Acinetobacter guillouiae PxCG3 strain of plutella xylostella (L) and application of acinetobacter guillouiae PxCG3 strain
A technology of diamondback moth and bacterial strains, applied in the field of agricultural microorganisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Isolation and cultivation of the bacterial strain PxCG3 of embodiment 1
[0024] (1) Preparation of selective separation medium:
[0025] LB medium (10g peptone, 5g yeast extract, 10g NaCl, 15g agar, dissolved in 1L sterile ddH2O water, adjust pH to 7.0);
[0026] Nutrient agar medium NA (3g beef extract, 10g peptone, 5g NaCl, 15g agar, dissolved in 1L sterile ddH2O, adjust pH to 7.0).
[0027] (2) Dissect and plate: Dissect the 3rd instar larvae of Plutella xylostella in an ultra-clean bench under sterile conditions and take the midgut contents, centrifuge to get the supernatant and sediment, dilute 5 concentration gradients, and dilute 10 -4 ~10 -5 After doubling, NA plates were respectively coated, placed in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C, and observed every 24 hours;
[0028] (3) Continuous purification culture and taking pictures: After a single colony grows in the selective medium, first pick a single colony according to the color, size and shape of t...
Embodiment 2
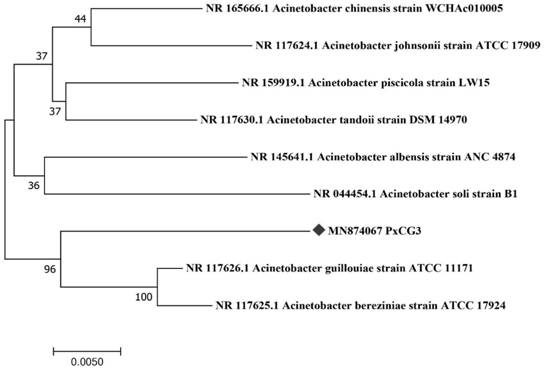
[0029] Example 2 Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Bacterial Strain PxCG3
[0030] 1. Traditional biological identification
[0031] (1) Colony Morphological Characteristics
[0032] From the morphological point of view, PxCG3 bacteria form round gray-white colonies with neat edges on the LB plate. Gram staining is sometimes not easy to decolorize. . This bacterium is obligate to aerobic, and the optimum growth temperature is 35°C; the nutrient requirements are not high, and it grows well on ordinary culture medium;
[0033] (2) Determination of physiological and biochemical characteristics of Acinetobacter guilin
[0034] Bacterial physiological and biochemical assays were carried out with reference to the method in the "Common Bacterial System Identification Manual", using bacterial micro-biochemical reaction tubes. The test results of available carbon sources are shown in Table 1. Galactose, lactose, sorbitol, rhamnose, arabinose, xylose, starch, melibiose, D-...
Embodiment 3
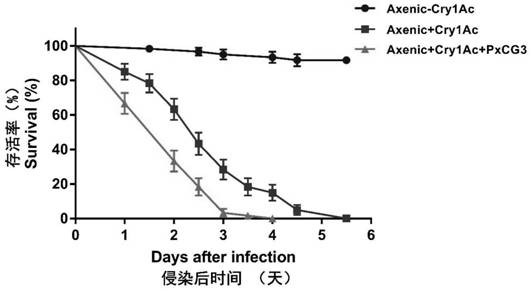
[0043] Example 3 The synergistic effect of PxCG3 strain on Bt
[0044] 1. Removal of intestinal bacteria in diamondback moth
[0045] Prepare antibiotic solution: 1mg / mL ciprofloxacin; 1mg / mL levofloxacin; 2mg / mL metronidazole;
[0046] The method of eliminating intestinal bacteria of diamondback moth and feeding antibiotics. Specific method: Collect diamondback moth egg cards and disinfect: collect egg cards produced during the peak oviposition period of diamondback moth, first place them in 5‰ sodium hypochlorite disinfectant for 10 minutes, and then soak them in clean water twice, each time for 5 minutes. Minutes, finally blotted with absorbent paper and placed in the insect box, after 24 hours, add feed to feed;
[0047] Antibiotic feeding treatment: take 4g of diamondback moth artificial feed in a sterile petri dish, then add ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin and metronidazole antibiotic solution prepared above 333 μL respectively, mix well and place in the insect culture box...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com