Method for recovering tungsten from waste SCR catalyst regeneration waste alkali liquor and application
A technology of SCR catalyst and waste lye, applied in the field of tungsten recovery, can solve the problems affecting metal recovery, waste of resources, and increase the difficulty of recycling tungsten elements, and achieve the effect of saving dosage and improving separation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
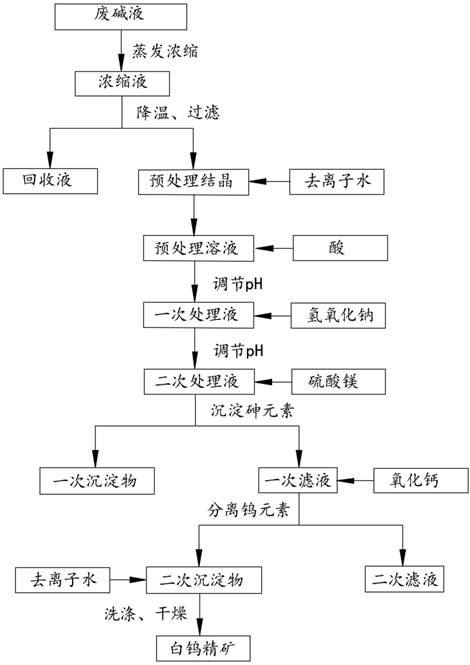
[0039] This embodiment provides a method for recovering tungsten from spent SCR catalyst regenerated spent lye, said method comprising the following steps:
[0040] The waste lye was sampled and tested to obtain the concentrations of sodium hydroxide, tungsten, arsenic, silicon and phosphorus in the waste lye.
[0041] Take a preset volume of spent lye, evaporate and concentrate the spent lye until the mass concentration of sodium hydroxide is 20wt.%, to obtain a concentrated solution, cool down the concentrated solution, crystallize and filter, and obtain pretreated crystallization and recovery solution. Wherein, the temperature range for the crystallization and filtration of the concentrated solution is 45°C to 50°C.
[0042] Deionized water is used to fully dissolve the pretreatment crystals to obtain a pretreatment solution. Wherein, the quality of the added deionized water is 1.5 times of the quality of the pretreated crystals.
[0043] A sulfuric acid solution is added...
Embodiment 2
[0050] This embodiment provides a method for recovering tungsten from spent SCR catalyst regenerated spent lye, said method comprising the following steps:
[0051] The waste lye was sampled and tested to obtain the concentrations of sodium hydroxide, tungsten, arsenic, silicon and phosphorus in the waste lye.
[0052] Take a preset volume of spent lye, evaporate and concentrate the spent lye until the mass concentration of sodium hydroxide is 20wt.%, to obtain a concentrated solution, cool down the concentrated solution, crystallize and filter, and obtain pretreated crystallization and recovery solution. Wherein, the temperature range for cooling the concentrated solution for crystallization and filtration is 45°C to 50°C.
[0053] Deionized water is used to fully dissolve the pretreatment crystals to obtain a pretreatment solution. Wherein, the quality of the added deionized water is 3.0 times of the pretreatment crystal quality.
[0054] Sulfuric acid solution is added to...
Embodiment 3
[0061] This embodiment provides a method for recovering tungsten from spent SCR catalyst regenerated spent lye, said method comprising the following steps:
[0062] The waste lye was sampled and tested to obtain the concentrations of sodium hydroxide, tungsten, arsenic, silicon and phosphorus in the waste lye.
[0063] Take a preset volume of spent lye, evaporate and concentrate the spent lye until the mass concentration of sodium hydroxide is 20wt.%, to obtain a concentrated solution, cool down the concentrated solution, crystallize and filter, and obtain pretreated crystallization and recovery solution. Wherein, the temperature range for cooling the concentrated solution for crystallization and filtration is 45°C to 50°C.
[0064] Deionized water is used to fully dissolve the pretreatment crystals to obtain a pretreatment solution. Wherein, the quality of the added deionized water is 3.0 times of the pretreatment crystal quality.
[0065] Sulfuric acid solution is added to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com