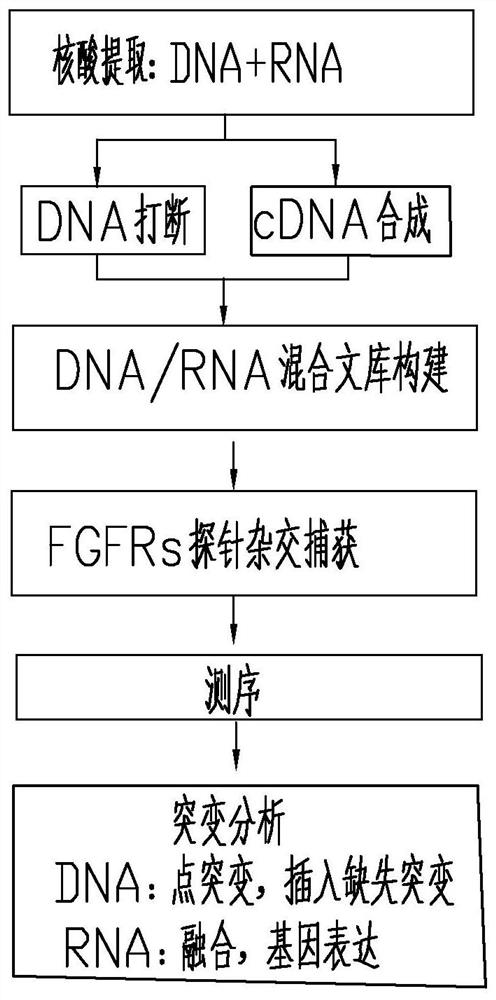
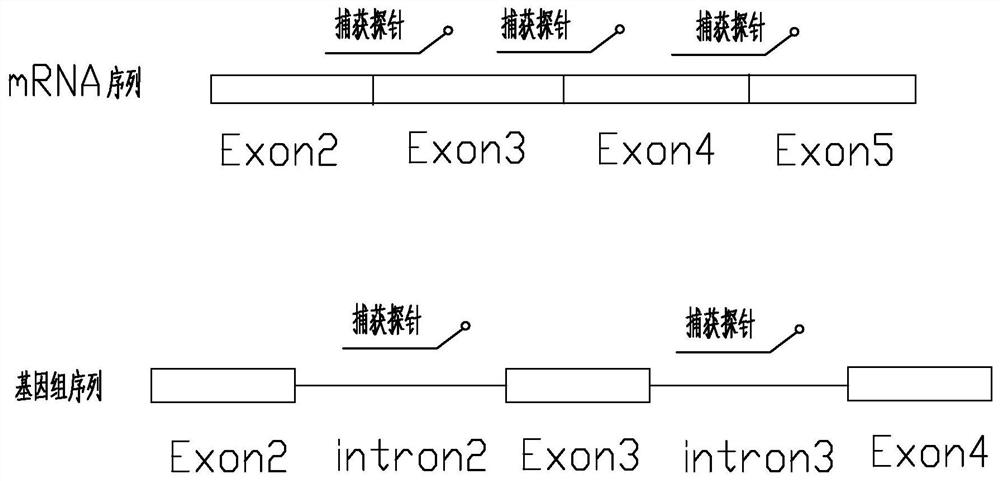
Method and probe sequence for detecting FGFRs gene mutation based on high-throughput sequencing
A detection method and FGFR2 technology, applied in the field of FGFRs gene mutation detection, can solve the problems of incomplete detection of mutation types, complicated detection operations, poor economy, etc., and achieve the effects of comprehensive detection of mutation types, simplified operation steps, and simple detection steps.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Standards are the core for evaluating the detection capabilities of different detection methods. Only by constructing standards with accurate mutation sites, types, and mutation frequencies can we evaluate different mutation detection systems fairly and equitably. The present invention takes FGFRs gene mutations as the research object, and evaluates the ability of the present invention to detect FGFRs gene mutations by constructing FGFRs gene point mutations and fusion mutations. The specific mutation types are shown in Table 2.
[0036]
[0037] (1) Preparation of standard products
[0038]Point mutation standard, use the tumor cell line (HCT-116, ATCC CCL-247) with known FGFRs mutation information, and use the corresponding wild-type cell line (HEK-293T, ATCC CRL-11268) to serially dilute the mutation frequency to 7.5%, 5%, 2.5%, 1% point mutation standard mixed cell line; fusion standard, using commercial standard RNA (CBP20080R and CBP20105R) with known FGFR2 fus...
Embodiment 2
[0068] In order to illustrate the accuracy of the present invention's detection of FGFRs fusion mutations, from 122 cases of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma FFPE samples of known FGFR2 gene fusion FISH platform detection results (wherein 12 cases of FGFR2 gene fusion positive samples detected by FISH, 110 cases of FGFR2 gene fusion negative samples Example) Genomic DNA and total RNA were extracted from these samples, and detected using the detection method for FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3, and FGFR4 gene mutations of the present invention. Analyze and compare the data obtained by sequencing. Reflecting the accuracy of FGFR2 fusion mutation detection of the present invention and the ability to detect other FGFRs gene mutations at the same time, the detection statistical results are shown in Table 2 below.
[0069] Conclusion: For the negative and positive detection of FGFR2 fusion, the results of the present invention are completely consistent with those of FISH; in addition, the presen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com