High-strength and high-efficiency bismuth telluride block and preparation method and application thereof
A bismuth telluride and bismuth telluride-based technology, applied in the manufacture/processing of thermoelectric devices, thermoelectric device junction lead-out materials, etc., can solve the problems of introducing harmful impurity ions, different crystal grains, and moisture absorption of powders, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
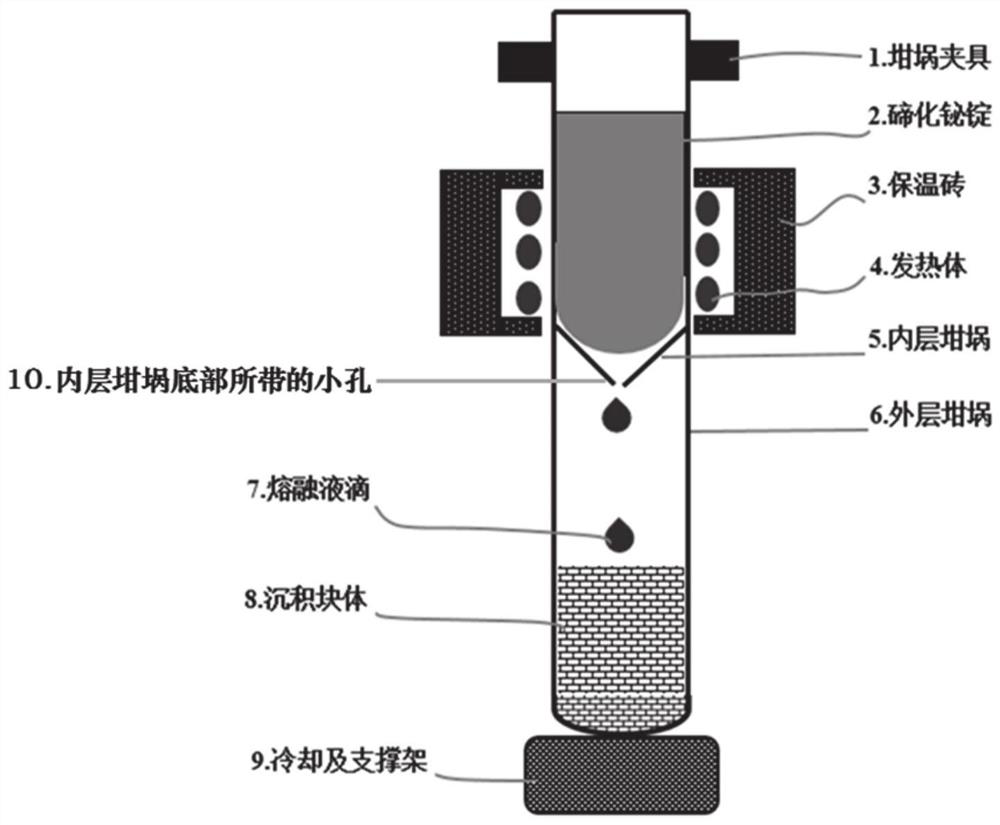
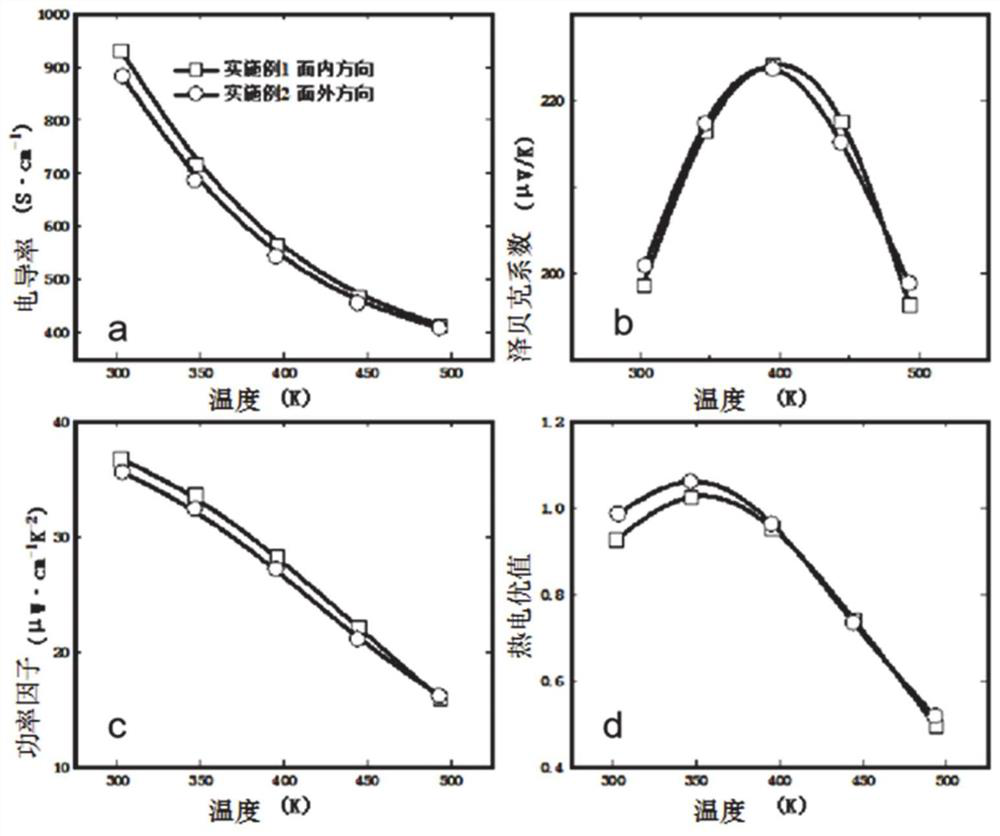
[0103] Using 5N Bi, Te and Sb as raw materials, according to the stoichiometric ratio Bi 0.5 Sb 1.5 Te 3 Batching, put into the quartz crucible, the diameter of the quartz crucible is 20mm, vacuumize to less than 10pa and seal the quartz crucible with hydrogen oxygen flame. The quartz crucible is placed in an italic tube furnace, and the angle between the axial direction and the horizontal direction of the italic tube furnace is 30°. The temperature in the furnace is controlled at 750°C, fully smelted and synthesized, then cooled to room temperature to obtain bismuth telluride-based polycrystalline rods. Reseal the bismuth telluride-based polycrystalline rod into a double-layer quartz crucible with a small hole, the diameter of the small hole is 2 mm, the distance between the small hole and the bottom of the outer crucible is 80 cm, and the inner and outer crucibles are evacuated to 10pa. Fix the crucible to the figure 1 On the zone melting furnace, adjust the heating tem...
Embodiment 2
[0106] Using 5N Bi, Te and Se simple substances as raw materials, according to the stoichiometric ratio Bi 2 Te 2.8 Se 0.2 The ingredients are put into the quartz crucible, the diameter of the quartz crucible is 20mm, the vacuum is lowered to less than 10pa, and the quartz crucible is sealed with an oxyhydrogen flame. The ingot is completely melted at a temperature of 750° C., fully melted and synthesized, and then cooled to room temperature to obtain a bismuth telluride-based polycrystalline rod. Reseal the bismuth telluride-based polycrystalline rod into a double-layer quartz crucible with a small hole, the diameter of the small hole is 2 mm, the distance between the small hole and the bottom of the outer crucible is 80 cm, and the inner and outer crucibles are evacuated to less than 10pa. Fix the crucible to the figure 1 On the zone melting furnace, adjust the heating temperature of the zone furnace to 700°C, adjust the relative position between the zone furnace and the...
Embodiment 3
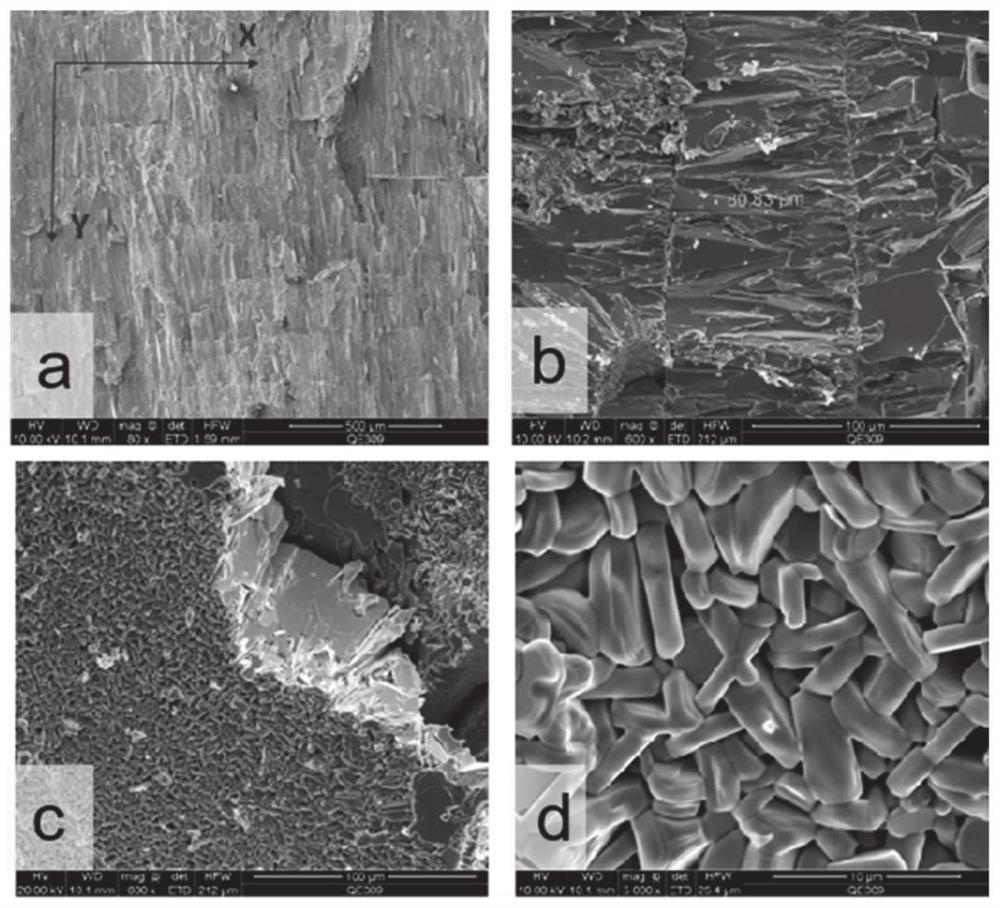
[0108] The difference from Example 1 is that during the fused deposition process, the metal support at the bottom of the outer crucible is actively cooled, and the temperature of the metal support is -150°C by externally connecting liquid nitrogen coolant. When the molten drop hits the bottom of the outer crucible After turning into a liquid film, the purpose of rapid cooling is achieved. The cooling rate is 250K / S. The ultra-low temperature deposition environment can effectively inhibit the growth of the grains of the molten droplets during the cooling process, and obtain directional deposition blocks with smaller grain sizes. , followed by vacuum hot-press sintering to obtain high-strength P-type bismuth telluride-based thermoelectric materials.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Vickers hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| electrical conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com