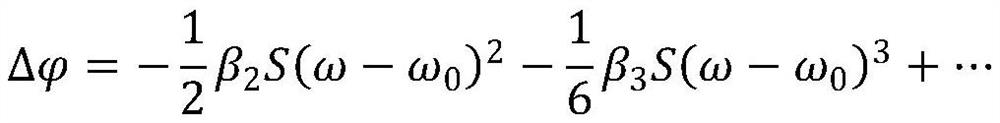Cascade large-scale optical real-time delay network with dispersive and non-dispersive devices based on wavelength division multiplexing
A true optical time-delay and non-dispersive technology, applied in the field of microwave photonics, can solve the problems of large system size, time-delay volume constraints, and large volume of space optics solutions.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
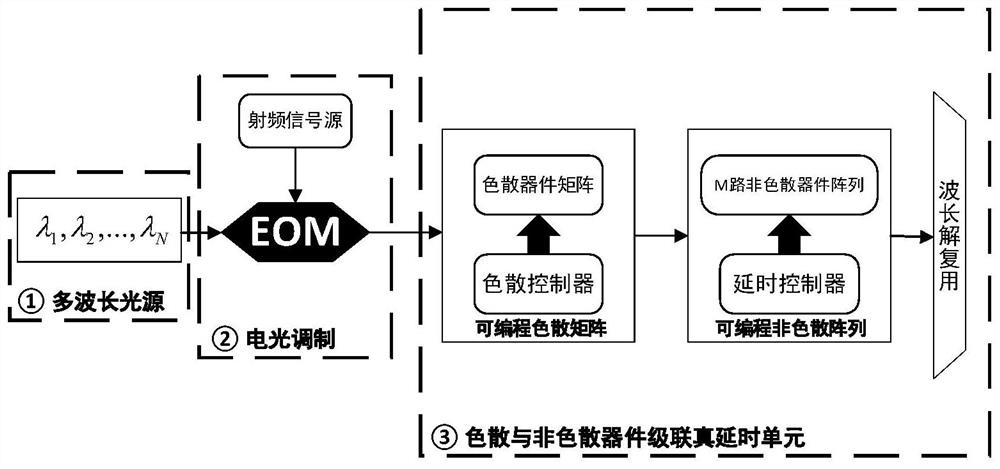
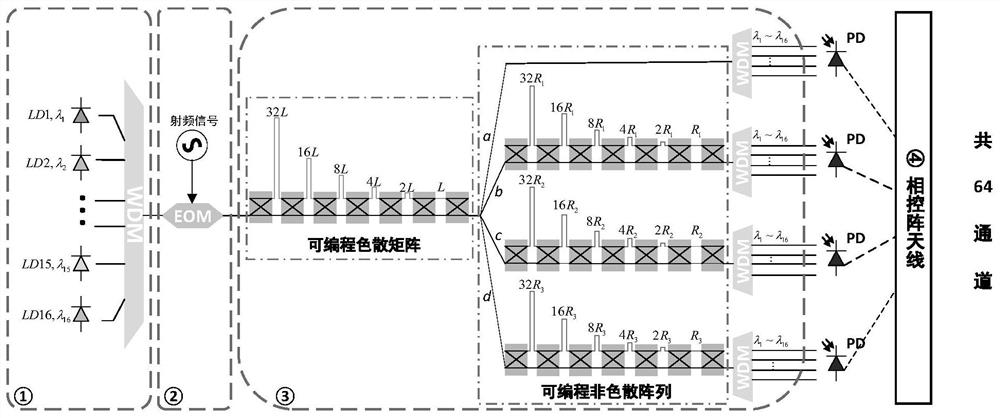
[0035] figure 2 It is an embodiment of the present invention, capable of realizing a 64-channel true delay network with K=6bit delay control. Its specific structure is described as follows:
[0036] The multi-wavelength light source ① adopts tunable semiconductor lasers with N=16 output light wavelengths at equal intervals, and the output light wavelengths at equal intervals are λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...,λ 16 , to control the output optical power of each tunable semiconductor laser to be equal. 16 channels of laser input into a 16-channel wavelength division multiplexer WDM, through wavelength division multiplexing into a channel containing λ 1 ,λ 2 ,...,λ 16 A multi-wavelength light source with wavelength components.
[0037] In the electro-optic modulation unit ②, the radio frequency signal source is modulated onto the optical carrier output by the multi-wavelength light source ① through the electro-optic modulator to obtain a modulated signal.
[0038] In the programmable disp...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The multi-wavelength light source can be realized by an optical frequency comb and a waveform controller, and the rest are the same as those in Embodiment 1, and will not be repeated here.
[0048] To sum up, compared with the optically controlled true delay network in the past, the present invention jumps out of the limitations of the number of multi-wavelength light sources, wavelength division multiplexing and demultiplexing capabilities, and innovatively combines dispersive devices with non-dispersive devices to form a dispersive The true delay unit is cascaded with non-dispersive devices, using wavelength division multiplexing, while reducing the number of carrier wavelengths required by wavelength division multiplexing, the number of true delay network channels is increased, and a multi-channel with simple structure and high channel consistency is obtained. Large scale true latency network. Using the output radio frequency signal of the true delay network proposed...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com