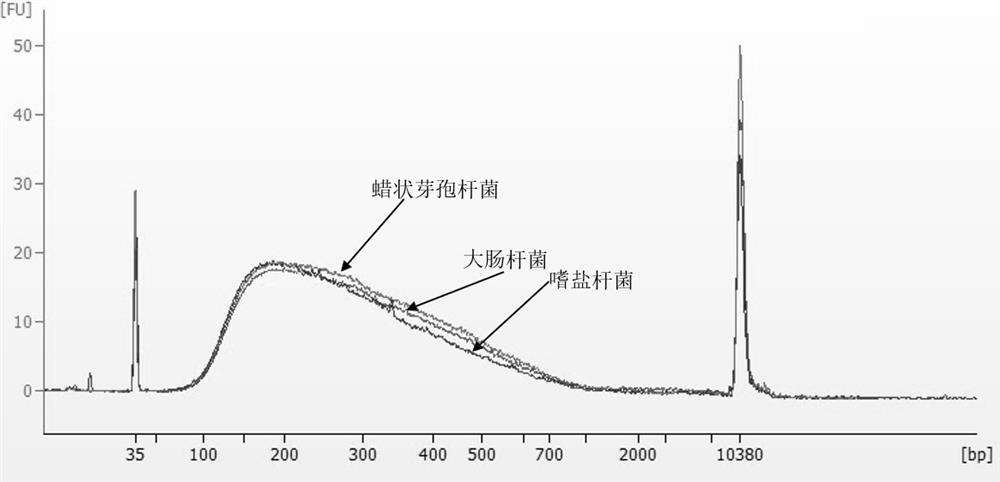
DNase I mutants as well as coding nucleotide sequences and application thereof
A mutant and sequence technology, applied in the field of DNaseI mutants, can solve the problems of large loss, unstable effect of micro-sample interruption, and sequencing quality needs to be improved, so as to achieve small sample loss, excellent sequencing quality, and low GC preference. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1 is tested to the different enzyme amount of mutant 7
[0037] 1. Genome disruption
[0038] In this example, 500 ng of calf thymus gDNA (Yeasen, Cat#60612ES03) was used as the fragmentation template, and 5 μL of 10×Fragment buffer was added. 50 μL. Place it in a PCR instrument for the interruption reaction, set the enzyme cutting temperature to 30°C, and the inactivation temperature to 80°C.
[0039] PCR program
[0040] temperature time 4℃ 1 minute 30℃ 15 minutes 80℃ 10 minutes
[0041] 2. Interrupt result detection
[0042] After the reaction program was finished, 15 μL was taken for agarose gel electrophoresis detection. Interrupt results see attached figure 1 .
[0043] 3. Interrupt result analysis
[0044] 1) As the amount of enzyme increases, the interrupted fragments gradually decrease
[0045] 2) 0.6 μL of enzyme can interrupt the genome to about 300bp of the main band.
Embodiment 2
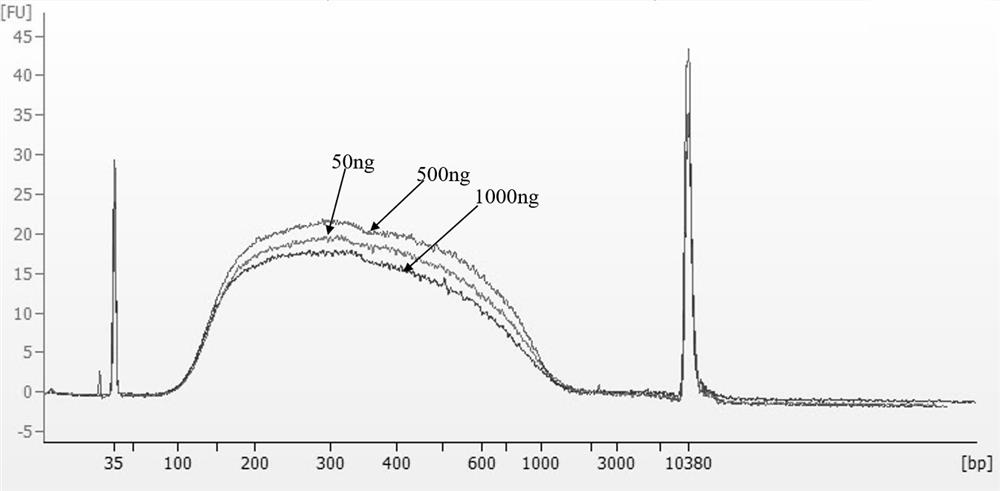
[0046] Example 2 Interruption test of mutant 7 with different input amounts of DNA
[0047] 1. Genome disruption
[0048] In this example, 50, 500, and 1,000 ng of calf thymus gDNA were used as fragmentation templates, and 5 μL of 10×Fragment buffer was added. For mutants, 0.6 μL of enzyme was added, and water was added to 50 μL. Place it in a PCR instrument for interruption, set the enzyme cutting temperature to 30°C, and the inactivation temperature to 80°C.
[0049] PCR program
[0050] temperature time 4℃ 1 minute 30℃ 15 minutes 80℃ 10 minutes
[0051] 2. Interrupt product purification
[0052] In the example, the fragmented product was passed through Hieff NGS TM DNA Selection Beads magnetic beads (Yeaen, Cat#12601) were purified and recovered according to the reagent instructions at a magnetic bead ratio of 1.5× to obtain the fragmented product.
[0053] 3. Interrupt the result of 2100 detection
[0054] The fragmented purified pr...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 Different interruption time tests for mutant 7
[0058] 1. Genome disruption
[0059] In this example, 500 ng of calf thymus gDNA was used as a fragmentation template, and 5 μL of 10×Fragment buffer was added. The amount of enzyme added to mutant 7 was 0.6 μL, and water was added to 50 μL to prepare 5 groups. The enzyme digestion time was set to 10 and 15 respectively. , 20, 25, 30 min. Place it in a PCR instrument for interruption, the nuclease cutting temperature is 30°C, and the inactivation temperature is 80°C.
[0060] PCR program
[0061] temperature time 4℃ 1 minute 30℃ 10 / 15 / 20 / 25 / 30 min 80℃ 10 minutes
[0062] 2. Interrupt result detection
[0063] In the example, the fragmented product was passed through Hieff NGS TM DNA Selection Beads magnetic beads were purified and recovered at a ratio of 1.5× magnetic beads according to the reagent instructions to obtain the fragmentation product.
[0064] 3. Interrupt th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com