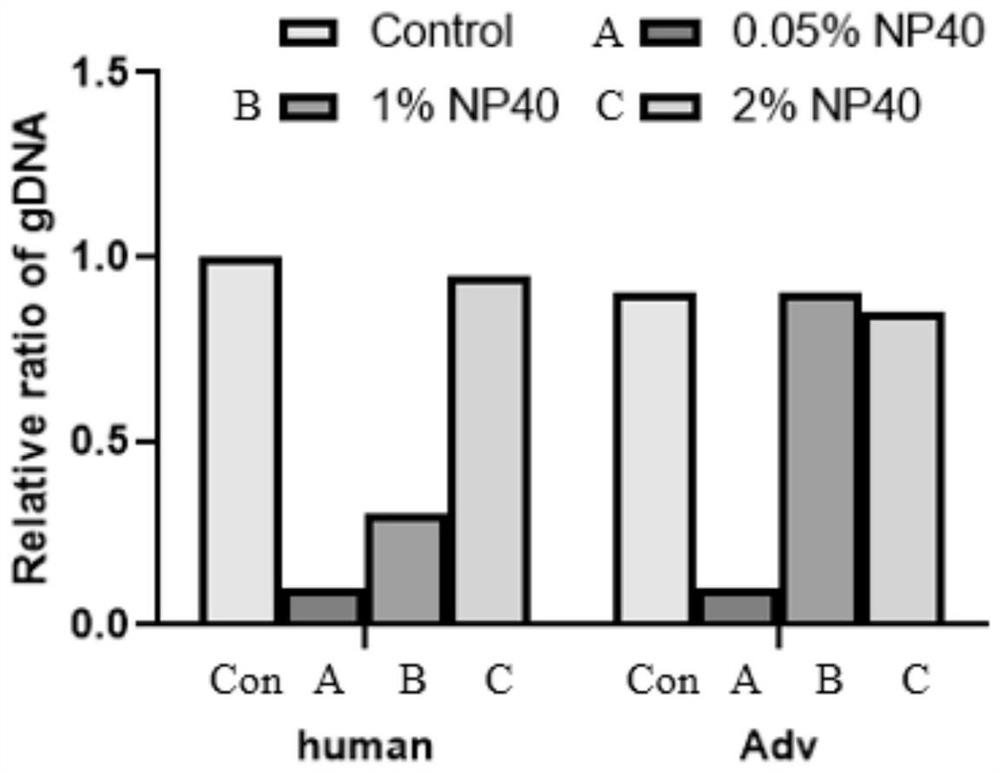
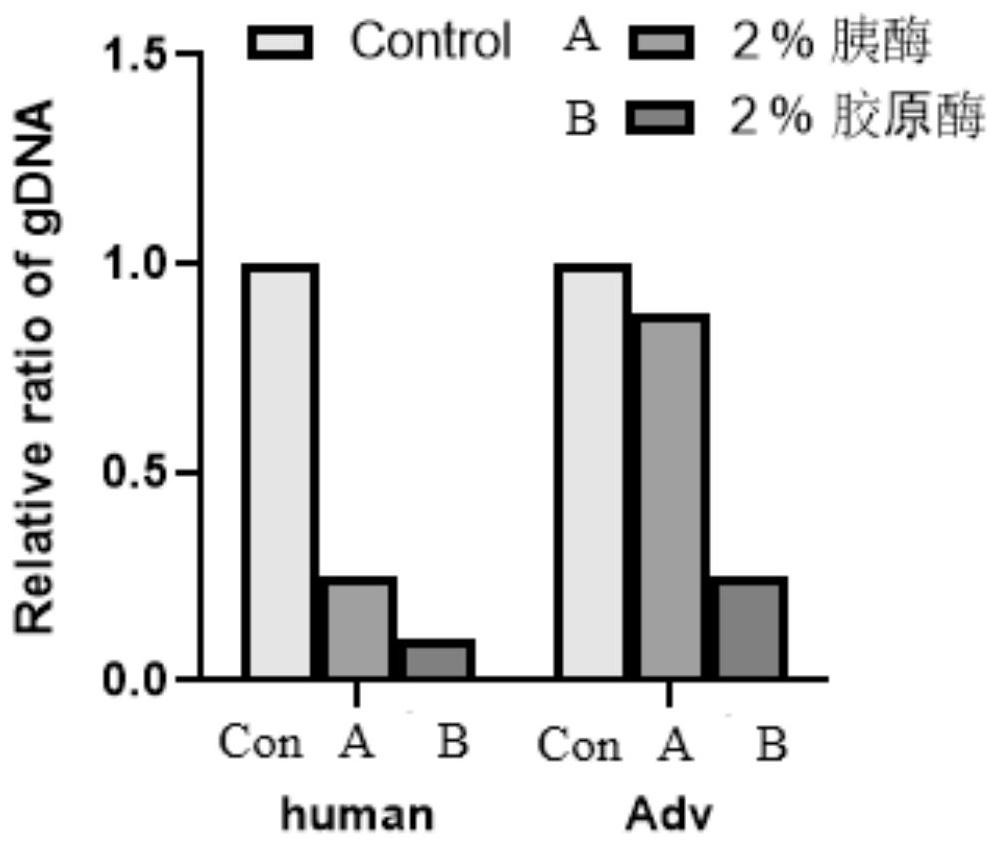
Method and reagent for enriching intracellular microorganisms
A technology of microorganisms and cells, which is applied in the measurement/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, and the separation of microorganisms. It can solve the problems of improving sequencing depth and increasing sequencing costs, and achieve the effect of increasing the sequence ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A method for enriching intracellular microorganisms, comprising the following steps:
[0047] 1. Collect cells
[0048] Cellular components of the sample are collected.
[0049] 1.1 Whole blood sample: Place the blood collection tube (containing whole blood, about 5-10ml) in a centrifuge, centrifuge at 1600g for 10min, transfer the upper layer of plasma, and use a pipette to absorb the middle layer of white blood cells.
[0050] 1.2 Other clinical infection samples containing cells: take 500-1000 μl of samples, centrifuge at 10,000-12,000 rpm for 5 minutes, and collect cells.
[0051] 2. Release microorganisms
[0052] Use cell treatment agents to make cell membranes more permeable and release intracellular microorganisms, specifically:
[0053] Take the cell fraction collected in step 1, and use 400-600 μl cell treatment agent to treat the cells (about 5x10 6 ), incubate on ice for 5-20 min, and shake and mix continuously during the period to increase the permeabil...
Embodiment 2
[0066] In this example, the method in Example 1 is used to detect whole blood samples.
[0067] 1. Sample preparation.
[0068] Divide the 5ml whole blood sample into 2 parts, one of which is centrifuged at 1600g for 10min, collect the upper layer plasma and the middle layer white blood cell samples into 2.0ml EP tubes, respectively marked as A and B, and the other whole blood sample Marked as C.
[0069] 2. Sample pretreatment and preparation.
[0070] Sample B (white blood cells) was treated with reference to steps 2-6 in Example 1; after sample A was directly extracted with the Micro DNA Extraction Kit (DP316) of Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd., refer to Example 1 Steps 5-6 for processing; Sample C is processed with reference to steps 4-6 in Example 1. All three samples were constructed as qualified high-throughput (NGS) sequencing libraries.
[0071] 3. Detection
[0072] The A, B and C samples in the above step 2 were sequenced on the machine at th...
Embodiment 3
[0081] In this example, the method in Example 1 is used to detect the lower respiratory tract sample (alveolar lavage fluid).
[0082] 1. Sample preparation.
[0083] Divide 2ml of alveolar lavage fluid sample into 2 parts, one of which takes a certain volume (500-1000μl) sample, centrifuges at 10,000-12,000rpm for 5min, collects cells, and marks it as D; the other takes the same volume as sample D The original sample, labeled E.
[0084] 2. Sample pretreatment and preparation.
[0085] Sample D was processed with reference to steps 2-6 in Example 1; sample E was processed with reference to steps 4-6 in Example 1. Both samples were constructed into qualified high-throughput (NGS) sequencing libraries.
[0086] 3. Detection
[0087] The D and E samples in the above step 2 were sequenced on the machine at the same time, and the same sequencing depth was adopted, and the results were as follows:
[0088] Table 2 The sequencing results of the above D and E samples
[0089] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com