Heat-resistant ceramic pot
A ceramic pot and heat-resistant technology, applied in the field of ceramics, can solve the problems of surface damage, explosion, poor heat resistance, etc., and achieve the effects of easy cleaning, no pinholes, and good gloss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
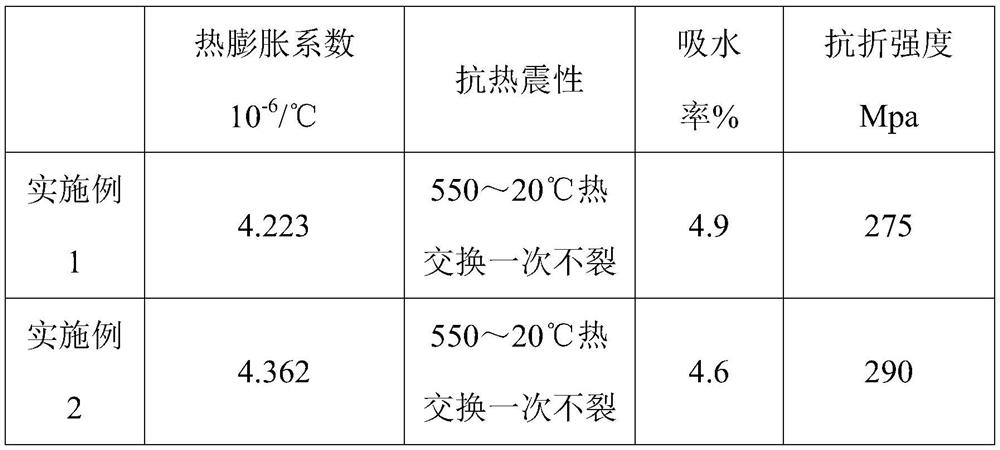
Embodiment 1
[0018] This embodiment discloses a heat-resistant ceramic pot, and the manufacturing method includes the following steps:
[0019] (1) Preparation of green body: get the blank by weight parts: 17 parts of chapierite, 16 parts of demantoid, 4 parts of zircon, 9 parts of black mud, 2 parts of alumina, 3 parts of sillimanite, 2 parts of phillips 7 parts of bamboo charcoal powder, 5 parts of goose pipe stone, 12 parts of glauconite. After mixing, put it into a ball mill for wet ball milling. The amount of water added during ball milling is calculated as: 25% by weight based on the weight % of the water weight to the water weight and the total dry material. After being stale for 24 hours, pass through a 200-mesh sieve to form a mud for subsequent use;
[0020] (2) Prepare the glaze: get the glaze in parts by weight: 2 parts of barium carbonate, 18 parts of burnt talc, 4 parts of sodium carbonate, 25 parts of glaze fruit, 1 part of tin oxide, 19 parts of silicon dioxide, 3 parts of ...
Embodiment 2
[0024] This embodiment discloses a heat-resistant ceramic pot, and the manufacturing method includes the following steps:
[0025] (1) Preparation of green body: get the blank by weight parts: 23 parts of chapierite, 11 parts of demantoid, 8 parts of zircon, 5 parts of black mud, 5 parts of alumina, 1 part of sillimanite, 5 parts of phillips 3 parts of bamboo charcoal powder, 8 parts of goose tube stone, and 9 parts of glauconite. After mixing, put it into a ball mill for wet ball milling. The amount of water added during ball milling is calculated as: 30% by weight based on the weight of the water weight to the water weight and the total dry material. After being stale for 20 hours, pass through a 250-mesh sieve to form a mud for subsequent use;
[0026] (2) Prepare the glaze: get the glaze in parts by weight: 4 parts of barium carbonate, 12 parts of burnt talc, 7 parts of sodium carbonate, 18 parts of glaze fruit, 3 parts of tin oxide, 14 parts of silicon dioxide, 6 parts of...
Embodiment 3
[0030] This embodiment discloses a heat-resistant ceramic pot, and the manufacturing method includes the following steps:
[0031] (1) Preparation of green body: get the blank by weight parts: 20 parts of chapierite, 12 parts of demantoid, 6 parts of zircon, 7 parts of black mud, 3 parts of alumina, 2 parts of sillimanite, 4 parts of phillips 5 parts of bamboo charcoal powder, 7 parts of goose pipe stone, 11 parts of glauconite. After mixing, put it into a ball mill for wet ball milling. The amount of water added during the ball milling is calculated as: 35% by weight based on the weight of the water weight to the water weight and the total dry material. After being stale for 18 hours, pass through a 280-mesh sieve to form a mud for subsequent use;
[0032] (2) Prepare the glaze: get the glaze in parts by weight: 3 parts of barium carbonate, 15 parts of burnt talc, 5 parts of sodium carbonate, 22 parts of glaze fruit, 2 parts of tin oxide, 16 parts of silicon dioxide, 4 parts ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com