Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor for detecting glutamic acid concentration and detection method adopting non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor
A detection method, glutamic acid technology, applied in the direction of material electrochemical variables, scientific instruments, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that non-enzyme sensors cannot be applied to biological sample detection, and achieve the effect of a shortcut method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
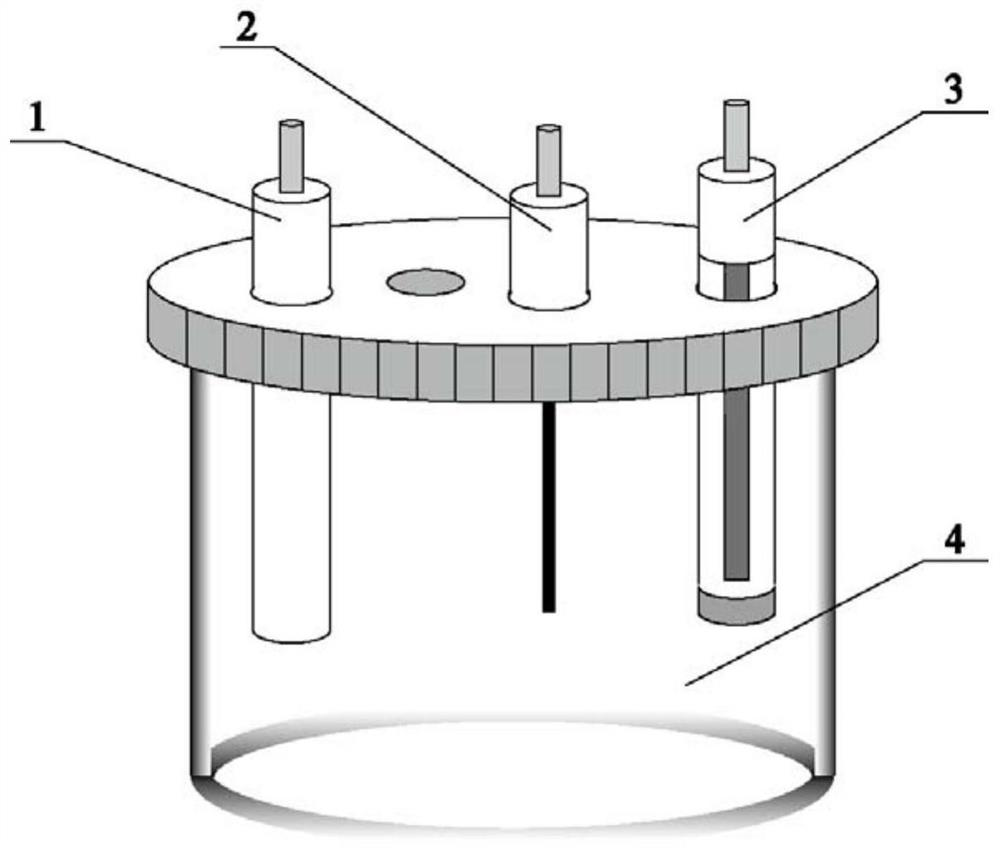
[0065] This embodiment provides a non-enzyme electrochemical sensor for detecting glutamic acid, the electrochemical sensor such as figure 1 As shown, the reaction cell 4 is included, and the working electrode 1, the auxiliary electrode 2 and the reference electrode 3 are arranged in the reaction cell 4; the three-electrode system is constructed by the working electrode 1, the auxiliary electrode 2 and the reference electrode 3, and the reaction cell Glutamic acid in the solution to be tested in 4 is carried out trace detection. The working electrode 1 is a carbon-based electrode whose surface is modified with nickel oxide-reduced graphene oxide nanomaterials, and the nickel oxide in the nickel oxide-reduced graphene oxide nanomaterials includes nickel oxide and nickel oxide. The reference electrode 3 is a carbon-based electrode, and the auxiliary electrode 2 is an Ag / AgCl electrode.
[0066] The nickel oxide-reduced graphene oxide nanomaterial is modified to the surface of t...
Embodiment 2
[0071] The non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor provided in Example 1 is used to carry out the method for trace detection of glutamic acid in the solution to be tested, and the detection method specifically includes the following steps:
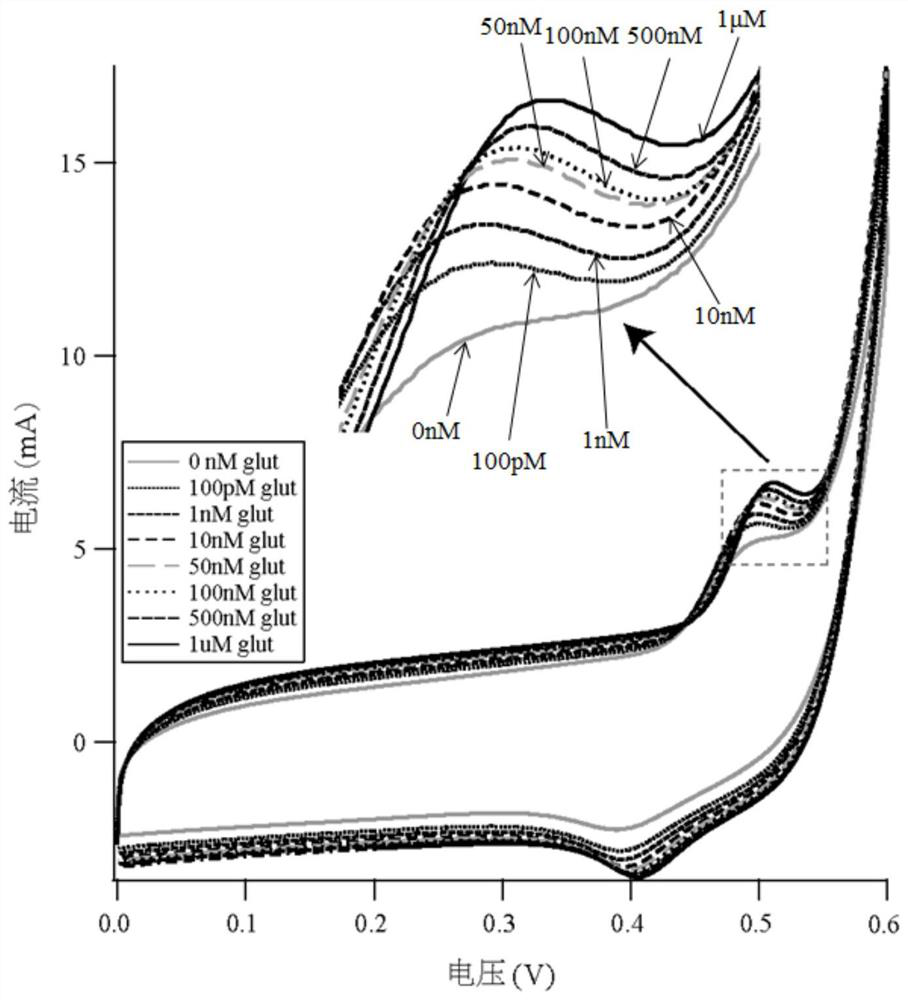
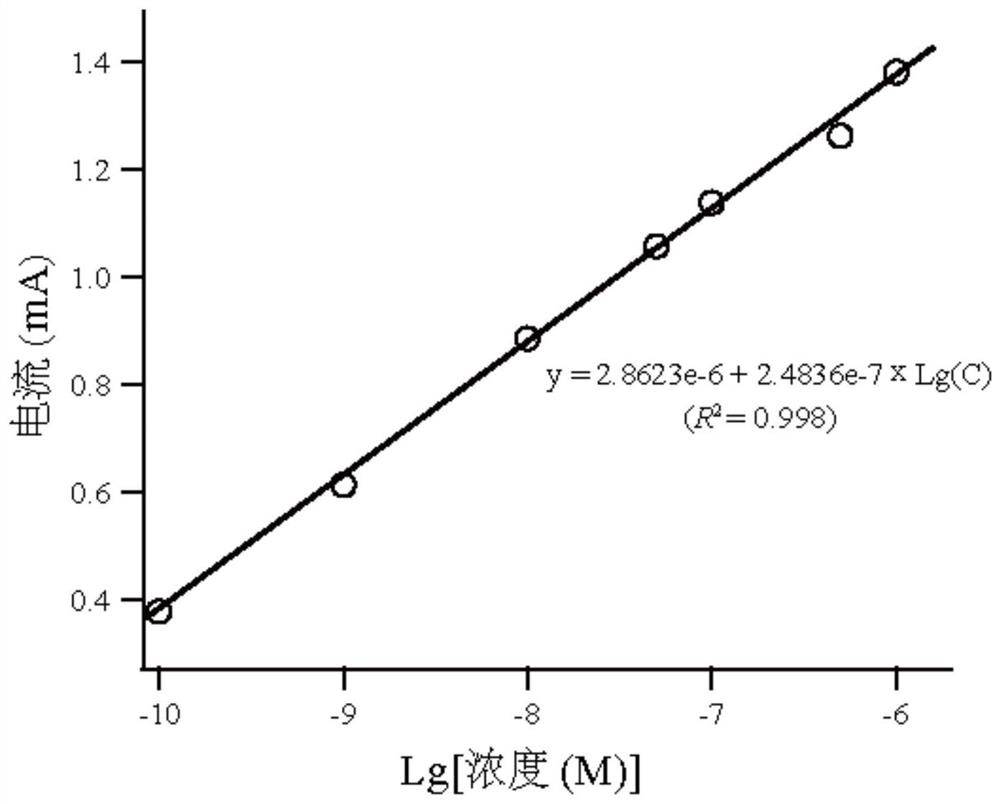
[0072] (1) Using a non-enzyme electrochemical sensor to carry out cyclic voltammetry detection on 7 groups of base fluids with known glutamic acid concentration, during the cyclic voltammetry detection process, glutamic acid in the working electrode of the non-enzyme electrochemical sensor 1 Catalytic oxidation reaction occurs on the surface, so that the oxidation peak of glutamic acid appears in the voltage range of 0.4 ~ 0.55V, the base fluid is alkaline phosphate buffer solution containing glutamic acid, the pH of the base fluid is 13, set the cycle voltage The scanning voltage range of Anfa is 0~1.0V, and the scanning speed is 0.1V / s;
[0073] The concentration of glutamic acid in the base fluid with known glutamic acid concentration in t...
Embodiment 3
[0080] The non-enzymatic electrochemical sensor provided in Example 1 is used for the method of trace detection of glutamic acid in the test solution containing interfering substances, wherein the interfering substances in the test solution include 20 μM uric acid, 100 μM ascorbic acid and 2 mM glucose. Described detection method specifically comprises the following steps:
[0081] (1) Using a non-enzyme electrochemical sensor to carry out cyclic voltammetry detection on 7 groups of base fluids with known glutamic acid concentration, during the cyclic voltammetry detection process, glutamic acid in the working electrode of the non-enzyme electrochemical sensor 1 Catalytic oxidation reaction occurs on the surface, so that the oxidation peak of glutamic acid appears in the voltage range of 0.4 ~ 0.55V, the base fluid is alkaline phosphate buffer solution containing glutamic acid, the pH of the base fluid is 13, set the cycle voltage The scanning voltage range of Anfa is 0~1.0V, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com