An ultra-thin permanent magnet with a surface-deposited coating
A surface deposition, permanent magnet technology, applied in the coating, permanent magnet, superimposed layer plating and other directions, can solve problems such as magnetic performance decline, and achieve the effect of reducing adverse effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
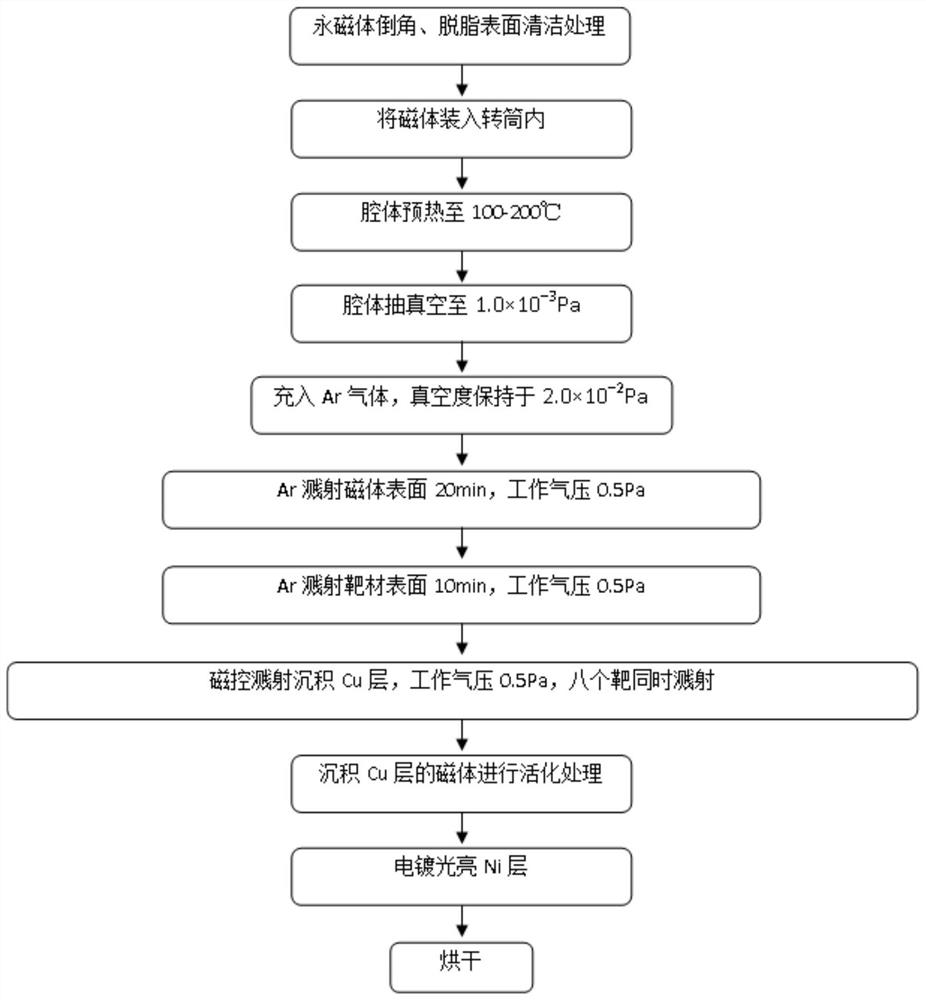
[0038] The present invention also provides a method for preparing a protective coating on the surface of an ultra-thin NdFeB permanent magnet, comprising the following steps:
[0039] 1) The surface-cleaned NdFeB magnet is subjected to DC magnetron sputtering coating to obtain a NdFeB magnet with Cu-Sn / Cu gradient coating deposited on the surface;
[0040] 2) The NdFeB magnet with a copper layer deposited on the surface is obtained by the above steps, and then the surface is pretreated, and then a nickel-based coating is applied to obtain a NdFeB magnet with a Cu-Ni composite coating deposited on the surface.
[0041] In the above-mentioned steps of the present invention, the selection principles and preferred ranges of the raw materials and structures used, if not specified, correspond to the selection principles and preferred ranges of the raw materials and structures in the aforementioned NdFeB magnets whose surface is coated with a Cu-Ni composite coating , which will not ...
Embodiment 1
[0055] 1) Soak the NdFeB magnet in a degreasing agent solution for 15 minutes, ultrasonically clean it for 1 minute, rinse it twice with clean water without removing the surface dirt, and place it on the workpiece bracket after drying;
[0056] 2) Turn on the heating device to keep the chamber temperature at 150°C, and at the same time turn on the vacuum pump to stabilize the vacuum degree of the chamber at 1.0×10-3Pa;
[0057] 3) Argon is used as the cleaning gas to remove oxides on the surface of the magnet and the surface of the target by sputtering;
[0058] 4) Turn on the ion source power supply, magnetron sputtering on the surface of the magnet, Cu-Sn / Cu gradient coating, the sputtering time is 1.5h, and the coating thickness is 5μm;
[0059] 5) activating the permanent magnet on which the copper layer was deposited using a dilute sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 0.5 wt%, for 5 s;
[0060] 6) Plating bright nickel on the surface of the above-mentioned perm...
Embodiment 2
[0063] 1) Soak the NdFeB magnet in a degreasing agent solution for 15 minutes, ultrasonically clean it for 1 minute, rinse it twice with clean water without removing the surface dirt, and place it on the workpiece bracket after drying;
[0064] 2) Turn on the heating device to keep the chamber temperature at 150°C, and at the same time turn on the vacuum pump to stabilize the vacuum degree of the chamber at 1.0×10-3Pa;
[0065] 3) Argon is used as the cleaning gas to remove oxides on the surface of the magnet and the surface of the target by sputtering;
[0066] 4) Turn on the ion source power supply, magnetron sputtering on the surface of the magnet, Cu-Sn / Cu gradient coating, the sputtering time is 2.0h, and the coating thickness is 6.5μm;
[0067] 5) activating the permanent magnet on which the copper layer was deposited using a dilute sulfuric acid solution with a concentration of 0.5 wt%, for 5 s;
[0068] 6) Plating bright nickel on the surface of the above-mentioned pe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com