Method for semi-continuous fermentation culture of pichia pastoris engineering bacteria
A Pichia pastoris, fermentation and culture technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of large material resource consumption, cumbersome procedures, low production efficiency and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] ①Use a 30L fermenter, inoculate 500ml of seed liquid into 10LBSM medium according to the inoculation ratio of 5%, stir at 300rpm, ventilate at 1vvm, tank pressure at 0.05MP, cultivate at 30°C and pH5.0 until the dissolved oxygen suddenly rises, and cultivate During the process, when the dissolved oxygen drops below 20%, the rotating speed is gradually increased to 700rpm.
[0045] ② Add 800ml of 50% glycerin (including 12ml / L PTM1), control the rate so that the dissolved oxygen is not lower than 20%, after the completion, take a sample to measure the wet weight of about 180g / L, and the whole process takes about 8 hours.
[0046] ③ Feed methanol (containing 12ml / L PTM1) for induction, control the rate so that the dissolved oxygen is not lower than 20%, and continue for 120h.
[0047] ④ After 120 hours of induction, release 50% of the feed liquid for harvesting, and add sterile BSM basic fermentation medium (without glycerol) to the fermenter until the wet weight is equal...
Embodiment 2
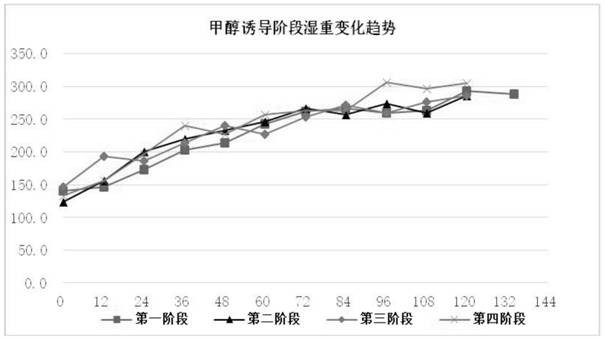
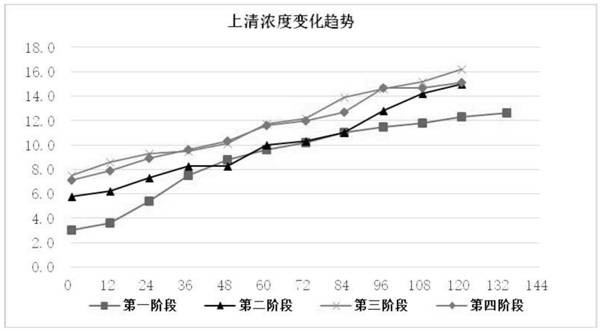
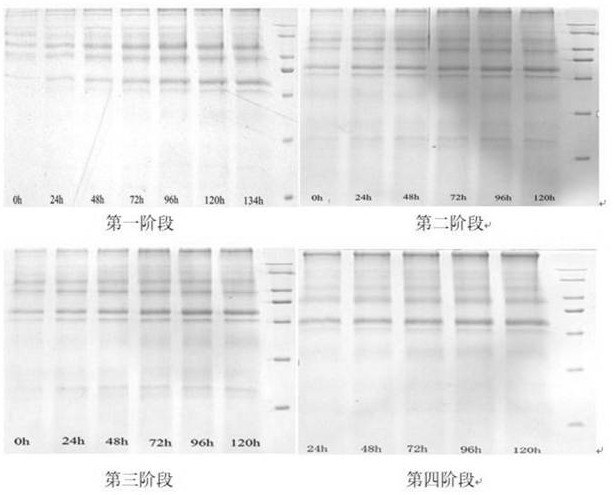
[0055] Wet weight, concentration and electrophoresis analysis were carried out on the samples during the fermentation process. The measurement method is: take 30ml of fermentation liquid from the sampling port of the fermentation tank, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 minutes with a centrifuge tube of known weight, wet weight: discard the supernatant and weigh, subtract the weight of the centrifuge tube from the weight to get the wet weight; concentration: take The protein concentration of the supernatant was determined by the G250 method; electrophoresis: electrophoresis analysis was carried out by SDS-PAGE Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. The result is as Figure 1 ~ Figure 3 , Table 2 ~ Table 3 shown.
[0056] Depend on figure 1 , figure 2 , image 3 It can be seen that the wet weight, supernatant protein concentration, and target protein content of the four stages have the same change trend. Through three consecutive fermentation cycles, the fermentation time from th...
Embodiment 3
[0063] After the fermentation broth was harvested, the fermentation supernatant was purified using a nickel column, and the results were as follows:
[0064] Table 4: Summary of purification results
[0065]
[0066]
[0067] Comparison of production efficiency between semi-continuous fermentation and batch fermentation:
[0068] table 5
[0069]
[0070] The labor and energy consumption ratio of semi-continuous fermentation and batch fermentation:
[0071] Table 6
[0072] Fermentation type average labor average energy consumption average water consumption semi-continuous fermentation 1.25 people / day 25 degrees / day 2.5L / day batch fermentation 1.8 people / day 32 degrees / day 10L / day ratio 0.69:1 0.78:1 0.25:1
[0073] The results show that the semi-continuous fermentation cells are reused, the continuity is strong, the technological process is simplified compared with batch fermentation, and the work intensity and wor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com