Computer optometry unit
A refractometer and computer technology, applied in the field of computer refractor, can solve the problems of difficulty in achieving high precision and high repeatability, insufficient accuracy and thoroughness of human eye inspection, affecting the accuracy of measurement data, etc., so as to avoid subjective deviation and ensure accurate and thorough inspection. , the effect of high precision and high repeatability measurement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
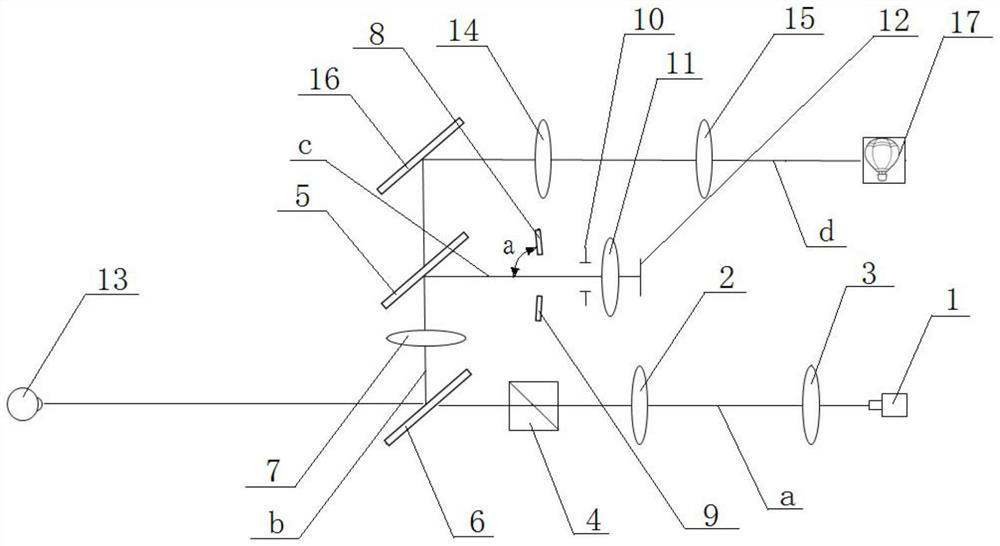
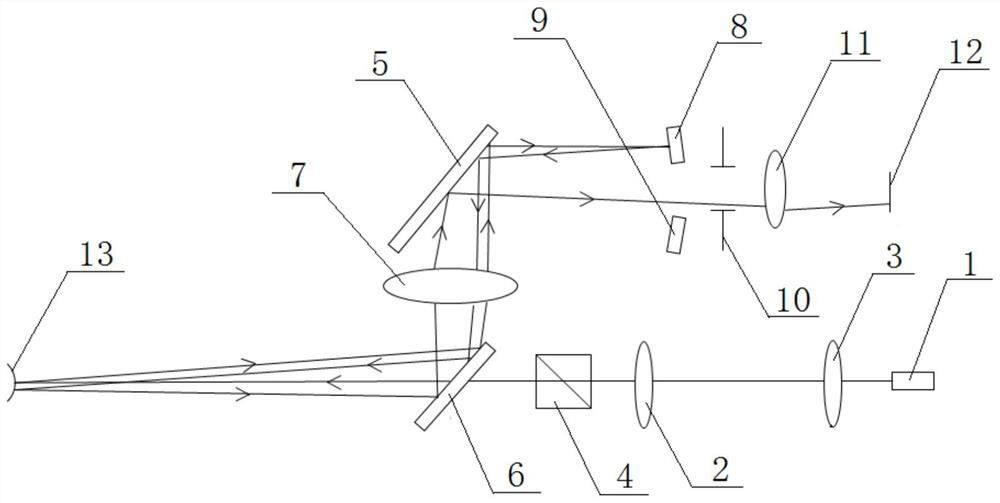
[0022] Embodiment 1: As shown in the figure, a computer optometry instrument includes a fog optical path and a focusing optical path. The focusing optical path includes a laser 1, a first light source lens 2, a second light source lens 3, a PBS (polarization beam splitter) 4, and a second light source lens. A beam splitter 5, a second beam splitter 6, an objective lens 7, a first focusing mirror 8, a second focusing mirror 9, a telecentric diaphragm 10, a corneal objective lens 11 and a first detector 12, a second beam splitting mirror 6, and a PBS 4 , the first light source lens 2, the second light source lens 3 and the laser 1 are located on the first optical axis a and arranged in sequence with the optical axis, the first light source lens 2 is a positive lens, and the second beam splitter 6 is located on the side close to the eyeball 13 , the second beamsplitter 6 is located on the second optical axis b with the objective lens 7 and the first beamsplitter 5 and is arranged ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Embodiment 2: As shown in the figure, on the basis of Embodiment 1, the computer refractometer is provided with an aberration analysis optical path that can be used to analyze high and low price aberrations of the human eye. The aberration analysis optical path includes the second Detector 18, microlens array 19, first lens 20, second lens 21, first relay lens 22, second relay lens 23 and second mirror 24, first lens 20, second lens 21 and the first The two relay lenses 23 are all positive lenses, the second mirror 24, the first lens 20 and the PBS 4 are located on the fifth optical axis e and are arranged in sequence with the optical axis, and the second mirror 24 is connected with the first relay lens 22 at the same time. , the second relay lens 23, the second lens 21, the microlens array 19, and the second detector 18 are located on the sixth optical axis f and are arranged in sequence with the optical axis, and the second mirror 24 is used to pass through the first l...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com