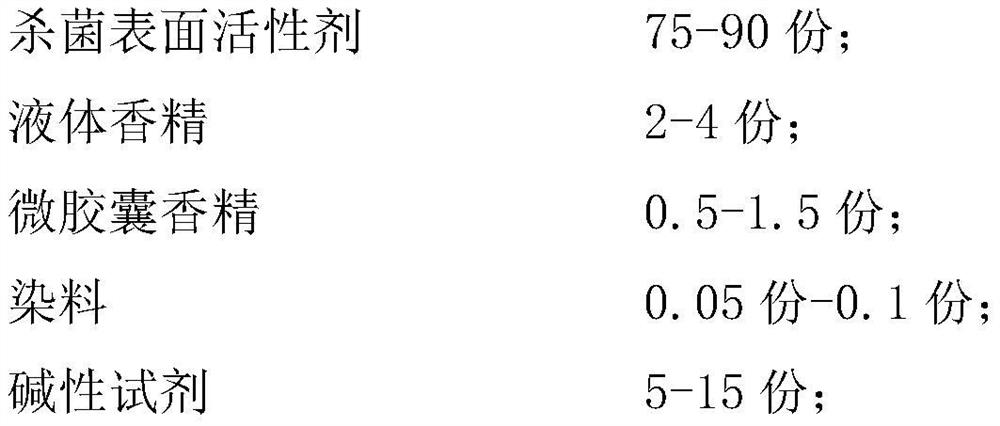
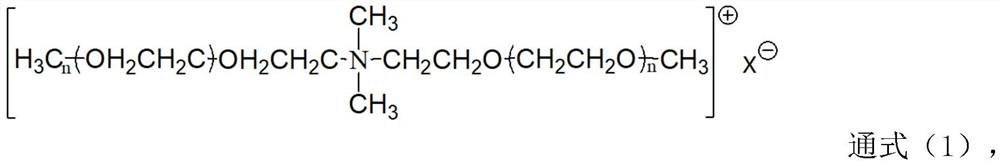Bactericidal surfactant, fragrant bead containing bactericidal surfactant and having bactericidal function and preparation method of fragrant bead
A technology of surfactants and fragrant beads, which is applied in the field of organic chemistry and daily chemicals, can solve problems such as harming human health, clothing adsorption, microbial growth, etc., and achieve good bactericidal performance and good defoaming performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0067] The technical solutions of the present application will be clearly and completely described below in conjunction with the embodiments of the present application. All reagents and raw materials used were purchased commercially unless otherwise specified. For the experimental methods that do not specify specific conditions in the following examples, select according to conventional methods and conditions, or according to the product instructions.
[0068] In the following examples, the type of liquid essence is plant essence, preferably rose essence purchased from Jiangmen Huayunya Fragrance Co., Ltd. The type of microcapsule essence is the herbaceous fragrance type microcapsule essence purchased from Anhui Meikedi Intelligent Microcapsule Technology Co., Ltd.
[0069] Synthetic example
Embodiment 1
[0071] (1) Add 120g of N-methyldiethanolamine and 11g of sodium methoxide sequentially into the high-temperature autoclave, stir and dissolve, then raise the temperature to 90-110°C, and vacuum for 1 hour to remove methanol. Continue to raise the temperature to 130-140°C, feed 3520g of ethylene oxide at -0.1MPa to react, control the reaction temperature at 130-150°C, and control the pressure at 0.1-0.3MPa. After the ethylene oxide reaction is completed, it is aged for 1 hour, and then degassed at -0.1MPa for 30 minutes. After the degassing is completed, cool down to 65-75°C, add 70g of sodium methoxide, stir and dissolve, degas at -0.1MPa for 90min, continue to feed 167g of methyl chloride, react at 0.1-0.3MPa for 10h, then heat up to 90-100°C , Degassing at -0.1MPa for 60min. After degassing, 28 g of acetic acid was added to neutralize to neutrality to obtain an alkylated and quaternized modified N-methyldiethanolamine polyethylene glycol ether with a number average molecula...
Embodiment 2
[0074] (1) Add 120g of N-methyldiethanolamine and 16g of sodium methoxide sequentially into the high-temperature autoclave, stir and dissolve, then raise the temperature to 90-110°C, and vacuum for 1 hour to remove methanol. Continue to raise the temperature to 130-140°C, feed 8008g of ethylene oxide at -0.1MPa to react, control the reaction temperature at 130-150°C, and control the pressure at 0.1-0.3MPa. After the ethylene oxide reaction is completed, it is aged for 1 hour, and then degassed at -0.1MPa for 30 minutes. After degassing is completed, cool down to 65-75°C, add 71g of sodium methoxide, stir to dissolve, degas at -0.1MPa for 100min, continue to feed 152g of methyl chloride, react at 0.1-0.3MPa for 13h, then heat up to 90-100°C , Degassing at -0.1MPa for 90min. After degassing, 23g of acetic acid was added to neutralize to neutrality to obtain an alkylated and quaternized modified N-methyldiethanolamine polyethylene glycol ether with a number average molecular wei...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com