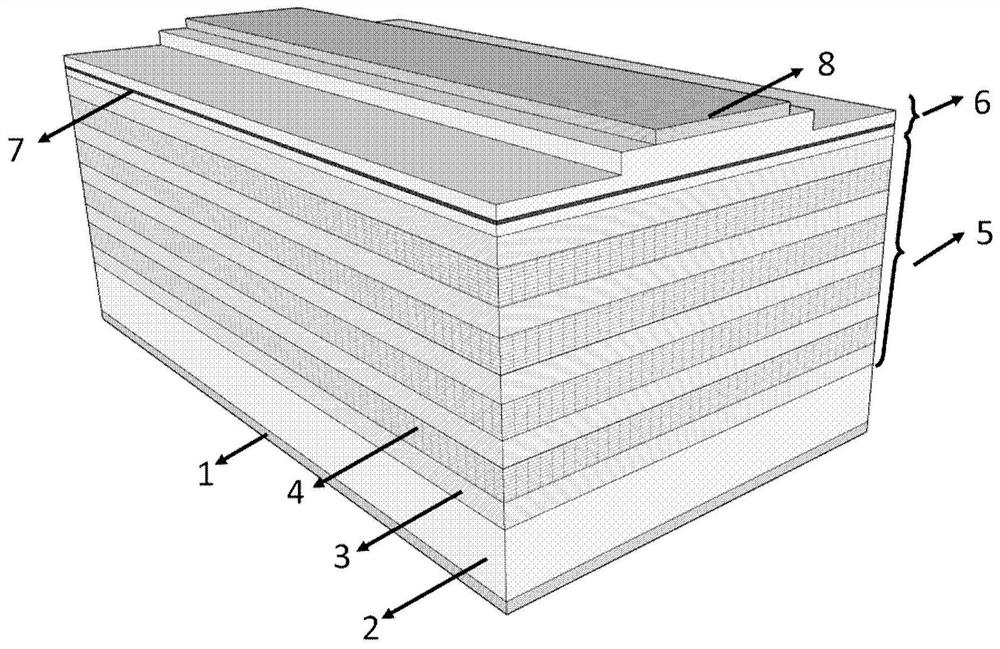
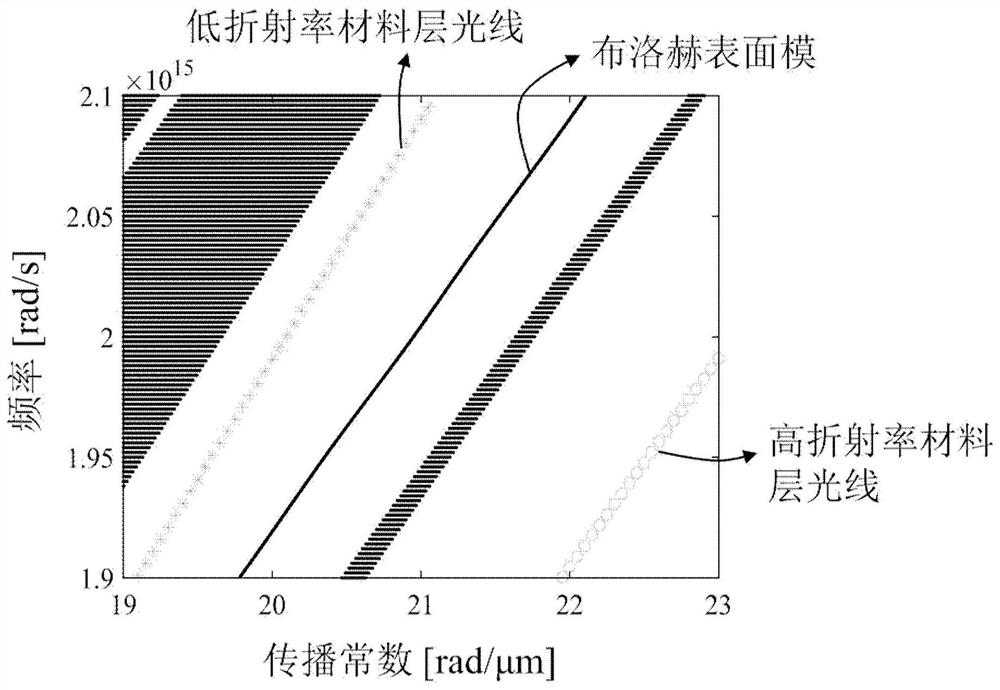
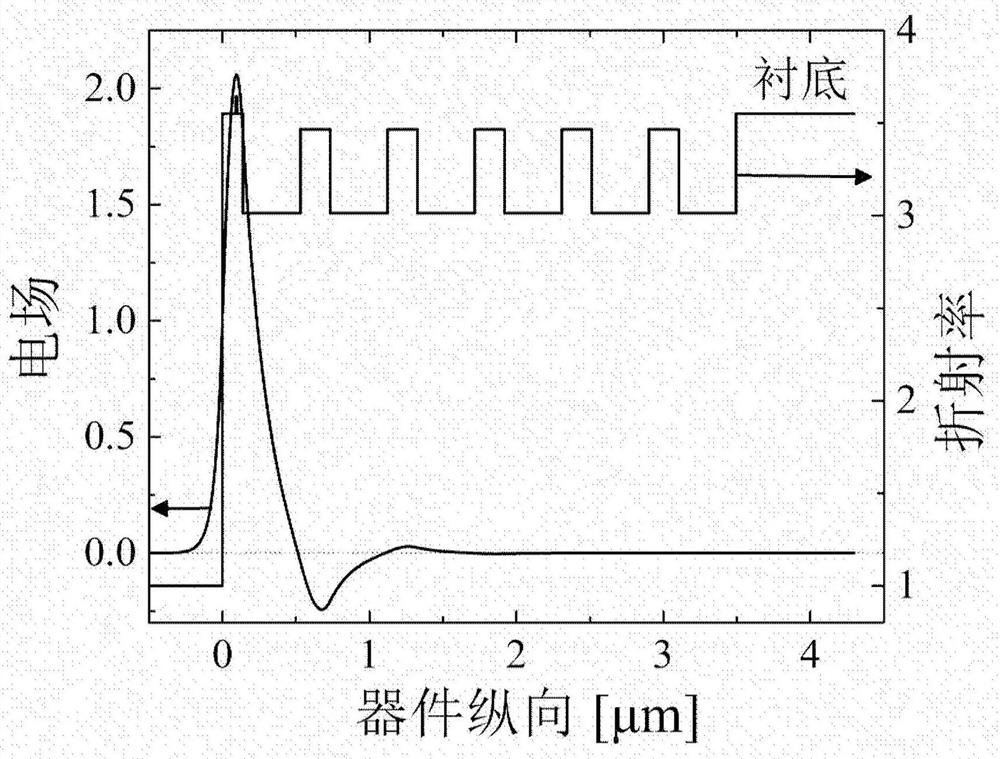
[0059] The structure of monolithic integrated edge-emitting laser is as follows figure 1 As shown: the first electrode 1 is the negative electrode, and the material is AuGeNiAu; the second electrode 8 is the positive electrode, and the material is TiPtAu; the material of the substrate 2 is n-type GaAs; the low refractive index material layer 3 is n-type Al 0.9 Ga 0.1 As layer, the thickness is 334nm, the first high refractive index material layer 4 is n-type Al 0.12 Ga 0.88 The As layer has a thickness of 157nm. The low-refractive-index material layer 3 and the first high-refractive-index material layer 4 are periodically alternately grown in 5.5 groups during material epitaxy, forming a multilayer structure 5 similar to a Bragg mirror structure. The multilayer structure 5 is formed on the substrate, and the multilay...
Embodiment 2
[0064] In this embodiment, the monolithic integrated edge-emitting laser operates at a wavelength of 940 nm and is based on gallium arsenide (GaAs) material.
[0065] The structure of monolithic integrated edge-emitting laser is as follows Figure 5 As shown: the first electrode 1 is the negative electrode, and the material is AuGeNiAu; the second electrode 8 is the positive electrode, and the material is TiAu; the material of the substrate 2 is n-type GaAs; the low-refractive index material layer 3 is n-type Al 0.9 Ga 0.1 As layer, the thickness is 334nm, the first high refractive index material layer 4 is n-type Al 0.12 Ga 0.88 The As layer has a thickness of 157nm. The low-refractive-index material layer 3 and the first high-refractive-index material layer 4 are periodically alternately grown in 5.5 groups during material epitaxy, forming a multilayer structure 5 similar to a Bragg mirror structure. The multilayer structure 5 is formed on the substrate, and the multilaye...
Embodiment 3
[0067] In this embodiment, the monolithic integrated edge-emitting laser operates at a wavelength of 940 nm and is based on gallium arsenide (GaAs) material. Its structure is similar to that of Embodiment 2, except that a one-dimensional periodic surface micro-nano structure is introduced into the ridge waveguide 9, that is, a one-dimensional surface grating, which is fabricated by electron beam exposure and dry etching to realize longitudinal mode selection. Figure 6 Shown is a schematic top view of a one-dimensional surface grating.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com