High-gamma'-content nickel-based high-temperature alloy powder for additive manufacturing, using method therefore and nickel-based high-temperature alloy component
A nickel-based superalloy and additive manufacturing technology, which is applied in the field of high-γ′-content nickel-based superalloy powder for additive manufacturing and nickel-based superalloy components, can solve problems such as thermal cracks that cannot be completely avoided, and achieve high-temperature mechanical properties Good, the crack sensitivity is reduced, and the effect of meeting the needs of use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] A nickel-based high-temperature alloy powder with a new type of add material, according to weight percent, chemical composition:
[0101] Cr: 13.2%, CO: 8.6%, Al: 4.0%, Ti: 3.9%, Fe: 3.6%, W: 2.8%, TA: 1.9%, MO: 1.9%, HF: 1.6%, NB: 1%, C: 0.06%, Si: 0.04%, Mn: 0.01%, Zr: 0.02%, B: 0.007%, the margin is Ni and impurity elements.
[0102] The alloy powder has a particle size distribution and a spherical form of 15 to 53 μm. The alloy powder was produced by vacuum induction smelting, and then manufactured by a vacuum atomization method or plasma rotating electrode powder.
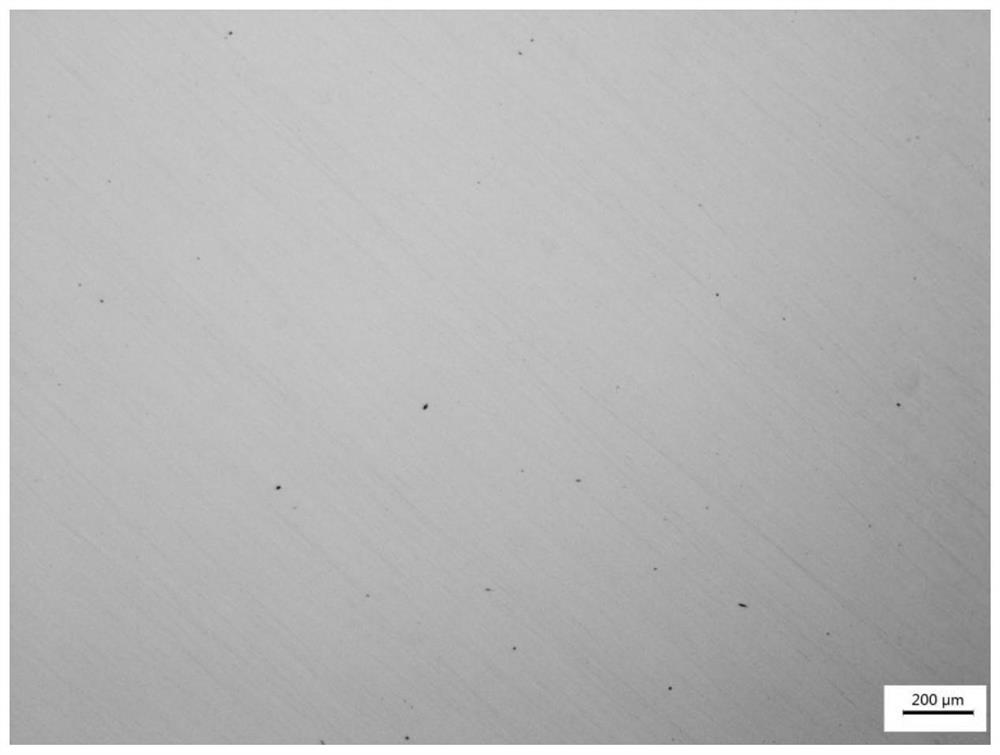
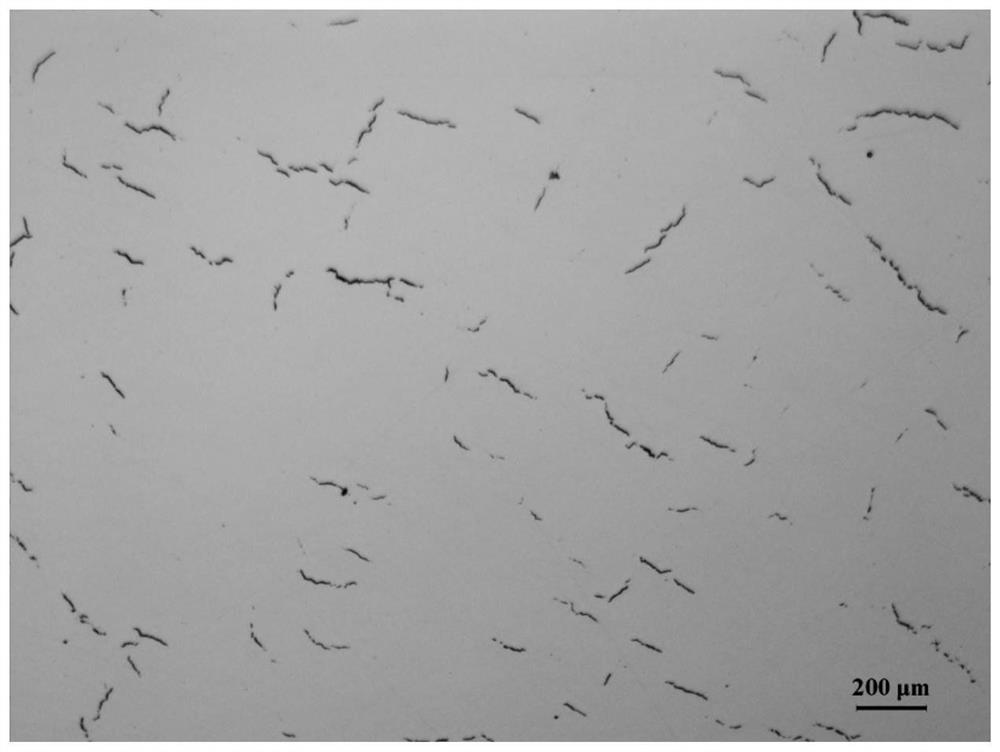
[0103] Using the high-temperature alloy powder according to Embodiment 1, a high-temperature alloy sample was prepared by the selection laser molten process. During printing process, 220W laser power, 1200 mm / s laser scanning speed, 100 μm spot diameter, 90 μm laser spacing, 30 μm were used during printing process. Popping thickness. It is observed to observe and cause density detection to obtain a unifor...
Embodiment 2
[0112] The difference from the first embodiment is that the nickel-based high-temperature alloy powder for the addition of materials is measured by weight, and chemical components are: Cr: 12%, CO: 8%, Al: 3.8%, Ti: 3.8%, Fe: 3%, W: 2.4%, TA: 1.9%, MO: 1.6%, HF: 0.1%, Nb: 1%, C: 0.06%, Si: 0.04%, Mn: 0.01%, Zr: 0.02%, B: 0.007%, the margin is Ni and impurity elements.
Embodiment 3
[0114] The difference between the present embodiment and the first embodiment is that the addition of nickel-based high-temperature alloy powders for the production of materials, the chemical composition is: Cr: 14%, CO: 9%, Al: 4.2%, Ti: 4.2%, W: 2.8%, Fe: 2.8%, TA: 2.1%, MO: 2%, HF: 2%, Nb: 1.2%, C: 0.12%, Si: 0.1%, Mn: 0.02%, Zr: 0.02%, B: 0.01%, the margin is Ni and impurity elements.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com