Application of bacillus cereus B-28 in aspect of repairing environment polluted by heavy metal Cr
A technology of Bacillus cereus and B-28, applied in the fields of application, chemical instruments and methods, botany equipment and methods, to achieve the effect of promoting the increase of chlorophyll content of plant leaves, increasing biomass, and promoting plant growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
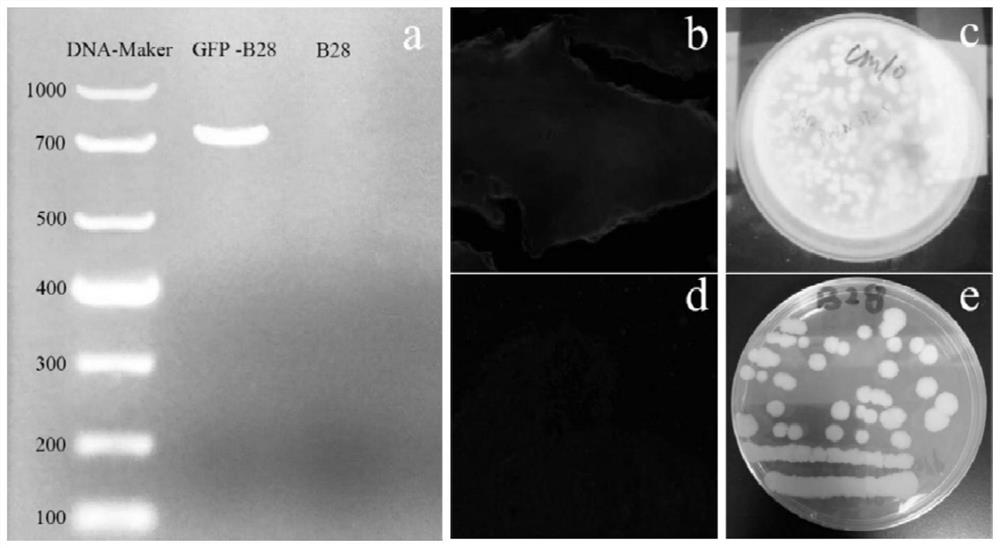
[0044] The green fluorescent protein gene transduction of test strain of embodiment 1
[0045] 1. Experimental method
[0046] (1) Plasmid DNA extraction and plasmid desalting
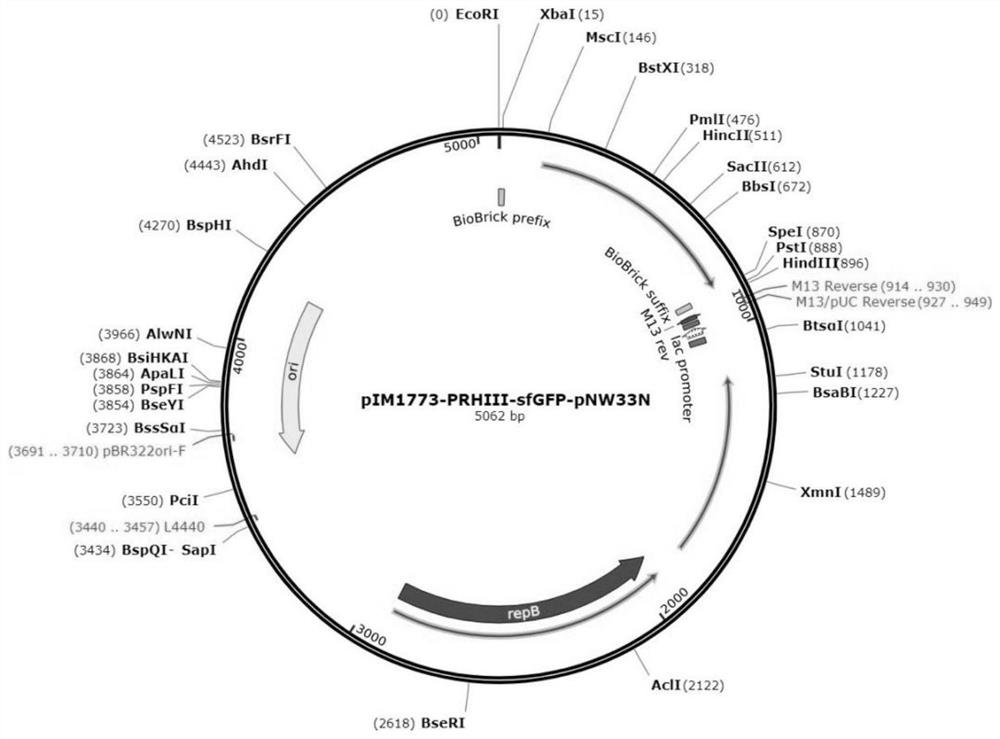
[0047] The pNW33 plasmid was extracted from Escherichia coli containing the pNW33 plasmid using the SanPrep column plasmid DNA mini-extraction kit (Shanghai Sangon Bioengineering Co., Ltd.), and the steps of plasmid extraction were referred to the kit instructions.
[0048] 0.1mol -1Melt glucose and 1% agarose in water Take 1mL to a 1.5mL microcentrifuge tube, then insert a 0.5mL microcentrifuge tube into a 1.5mL microcentrifuge tube. After solidification, remove the 0.5 mL microcentrifuge tube, then transfer the plasmid DNA sample to a desalting cone and desalt on ice for 2 h. Finally, the plasmid DNA was collected and the concentration of the plasmid DNA was measured using a micro-volume ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer (ThermoFisher NanoDropOne) and stored at 4°C.
[0049] (2) Competent pre...
Embodiment 2
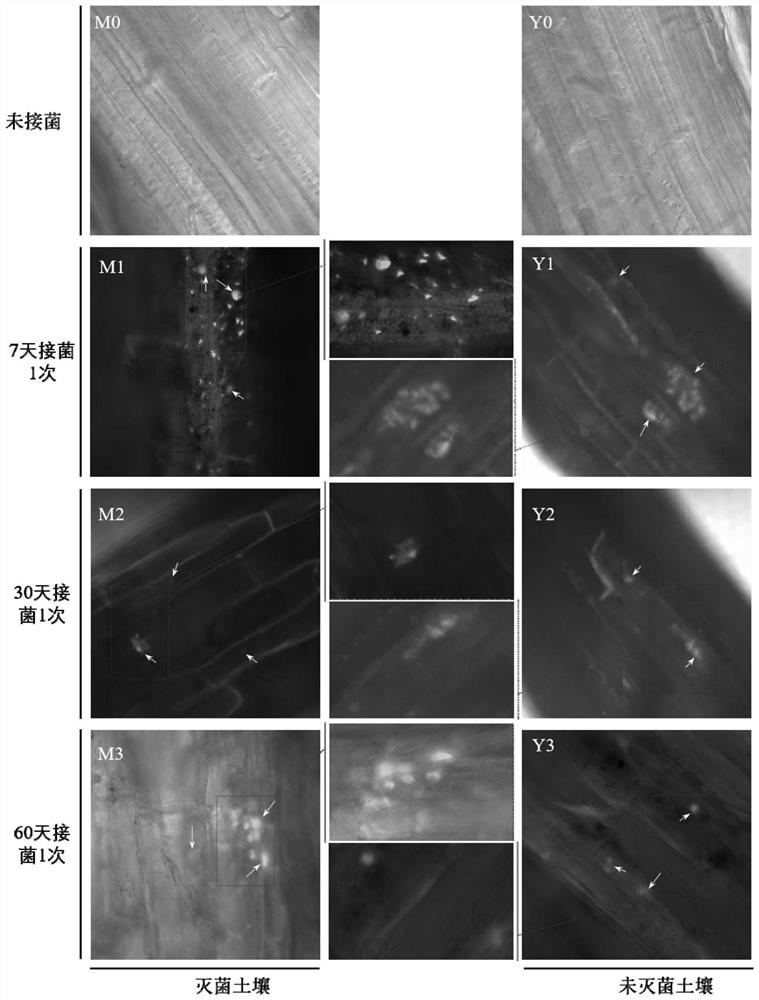
[0056] Example 2 Determination of bacterial strain B-28 colonization status in corn roots
[0057] 1. Experimental method
[0058] In this study, soil pot experiments were conducted to study the colonization of the strains in maize roots and their effects on maize growth and Cr uptake under different inoculation frequencies. The inoculation is inoculated with the B-28 strain transduced with the pNW33N plasmid in Example 1.
[0059] (1) Soil pot experiment design
[0060] There are 8 treatments in the soil pot test, which are: M0 (no inoculation, planting in sterilized soil); M1 (inoculation once every 7 days; planting in sterilized soil); M2 (inoculation once every 30 days; planting in sterilized soil) ); M3 (inoculation once every 60 days; planting in sterilized soil); Y0 (no inoculation, planting in non-sterile soil); Y1 (inoculation once every 7 days; planting in non-sterile soil); Y2 (inoculation every 30 days Bacteria once; plant in non-sterile soil); Y3 (inoculate onc...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Example 3 Effect of Inoculation on Chlorophyll Content and Antioxidative Enzyme Activity of Maize
[0068] 1, cultivation and inoculation method are the same as the soil pot experiment design method among the embodiment 2.
[0069] 2. Experimental results
[0070] Table 1 shows the effects of different treatments on the chlorophyll content of maize leaves and the activities of antioxidant enzymes in roots under soil pot experiments. Among them, M0, M1, M2 and M3 respectively represent the treatments of no inoculation, inoculation every 7 days, inoculation every 30 days and inoculation every 60 days in the sterilization soil treatment. Y0, Y1, Y2 and Y3 respectively represent the treatments of no inoculation, inoculation every 7 days, inoculation every 30 days and inoculation every 60 days in the non-sterile soil treatment.
[0071] Table 1 Chlorophyll content of corn leaves and antioxidant enzyme activity in roots of soil culture experiment
[0072]
[0073] Diffe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com