Vaccines and compositions based on S antigen protein of SARS-CoV-2
A sars-cov-2, protein technology, applied in the direction of DNA / RNA vaccination, vaccines, virus antigen components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] Example 1. Optimization of mRNA sequence
[0068] Sequence optimization of the coding sequence of SARS-CoV-2S protein (SEQ ID NO.1) was carried out through DNAWorks (v3.2.4) online software, including: adjusting codon bias for expression in the human body, Use the frequency to adjust, increase the GC content of the sequence, etc. The optimized nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. This nucleotide sequence makes the mRNA structure more stable after transcription, and the translation efficiency of the target protein in mammals and humans is higher.
Embodiment 2
[0069] Example 2. Expression of the SARS-CoV-2S trimeric protein in a pre-fusion stable form
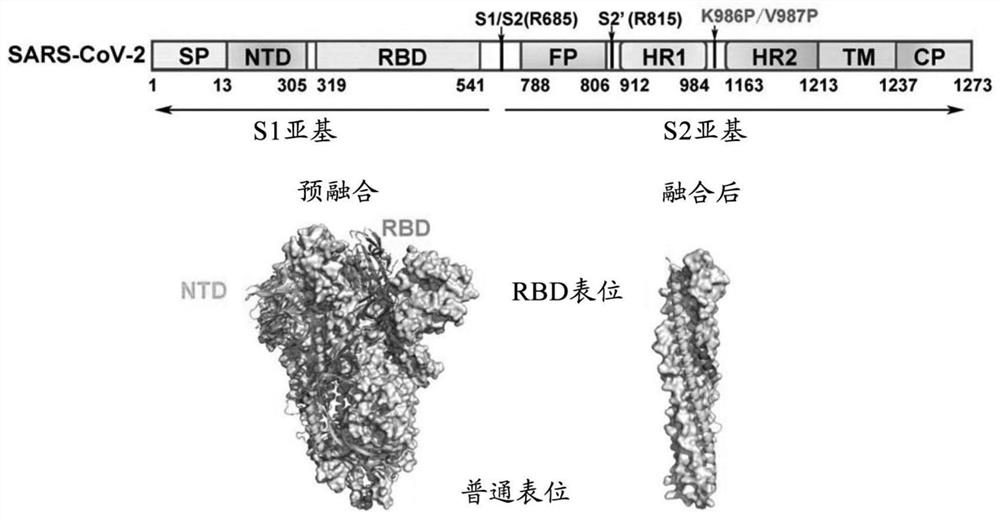
[0070] The S protein consists of an extracellular domain (ECD), a transmembrane domain (TM) and a C-terminal cytoplasmic domain (CP). Among them, the extracellular domain can be further divided into signal peptide region (SP), N-terminal region (NTD), receptor binding domain (RBD), an internal membrane fusion peptide (FP) and two 7-peptide repeats (HR ), belonging to the first class of viral membrane fusion proteins. Schematic diagram of the domain structure of the S protein figure 1 As shown, the pre-fusion structure is the functional conformation of S protein, and a large number of sensitive neutralizing epitopes that only exist in the pre-fusion form are masked after fusion. Expression of a prefusion-stabilized form of the SARS-CoV-2S trimeric protein is key to the development of a safe and effective SARS-CoV-2 vaccine.
[0071] In this example, the following strategy was used ...
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3.mRNA preparation
[0082] The mRNA encoding the prefusion-stabilized form of the SARS-CoV-2 viral S protein was prepared by in vitro transcription. The nucleic acid sequence of the coding region of the S protein is obtained by the whole gene synthesis method, and the nucleic acid sequence of the coding region is connected with a plasmid vector by a conventional molecular cloning method to obtain a DNA plasmid template for in vitro transcription.
[0083] Table 1. Transcription start sites
[0084]
[0085] The elements contained in the plasmid vector include a T7 promoter sequence (TAATACGACTCACTATA), and the starting nucleic acid sequence can be any of AGG / GGG / CGG, as shown in Table 1; 5'-UTR sequence (SEQ ID NO.41), 3'-UTR sequence (SEQID NO.43), 120nt 3'-terminal polyadenylic acid (polyA) sequence, including Xbal restriction site (TCTAGA) after the 3'-terminal polyadenylic acid sequence.
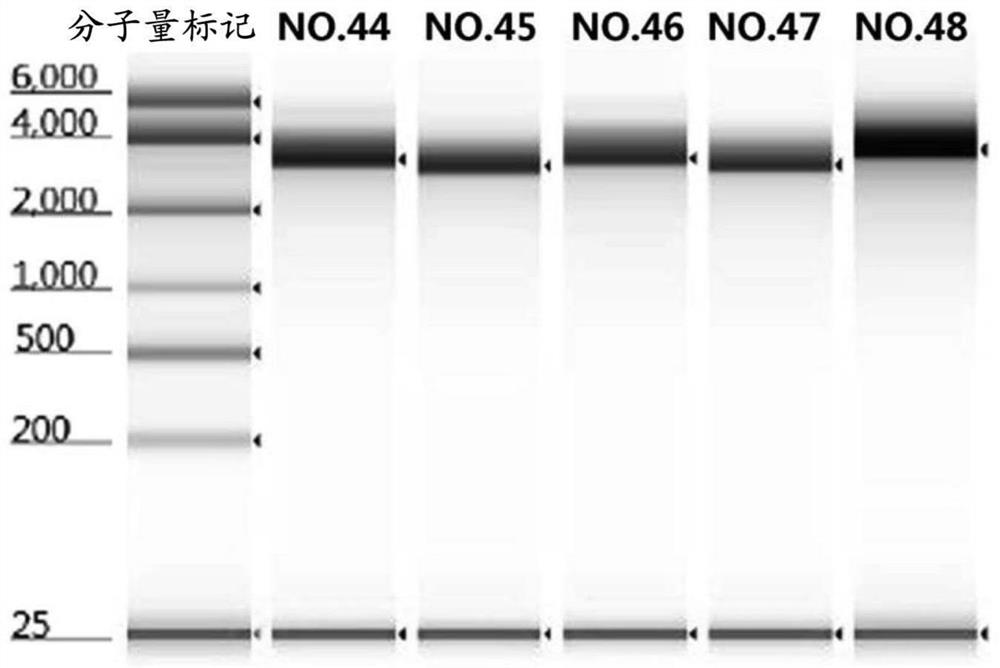
[0086] The mRNA sequence obtained by transcribing is shown i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com