Method for strengthening anaerobic reduction of nitrobenzene by electrochemically regulating sulfur circulation
A technology of sulfur cycle and electrochemistry, which is applied in the fields of electrochemical regulation of sulfur cycle, sulfate mixed wastewater, and nitrobenzene, can solve the problems of reducing the effect of anaerobic treatment of NACs and the failure of anaerobic biological treatment, and achieve enhanced reduction conversion efficiency, solve the effect of low treatment efficiency and enhanced reduction conversion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] This embodiment adopts the upflow bioelectrochemical reactor (UBER), figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the upflow bioelectrochemical reactor of the present invention. Specifically, the UBER of this embodiment adopts a modular design and is assembled from 5 polytetrafluoroethylene plates with a width of 3.0 cm. The appearance of the reactor is prismatic , the specific size is 16×12×12cm, the internal reaction zone is a cylindrical structure (ID 8.0cm×H 12.0cm), and the total internal volume is about 600mL. The lower part is the cathode area, and the upper part is the anode area. The height of each area occupied by the cathode and anode is about 6cm, and the middle is the sampling area with a height of 4cm.
[0048] Two pieces of graphite felt with a diameter of 6cm and a thickness of 1cm are used as the cathode and anode to increase the contact area of the cathode and anode. Before use, the graphite felt is cleaned and soaked with 32% hydrochloric ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] The operating steps of this embodiment are basically the same as those in Embodiment 1, the difference being:
[0062] This embodiment is by selecting glucose, sodium acetate, sodium propionate as electron donor (carbon source), compares the removal efficiency of these three kinds of electron donors at different hydraulic retention times p-nitrobenzene and the removal efficiency of sulfate and in Effects on the Anaerobic Reduction Process to Determine Electron Donor Selection Criteria.
[0063] Using 500mg / L sodium propionate as the electron donor to continuously feed UBER, the HRT (hydraulic retention time) was reduced from 22h to 10h (influent load from 5.69mol m -3 d -1 increased to 12.49mol m -3 d -1 ), the removal rate of NB decreased from 99.32% to 76.14%, and the removal rate of sulfate decreased from 90.67% to 60.89%. The removal rate of NB corresponding to sodium acetate decreased from 98.82% to 68.14%, and the removal rate of sulfate decreased from 87.76% ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] The processing steps of this embodiment are basically the same as in Embodiment 1, the difference is that:
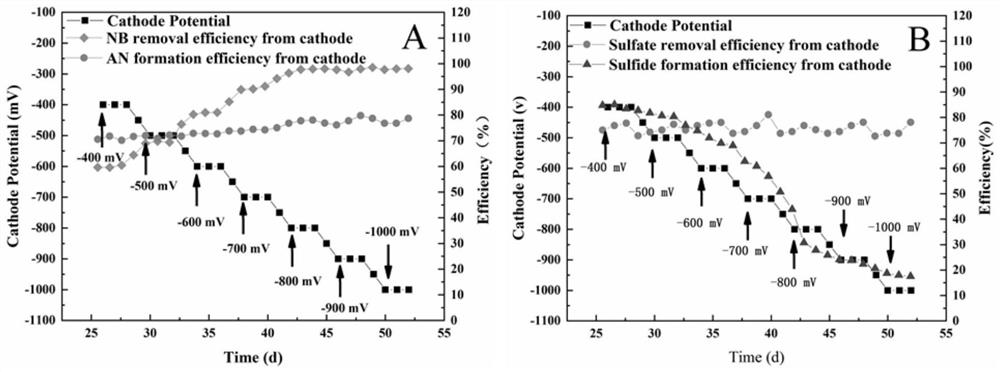
[0067] Keep the COD concentration stable at 500mg / L, and then gradually increase the sulfate concentration on this basis, and the C / S ratio decreases in turn, respectively 11.21:1, 5.6:1, 3.7:1, 2.5:1, 1.67:1 . Compare different COD / SO 4 2- Compare NB, SO 4 2- The effect of removal rate. The up-flow bioelectrochemical experimental group and the anaerobic reduction control group were set up. Except for the difference of applied voltage, the other parameters were the same. For the test results of the UBER experimental group and the anaerobic biological reduction control group, see Figure 4 (A) and Figure 4 (B).
[0068] Compared with the anaerobic reduction system, by Figure 4 (A) It can be seen that in the bioelectrochemical system, the removal rate of nitrobenzene will fluctuate slightly with the decrease of the carbon-sulfur ratio, showing a trend of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com