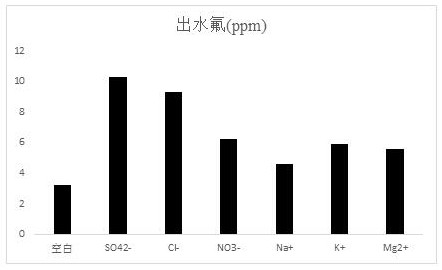
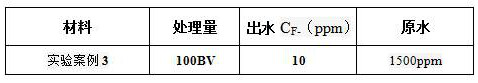
Preparation method of fluorine removal adsorbent modified by biopolymer composite material
A technology of biopolymers and composite materials, which is applied to the materials of anion exchangers, chemical instruments and methods, and water pollutants, and can solve problems such as high operating costs, metal ion leakage, and poor cycle stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] A preparation method of a fluorine-removing adsorbent modified by a biopolymer composite material, comprising the steps of:
[0031] Step 1: Dissolve 1-10 g chitosan in 100-200ml deionized water or 2%-10% acid, and stir for 1-6 hours under magnetic stirring;
[0032] Step 2: Dissolve 1-10 g pectin in 100-200ml deionized water or 2%-10% acid, and stir for 2-6 hours under magnetic stirring;
[0033] Step 3: Mix the two solutions obtained in the above steps 1 and 2, and stir at 40-80°C for 1-3 hours;
[0034] Step 4: Soak 2-10g of molecular sieves in deionized water for 1-3 hours, add to the mixed solution in step 3, and distill under reduced pressure at 60-100°C for 3-8 hours;
[0035] Step 5: Suction filter the excess mixed solution, wash with deionized water 3 times; add 1-5g chloroacetic acid, 20-200 ml 2%-10% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, and stir at room temperature for 2-3h;
[0036] Step 6: Dissolving 1-5 mol of metal nitrate in a mixed solution of ethanol a...
Embodiment 1
[0043] Step 1: Dissolve 1 g of chitosan in 100 ml of deionized water, and stir for 2 hours under magnetic stirring;
[0044] Step 2: Dissolve 1 g of pectin in 100 ml of 2% acetic acid, and stir for 2 hours under magnetic stirring;
[0045]Step 3: Mix the two solutions of Step 1 and Step 2, and stir at 80°C for 3 hours;
[0046] Step 4: After soaking 2g molecular sieve (100 mesh) in deionized water for 1 hour, add it to the mixed solution in step 3, and distill under reduced pressure at 60°C for 3 hours;
[0047] Step 5: Suction filter the excess mixed solution, wash with deionized water 3 times; add 1 g of chloroacetic acid, 50 ml of 2% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, and stir at room temperature for 3 h;
[0048] Step 6: Add 1mol metal nitrate: Fe(NO 3 ) 3 Dissolve in a mixed solution of ethanol and water with a volume ratio of 1:1, and stir at room temperature for 10 minutes;
[0049] Step 7: Add the solution filtered through molecular sieves in step 5 to the nitrate ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Step 1: Dissolve 1 g of chitosan in 100 ml of 2% acetic acid, and stir for 1 hour under magnetic stirring;
[0053] Step 2: 2 g pectin was dissolved in 150ml 3% acetic acid, and stirred for 2 hours under magnetic stirring;
[0054] Step 3: Mix the two solutions of Step 1 and Step 2, and stir at 50°C for 3 hours;
[0055] Step 4: Soak 6 g molecular sieves (200 mesh) in deionized water for 1 hour, add to the mixed solution in step 3, and distill under reduced pressure at 60°C for 2 h;
[0056] Step 5: Suction filter the excess mixed solution, wash with deionized water 3 times; add 2 g of chloroacetic acid, 100 ml of 2% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, and stir at room temperature for 2 h;
[0057] Step 6: 2mol metal nitrate: Fe(NO 3 ) 3 Dissolve in a mixed solution of ethanol and water with a volume ratio of 1:1, and stir at room temperature for 10 minutes;
[0058] Step 7: Add the solution filtered through molecular sieves in step 5 to the nitrate solution in step ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com