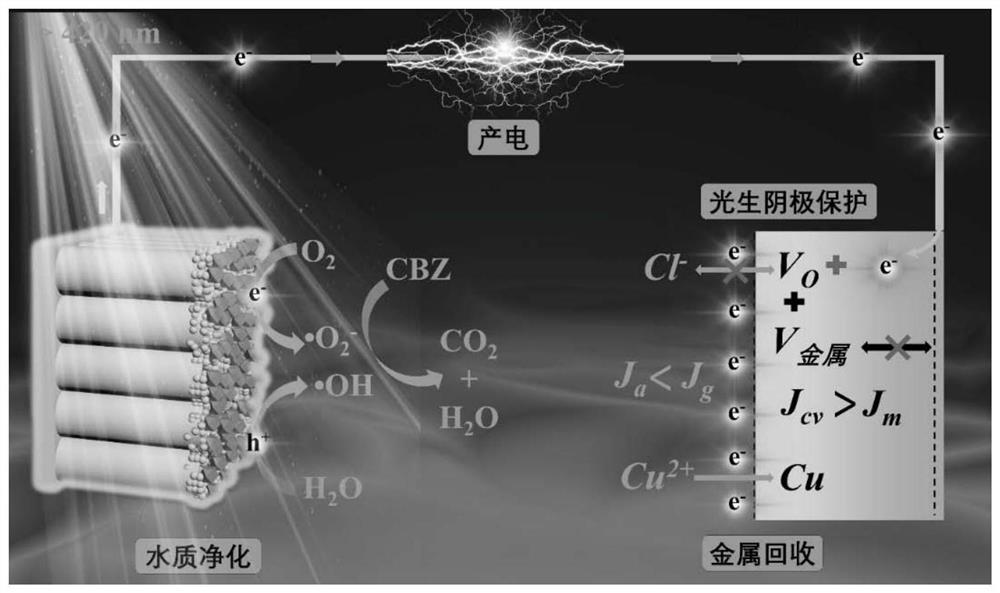
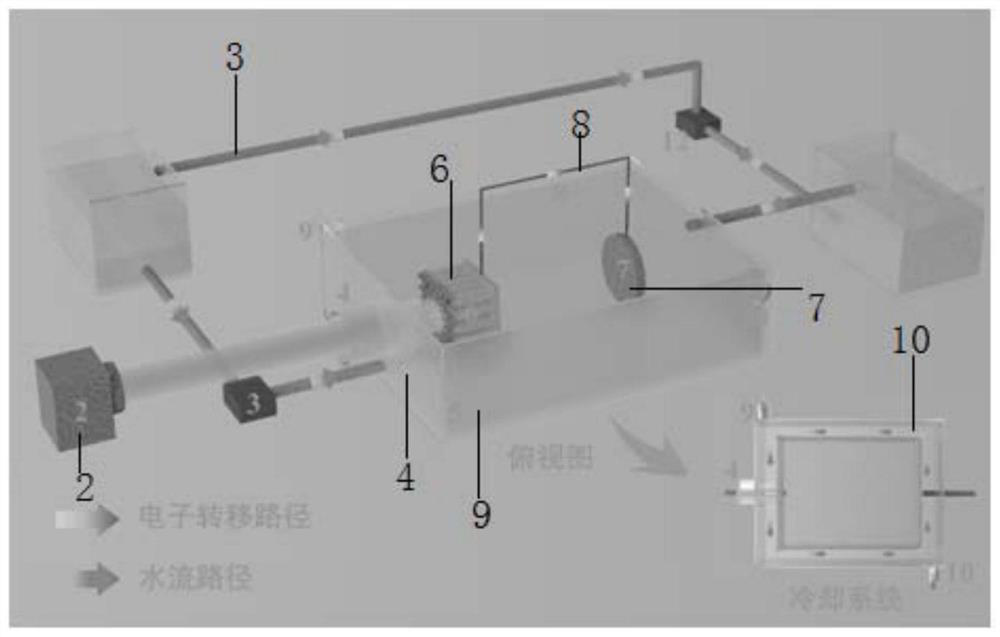
A flow-type photoelectrochemical system and method for resource recovery in high-salt wastewater
A photoelectrochemical, high-salt wastewater technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, electrochemical water/sewage treatment, water pollutants, etc., can solve problems such as increased wastewater treatment cost per ton, decreased electrode stability, and poor effluent quality. , to achieve the effect of good effluent quality, low cost and strong power generation capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0062] According to a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the photoanode is selected from one or more of titanium dioxide, carbon quantum dots, ferric oxide, tungsten oxide, molybdenum disulfide, bismuth vanadium tetroxide and Mxene, but not limited to The above materials are preferably selected from one or more of titanium dioxide, carbon quantum dots, tungsten oxide, molybdenum disulfide and Mxene, more preferably selected from one or more of titanium dioxide, carbon quantum dots, tungsten oxide and molybdenum disulfide kind.
[0063] The metal cathode is selected from stainless steel, aluminum alloy, carbon steel, brass, nickel-based materials or platinum sheets, but not limited to the above materials, preferably selected from stainless steel, carbon steel, brass or platinum sheets, more preferably selected from stainless steel or platinum sheets .
[0064] The external circuit includes wires connecting the photoanode and the metal cathode. The length of the wir...
Embodiment 1
[0089] use as figure 2 The photoanode shown is titanium dioxide, carbon quantum dots and tungsten oxide, the metal cathode is Pt (platinum), the length of the wire (made of brass) is 5 cm, and the flow type photoelectrochemical system for resource recovery is set with a light-transmitting quartz window. Organic matter (carbamazepine, CBZ) concentration was 5 mol / L, heavy metal (Cu 2+ ) concentration of 0.5 mol / L, salt concentration of 0.5% high-salt wastewater (solution volume 1 L), the flow rate was set at 5 mL / min. The light intensity is set to 1 sun.
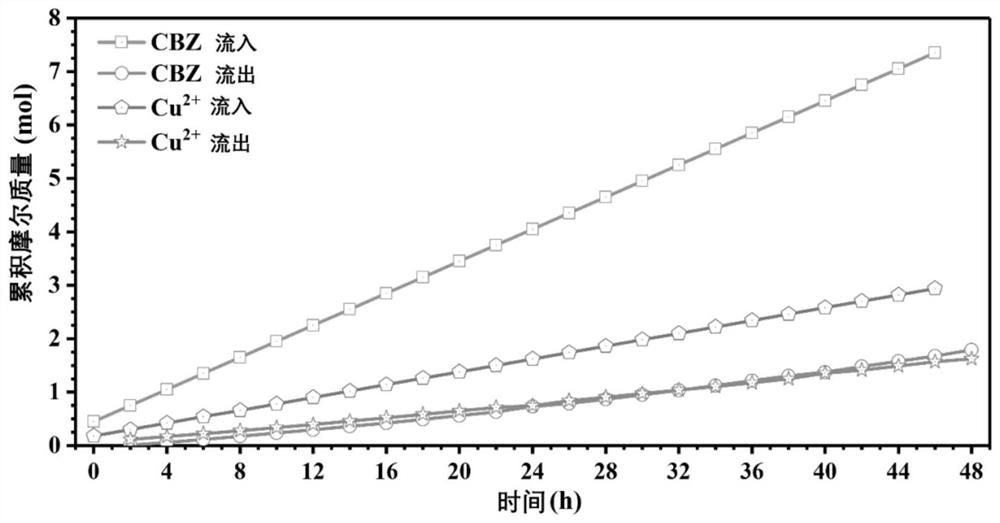
[0090] After 180 min of reaction, the degradation efficiency of CBZ in wastewater was measured to be 75.62%, Cu 2+ The recycling efficiency is 52.55%, and the electricity production is 56.57 W / (m 3 Solution×m 2 electrode area).
[0091] After 48 h of reaction, the degradation efficiency of CBZ in wastewater was measured to be 73.85%, Cu 2+ The recycling efficiency is 9.34%, and the electricity production is 45.34 W / (m ...
Embodiment 2
[0093] Repeat the process of Example 1, the only difference is: the photoanode is titanium dioxide, carbon quantum dots and molybdenum disulfide.
[0094] After 180 min of reaction, the degradation efficiency of CBZ in wastewater was measured to be 68.83%, Cu 2+ The recycling efficiency is 48.61%, and the electricity production is 52.84 W / (m 3 Solution×m 2 electrode area).
[0095] After 48 h of reaction, the degradation efficiency of CBZ in wastewater was measured to be 56.34%, Cu 2+ The recycling efficiency is 8.56%, and the electricity production is 37.09 W / (m 3 Solution×m 2 electrode area).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| recovery rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com